Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HRM
Uploaded by
aryan_hrsOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HRM
Uploaded by
aryan_hrsCopyright:
Available Formats
Definition of human resource management
Meaning:- human resource management is that of the organization which bring the people and organization together so that both can achieve their goals with the help of each other. And human resource management tries to maintain employee interest to their work and relation with the organization. Definition:- human resource management may be defined as it is the process of acquiring, training, appraising and compensating employee and attending to their labor relation help and safety concern human resource management concern with the most effective use of the people and resources to achieve organization and individual goal Meaning:- human resource management is that of the organization which
bring the people and organization together so that both can achieve their goals with the help of each other. And human resource management tries to maintain employee interest to their work and relation with the organization. Definition:- human resource management may be defined as it is the process of acquiring, training, apprising and compensating employee and attending to their labor relation help and safety concern human resource management concern with the most effective use of the people and resources to achieve organization and individual goal human resource management concern with the following :* Conducting job analysis * Planning labor needs and recruiting job candidates * Selection * Training new employees * Compensation * Appraising performance
* Communication counseling, interviewing, disciplining * Training and development
Nature of human resource management
Pervasive in nature: - all level of management is involved in HR. Integrating approach: - relations b/w people working at various levels in organization. Continuous process: - after accomplish a goal it tries to new one. Goal oriented: - it is goal oriented in nature because people and organization both achieve their goal.
Scope of Human Resource Management:Following are the scope of the human resource management ;
Employees selection Employees remuneration Employee motivation Health and safety of employees Industrial relation
HRM Functions
HRM Functions :mainly there are two types of functions 1. Managerial Functions 2. Operative Functions
Managerial Functions:managerial function are those which help in managing the
organization as well as individuals. following are the basic managerial functions of human resource management # planning: - It is a pre-determined course of action. # organizing;- It is essential to carry out the determined course of action. Thus, organization establishes relationships among the employees so that they can help in achieving organization goals # Leading & Directing:- leading the employee by giving appropriate direction to work or task # Controlling:- controlling the employee by rewards and punishment
Operative Functions:operative function of human resources refers to following specific activities :# Employment :1.Job Analysis 2.HR Planning 3.Recruitment 4.Selection 5.Placement # HR Development :1. Performance Appraisal 2.Training 3.Career Planning promotion transfer 4.Selection 5.Placement # Compensation :1. Job Evaluation 2. wages and salary administration 3. Fringe benefits housing, education and other facilities # Human Relations :1. motivation 2. communication 3. satisfaction 4. grievance handling 5. discipline
HR Objectives
Human resource management objectives:SOCIETAL OBJECTIVES:
Legal compliance Benefits Union-management relations
ORGANIZATIONAL OBJECTIVES:
Vision, mission, goal Employee relations Placement Assessment
FUNCTIONAL OBJECTIVES: 1. Planning 2. Organizing 3. Staffing 4. Leading 5. Controlling
HRM Environment
HRM Environment :Environment of HRM refers to the aggregate of conditions, events and influences that surround and affect it. following are the The external and internal environment in which the HRM has to function.-
#External Environment Economic, political, technological and demographic factors include the external environment.
# Internal environment :Internal environment comprises of the factors which affect an organizations human resources from inside the organizations boundaries. mission, hr policies, organization culture, hr system etc. are the variable of hr internal environment.
Meaning HRP :Human resource planning or manpower planning is essentially the predetermine process of getting the right number of qualified people into the right job at the right time. Definition of HRP :According to E. W. Vetter, Human resource planning is a process by which an organization should move from its current manpower position to its desired manpower position. Through planning, management strikes to have the right number and right kinds of people, at the right places, at the right time, doing things which result in both the organization and the individual receiving maximum long-run benefit. According to Bruce P. Coleman, Manpower Planning is defined as, the process of determining manpower requirement in order to carry out the integrated plan of the organization.
Process of human resource planning
RECRUITMENT
Meaning and Definition of Recruitment :it is the systematic process of finding and attracting the available candidates to apply to company or a particular job to become a employee.
According to C.B. Mamoria, Recruiting is the discovering of potential applicants for actual or anticipated organizational vacancies.
