Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sap Tcodess
Uploaded by
ranjitkusahuOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sap Tcodess
Uploaded by
ranjitkusahuCopyright:
Available Formats
1 of 33
7/2/2012
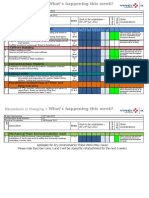
BASIC IMG IMG IMG IMG OB29 OB37 OB13 OB62 OBD4 OB53 OBBO OBBP OB52 OBA7 OBA0 OBA4 ? IMG OBC5 OBY6
SETTINGS CREATION OF COMPANY CREATION OF COMPANY CODE ASSIGN COMPANY CODE TO COMPANY DEFINE BUSINESS AREA MAINTAIN FISCAL YEAR VARIANT ASSIGN COMPANY CODE TO A FISCAL YEAR VARIANT CREATE CHART OF ACCOUNTS ASSIGN COMPANY CODE TO CHART OF ACCOUNTS CREATE ACCOUNT GROUPS DEFINE RETAINED EARNINGS ACCOUNTS DEFINE POSTING PERIOD VARIANT ASSIGN POSTING PERIOD VARIANT TO COMPANY CODE OPEN & CLOSE POSTING PERIODS DEFINE DOCUMENT TYPES AND NUMBER RANGES DEFINE TOLERANCE GROUPS FOR GL ACCOUNTS DEFINE TOLERANCE GROUPS FOR EMPLOYEES ASSIGN USERS TO TOLERANCE GROUPS MAINTAIN FIELD STATUS VARIANT (IMG>FA>FAGS>DOCUMENT>LINE ITEM>CONTROLS) ASSIGN COMPANY CODE TO FIELD STATUS VARIANT ENTER GLOBAL PARAMETERS
GENERAL LEDGER FS00 CREATION OF GL MASTERS F-02 GL POSTING FB03 DOCUMENT DISPLAY FS10N ACCOUNT DISPLAY FB00 TO MAKE DEFAULT LINE LAYOUT FS04 DISPLAY GL MASTER CHANGES F-65 DOCUMENT PARKING FBV3 DIPLAY PARKED DOCUMENTS FBV0 POST/DELETE PARKED DOCUMENTS OBBS DEFINE TRANSLATION RATIOS FOR CURRENCY TRANSACTION OB08 ENTER EXCHANGE RATE TYPES SAMPLE DOCUMENTS FBN1 DEFINE NUMBER RANGE GROUP X2 FOR SAMPLE DOCUMENTS F-01 CREATION OF SAMPLE DOCUMENT (TEMPLATE) FBM3 DISPLAY SAMPLE DOCUMENTS ACCRUAL/DEFERRAL DOCUMENTS IMG DEFINE REASONS FOR REVERSAL (IMG>FA>GL>BT>DOC RVRSL) FBS1 CREATION OF ACCRUAL/DEFERRAL DOCUMENT F.81 REVERSE ACCRUAL/DEFERRAL DOCUMENT RECURRING DOCUMENTS FBN1 DEFINE NUMBER RANGE GROUP X1 FOR RECURRING DOCS FBD1 CREATION OF RECURRING DOCUMENT (TEMPLATE) F.15 DISPLAY RECURRING DOCUMENTS
2 of 33
7/2/2012
EXECUTE RECURRING ENTRIES (SESSION IS CREATED) PROCESS BATCH INPUT SESSION OPEN ITEM MANAGEMENT FBL3N GL ACCOUNT DISPLAY FOR OPEN ITEM MANAGED ACCOUNT F-07 POSTING OUTGOING PAYMENT WITH CLEARING DOCUMENT REVERSALS IMG DEFINE REASONS FOR REVERSAL (IMG>FA>GL>BT>DOC RVRSL) FB08 INDIVIDUAL REVERSAL F-02 REVERSAL OF REVERSAL (POST WITH REFERANCE & GENERATE REVERSE POSTING) F.80 MASS REVERSAL FBRA CLEARED ITEM REVERSAL INTEREST CALCULATION (BALANCE INTEREST) OB46 DEFINE INTEREST CALCULATION TYPES OBAA DEFINE ACCOUNT BALANCE INTEREST CALCULATION OBAC DEFINE REFERENCE INTEREST RATES OB81 DEFINE TIME DEPENDANT TERMS OB83 ENTER INTEREST VALUES OBV2 ASSIGNMENT OF ACCOUNTS FOR AUTOMATIC