According to Flippo, Recruitment is the process of searching for prospective employees and stimulating them to apply for jobs in the organization. selection
Meaning and definition of selection :selection is the process of find out the right candidate (out of the pool of job candidates ) to fill the job in organization. according to dale yoder, selection is the process in which candidates for employment are divided into two classes those who are to be offered employment and those who are not. selection means a process by which qualified personnel may be chosen from the applicants offering their services to the organization for employment. steps in recruitment and selection process what are the steps in recruitment and selection process
methods of recruitment
Methods or Techniques of Recruitment :following are the methods techniques and source of recruitment Internal method of recruitment :# Promotion :- movement of employee from lower position to higher # transfer :- movement of employee from one job two another # retired & disable employee :- retired employee and disable employee can join available post. # employee referral :- It is a recommendation from a current employee regarding a job applicant.
External methods of recruitment :# Campus recruitment :- It is a method of recruiting by visiting and participating in college campuses and their placement centers. # Advertisements:- The ads generally give a brief outline of the job ads by newspapers magazines radio TV and hidings. # Private Employment Agencies :- These private agencies are brokers who bring employers and employees together. # State or Public Employment Agencies:- These agencies provide a wide range of services counseling, assistance in getting jobs, information about the labor market, labor and wage rates. # Employee Referrals:- It is a recommendation from a current employee regarding a job applicant. Friends and relatives of present employees are also a good source. # Trade Unions :- trade unions may provide manual and skilled workers in sufficient numbers as job requirement .
# online data bank :- www.naukri.com , www.timesjob.com, www.shine.com etc. are the online resume bank where they are matched against the resume data stored there in. What Is Training : process of teaching new knowledge and skills to perform their job effectively. the term training refers to giving skills and knowledge to new or present employee to perform their task or job. example showing a machine or tool how to operate. According to Dale S Beach, training is the organized procedure by which people learn new knowledge and skills for definite purpose. process of training :following is the process of training
Organizational Objectives and Strategies :nature of the business, and organizational mission, vision and goal consider in this step.
Assessment of Training Needs :identification of training needs 1. Organization needs assessment :- analysis of environment, strategies and resources to determine where to emphasize training. 2. Task needs assessment :- analysis of activities to be performed in order to determine needed competencies. 3. Employee needs assessment :- analysis of performance, knowledge and skills in order to determine who needs training.
Establishment of Training Goals :- pre determine result of training . Example :- the successful trainee will be expected to type 60 words per minute with no error.
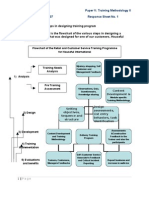
Designing Training and Development Programme :-
1) Who participates in the programme? 2) Who are the trainers? 3) What methods and techniques are to be used for training? 4) What should be the level of training? 5) What learning principles are needed? 6) Where is the program conducted? Implementation of the training :starting or first action to training . Evaluation of training :comparison of results with past performance.
Training Techniques :- basically there are two types of training methods
* On the job training * Off the job training
# # On the job training :- training a person to learn a task or job while working at it. a person learn a task when he actually performs it . following are the on the job training techniques :1. Apprenticeship Training :- it is a structured process by which person or trainee become skilled workers through a combination of classroom instruction and task performing. 2. Coaching :- a person having the sound knowledge in related field play the role of guiding and teaching a trainee. and tells him how to do a task or job and corrects the errors. 3. Job instruction training (JIT) :- listing of each jobs basic task, along with key points in order to provide step by step training for employee or trainee. the steps show what is to be done, where as the key points show how and why its to be done. 4. Understudy training :- it is a technique to prepare a trained individual for taking over the charge of his senior after his retirement, transfer, promotion, leave or death .
5. Job Rotation :- the term job rotation refers to transfer of a employee from one job to another or from one department to another or one section to another in a planned manner.
# # Off the job training :- training a person to learn a task or job without performs it. a person learn a task when he is not at job place and not actual performs the task . following are the methods and techniques of off the job training. 1. Case Study: Under this technique the cases based on actual business situations are prepared and given to the trainee managers for discussion and arriving at a proper decision. 2. Vestibule or simulated training :- in this technique trainees learn on the actual or simulated equipment they will use on the job but are actually trained off the job. example pilot training. 3. Role Playing :- the trainees have to assume a role of a person in the simulated situation. the have to perform as they would be doing a job. 4. Programmed learning :- involving presenting questions or facts, allowing the person to respond, and giving the learner immediate feedback on the accuracy of his or her answer. 5. Basket Method :- in this techniques a basket containing various kinds of correspondences such as reports, letters, applications each involving some problems and given to the trainee to solve. 6. Audio Visual Training :- audio visual techniques like films, video conferencing, audio video tapes help in learning. 7. Computer based training :- in computer based training the trainee uses a computer based system to learn knowledge and skills. Example CAD (computer aided design)
The Five-Step Training and Development Process :-
1. NEEDS ANALYSIS : Identify specific lob performance skills needed to improve performance and productivity. Analyze the audience to ensure that the program will be suited to their specific levels of education, experience, and skills, as well as their attitudes and personal motivations. Use research to develop specific measurable knowledge and performance objectives. 2. INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGN : Gather instructional objectives, methods, media, description of and sequence of content, examples, exercises, and activities. Organize them into a curriculum that supports adult learning theory and provides a blueprint for program development. Make sure all materials, such as video scripts, leaders guides, and participants workbooks, complement each other, are written clearly, and blend into unified training geared directly to the stated learning objectives. Carefully and professionally handle all program elementswhether reproduced on paper, film, or tapeto guarantee quality and effectiveness. 3. VALIDATION : Introduce and validate the training before a representative audience. Base final revisions on pilot results to ensure program effectiveness. 4. IMPLEMENTATION : When applicable, boost success with a train-the-trainer workshop that focuses on presentation knowledge and skills in addition to training content. 5. EVALUATION AND FOLLOW-UP : Assess program success according to: REACTION Document that learners immediate reactions to the training. LEARNING Use feedback devices or pre- and posttests to measure what learners have actually learned. BEHAVIOR Note supervisors reactions to learners performance following completion of the training. This is one way to measure the degree to which learners apply new skills and knowledge to their jobs. RESULTS Determine the level of improvement in job performance and assess needed maintenance.
Management Development programme:- management
development refers to any attempt current or future management performance by imparting knowledge, changing attitudes, or increasing skills. According to Mumford, management development programme is an attempt to improve managerial effectiveness through a planned and deliberate learning process.
Performance Appraisal :- is a method by which the job performance of an
employee is evaluated (generally in terms of quality, quantity, cost, and time) typically by the corresponding manager or supervisor. A performance appraisal is a part of guiding and managing career development. It is the process of obtaining, analyzing, and recording information about the relative worth of an employee to the organization. According to shubin, :- performance appraisal is a systematic appraisal of the employee personality traits and performance on the job and designed to determine his contribution and relative worth to the firm
Process Of Performance Appraisal:it is totally depend on organization structure and policy. basically following is the process of performance appraisal.
1. setting work standards :- pre determine level of work or task. 2. assessing employee performance:- assessing employee actual performance relative to these standards. 3. providing feedback :- providing feedback to the employee with the aim of motivating that person to eliminate performance deficiencies or to continue to above par.
Performance Appraisal methods :- following are the methods of performance appraisal 1. Graphic Rating Scale Method :- a scale that lists a number of traits and a range of performance for each. The employee is then rated by identifying the score that best describes his or her level of performance for each trait. 2. Alternation Rating method :- as name indicates - ranking employees from best to worst on a particular trait, choosing highest, then lowest, unti; all are ranked. 3. forced distribution method :- with this method predetermined percentages of ratees are placed in performance categories. for example you may decide to distribute employee as follows.
15 % high performer 20 % high average performance 30 % average performance 20 % low average performance 15 % low performance 4. Paired Comparison Method :- as name indicate comparing rating of all possible pairs of employees for each trait and find out which employee pair is better. 5. Critical incident method :- with the critical incident method, the supervisor keeps a log of desirable or undesirable examples or incidents of each subordinates work related behavior. then a time supervisor and subordinates meet and discuss the latters performance using the specific incident as example. 6. Management by objectives (MBO) :- is a process of defining objectives within an organization so that management and employees agree to the objectives and understand what they need to do in the organization. Management by objectives requires the manager to set specific measurable goals with each employee and then periodically discuss his or her progress toward these goal. 7. 360 degree appraisal :- is feedback that comes from all around an employee. "360" refers to the 360 degrees in a circle, with an individual figuratively in the centre of the circle. Feedback is provided by subordinates, peers, and supervisors. It also includes a self-assessment and, in some cases, feedback from external sources such as customers and suppliers or other interested stakeholders. It may be contrasted with "upward feedback," where managers are given feedback by their direct reports, or a "traditional performance appraisal," where the employees are most often reviewed only by their managers. 8. Behaviorally anchored rating scales (BARS) :- are scales used to rate performance. BARS are normally presented vertically with scale points ranging from five to nine. It is an appraisal method that aims to combine the benefits of narratives, critical incidents, and quantified ratings by anchoring a quantified scale with specific narrative examples of good, moderate, and poor performance.
Employee Compensation :- employee compensation refers to all forms of
pay or rewards going to employees and arising from their employment. compensation includes direct cash payment, indirect payment in the form of employee benefits and incentives to motivate employee to strive for higher levels of productivity.
Components of Compensation :-following are the components of compensation 1. financial compensation 2. non financial compensation
1. financial compensation :- following are the financial compensation. # wage and salary :- wages represents hourly rates of pay. and salary refers to monthly rates of pay. # Incentives :- payment by result incentive depend upon productivity, sales, profit or cost reduction efforts. # fringe benefits :- these include such benefits as provident fund, gravity, medical care, accident reliefs, heath insurance, canteen uniform, recreation and the like. # perquisites :- includes company car, club membership, paid holiday, etc.
2. non financial compensation :- following are the non financial compensation. # challenging job responsibility # growth prospects # comfortable working condition # job sharing and flexi time
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Assessing Health Needs of BME Children in LeedsDocument90 pagesAssessing Health Needs of BME Children in LeedsMohammad Riedho Cahya Atazsu100% (1)
- Basic Strategic Planning Toolkit PDFDocument45 pagesBasic Strategic Planning Toolkit PDFarie susanto100% (1)
- Training Evaluation ModelDocument397 pagesTraining Evaluation ModelAkanksha SinghNo ratings yet
- Performance ImprovementDocument130 pagesPerformance ImprovementAhmed Zeen EL AbedenNo ratings yet
- CPHIMS Flashcard Study Guide PDFDocument59 pagesCPHIMS Flashcard Study Guide PDFVenkat ThejaNo ratings yet
- GTF Capacity Needs Assessment ToolDocument68 pagesGTF Capacity Needs Assessment TooljilfNo ratings yet
- Technology Needs AssessmentDocument7 pagesTechnology Needs AssessmentMichael King100% (2)
- Purpose of Training and DevelopmentDocument5 pagesPurpose of Training and Developmentlucidleagueltd100% (5)
- Case StudyDocument6 pagesCase StudynoneNo ratings yet
- T&D Unit 1: Training ConceptsDocument20 pagesT&D Unit 1: Training Conceptsaryan_hrsNo ratings yet
- Supporting IssuesDocument10 pagesSupporting Issuesaryan_hrsNo ratings yet
- Store LayoutDocument25 pagesStore Layoutaryan_hrsNo ratings yet
- Distribution and Channel ManagementDocument40 pagesDistribution and Channel Managementaryan_hrsNo ratings yet
- Workplace Ethics Is About Making Ethics Real Within The Organisation by Devising andDocument3 pagesWorkplace Ethics Is About Making Ethics Real Within The Organisation by Devising andaryan_hrsNo ratings yet
- Industrial RelationDocument24 pagesIndustrial Relationaryan_hrsNo ratings yet
- Enhancing India's CoDocument3 pagesEnhancing India's Coaryan_hrsNo ratings yet
- 12 Technologies That Can Be Game Changers in 2014Document3 pages12 Technologies That Can Be Game Changers in 2014aryan_hrsNo ratings yet
- Game OneDocument12 pagesGame Onearyan_hrsNo ratings yet
- Flexible Workforce Downsizing Disposal of Peripheral Activities Outsourcing Project Based Work Team Work Part Time Employment Temporary Employment Tele Working / Home WorkingDocument15 pagesFlexible Workforce Downsizing Disposal of Peripheral Activities Outsourcing Project Based Work Team Work Part Time Employment Temporary Employment Tele Working / Home Workingaryan_hrsNo ratings yet
- Unit 2.2 CH 28 Organizing Process Orz StructureDocument25 pagesUnit 2.2 CH 28 Organizing Process Orz Structurearyan_hrsNo ratings yet
- NotessqlDocument16 pagesNotessqlaryan_hrsNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain ManagementDocument8 pagesSupply Chain Managementaryan_hrsNo ratings yet
- Ds-Human Resource ManagementDocument17 pagesDs-Human Resource Managementaryan_hrsNo ratings yet
- Recruitment and SelectionDocument7 pagesRecruitment and Selectionaryan_hrsNo ratings yet
- Service Tax RulesDocument22 pagesService Tax Rulesaryan_hrsNo ratings yet
- 6 SigmaDocument9 pages6 Sigmaaryan_hrsNo ratings yet
- PSU TOU 442 - Đề CươngDocument17 pagesPSU TOU 442 - Đề CươngThanh Thảng Phan ThịNo ratings yet
- 2020 School-Based INSET Program EvaluationDocument3 pages2020 School-Based INSET Program EvaluationGenesis Terana-PerezNo ratings yet
- BTN Sustainability Report Assurance StatementDocument2 pagesBTN Sustainability Report Assurance StatementSonia Dora DemoliaNo ratings yet
- School and Community Profile Assignment Zoe Romero OhsDocument23 pagesSchool and Community Profile Assignment Zoe Romero Ohsapi-253803594No ratings yet
- Community Needs Assessment: Learning ObjectiveDocument12 pagesCommunity Needs Assessment: Learning ObjectiveSHS Room 3 PC 3No ratings yet
- Answers Paper V Response Sheet 1Document11 pagesAnswers Paper V Response Sheet 1Avinash PhaseNo ratings yet
- Social Issues and Social PsychologyDocument40 pagesSocial Issues and Social PsychologyAyusmita DuttaNo ratings yet
- 2018 Family Service Centre Code of Social Work Practice CSWP Group Work Practice GuideDocument46 pages2018 Family Service Centre Code of Social Work Practice CSWP Group Work Practice GuideLeny CuestasNo ratings yet
- Needs Assessment: Allison RossettDocument14 pagesNeeds Assessment: Allison RossettGoogle SucksNo ratings yet
- Fin All WG Mom 09052017Document7 pagesFin All WG Mom 09052017Ozlem MepNo ratings yet
- Final Year Project Venture Capitalism inDocument86 pagesFinal Year Project Venture Capitalism inlex tecNo ratings yet
- Systematic Methods of Community Action in Understanding Community Background Information For LearnersDocument2 pagesSystematic Methods of Community Action in Understanding Community Background Information For Learnersapollo100% (3)
- Addis Birhanu Impact of Organizational Learning On Employees PerformanceDocument84 pagesAddis Birhanu Impact of Organizational Learning On Employees PerformanceLeulNo ratings yet
- Training Needs Analysis OutlineDocument4 pagesTraining Needs Analysis Outlineanahana57314 shahNo ratings yet
- Pepsi Beverages Co. (Sales Department: Tampa Region) : Presented By: Brittany CrawleyDocument14 pagesPepsi Beverages Co. (Sales Department: Tampa Region) : Presented By: Brittany CrawleyBrittany CrawleyNo ratings yet
- Need and Effectiveness of Traing and Maping TrainingDocument86 pagesNeed and Effectiveness of Traing and Maping TrainingriyasprojectNo ratings yet
- NSTP 2 Modules 1 To 8Document110 pagesNSTP 2 Modules 1 To 8Mika Brea GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Start With The End in Mind.Document55 pagesStart With The End in Mind.My HomeNo ratings yet
- Human Resource DevelopmentDocument71 pagesHuman Resource DevelopmentFaizan SheriNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12Document57 pagesLecture 12Ayesha HanifNo ratings yet
- Practical Guide to Mental Health Care for People Living with HIV/AIDSDocument205 pagesPractical Guide to Mental Health Care for People Living with HIV/AIDSDarrel Allan MandiasNo ratings yet