INT POSTINGS F.52 INTEREST CALCULATION RUN INTEREST CALCULATION (ITEM INTEREST) ? DEFINE INTEREST CALCULATION TYPES ? PREPARE INTEREST CALCULATION ON ARREARS OBAC DEFINE REFERENCE INTEREST RATES ? DEFINE TIME BASED TERMS ? ENTER INTEREST VALUES F.2B CALCULATION OF INTEREST ON ARREARS OBV1 ? CASH JOURNAL FS00 CREATION OF GL ACCOUNT FOR CASH JOURNAL OBA7 DEFINE DOCUMENT TYPE FOR CASH JOURNAL FBCJC1 DEFINE NUMBER RANGE INTERVAL FOR CASH JOURNAL DOC FBCJC0 SETUP CASH JOURNAL FBCJC2 CREATE/DELETE/CHANGE BUSINESS TRANSACTIONS FBCJ CASH JOURNAL POSTING FOREIGN CURRENCY REVALUATION OB59 DEFINE VALUATION METHODS FS00 CREATE GL ACCOUNTS FC LOAN ACCOUNT WITH ACCOUNT CURRENCY USD AND OPEN ITEM MANAGEMENT, FOREX PROFIT AND FOREX LOSS OBA1 PREPARE AUTOMATIC POSTINGS FOR FC VALUATION (EXCHANGE RATE DIFFERENCE IN OPEN ITEMS KDF & EXCHANGE RATE DIFFERENCE IN FC BALANCES KDB) FS00 ATTACH THE EXCHANGE RATE DIFFERENCE KEY IN FC LOAN ACCOUNT OB08 ENTER EXCHANGE RATES
F.14 SM35
3 of 33
7/2/2012
F.05
O7E6 FB00 IMG
FB50
VALUATION OF OPEN ITEMS IN FOREIGN CURRENCY (FOREX RUN ON CLOSING DATE) CONFIGURATION OF GL FAST ENTRY SCREEN MAINTAIN FAST ENTRY SCREENS FOR GL ACCOUNTS ATTACH THE SCREEN IN F-02 ENJOY TRANSACTIONS DEFINE DOCUMENT TYPES FOR ENJOY TRANSACTIONS (IMG>FA>GL>BT>GL POSTING>ENJOY>DEFINE DOC TYPE FOR ENJOY SCREENS) ATTACH THE DOC TYPE FOR ENJOY SCREEN
ACCOUNTS PAYABLE OBD3 DEFINE VENDOR ACCOUNT GROUPS XKN1 CREATE NUMBER RANGES FOR VENDOR ACCOUNTS OBAS ASSIGN NUMBER RANGES TO VENDOR ACCOUNT GROUPS OBA3 DEFINE TOLERANCE GROUPS FOR VENDORS OBA7 DOCUMENT TYPES AND NUMBER RANGES FS00 CREATE RECONCILIATION ACCOUNT SUNDRY CREDITORS XK01 CREATION OF VENDOR MASTER F-43 VENDOR INVOICE POSTING FBL1N VENDOR ACCOUNT DISPLAY FK10N VENDOR ACCOUNT DISPLAY BANK ACCOUNTING FS00 CREATION OF BANK GL ACCOUNT FI12 DEFINE HOUSE BANKS (ASSIGN BANK GL TO ACCOUNT ID) FCHI CREATION OF CHECK LOTS OUTGOING PAYMENTS F-53 OUTGOING PAYMENT POSTING WITH CLEARING FCH5 MANUAL CHECK UPDATION FCHN CHECK REGISTER DISPLAY FCH6 CHECK ENCASHMENT DATE UPDATE FCHV DEFINE VOID REASON CODES FOR CHECK CANCELLATION FCH3 UNUSED CHECK CANCELLATION FCH8 ISSUED CHECK CANCELLATION (RESETS THE CLEARED ITEM, CANCELS THE CHECK & REVERSES THE PAYMENT) DOWN PAYMENTS TO VENDORS (SPECIAL GL INDICATOR: A) FS00 CREATION OF SPECIAL GL ACCOUNT ADVANCES TO VENDORS OBYR DEFINE ALTERNATIVE RECONCILIATION A/C FOR DOWN PMTS (LINKING SUNDRY CREDITORS & ADVANCES TO VENDORS) IMG SETUP ALL COMPANY CODES FOR PAYMENT TRANSACTIONS (IMG>FA>AR&AP>BT>OUTGOING PMTS>AUTO OG PMTS>PMT METHOD/BANK SELECTION FOR PMT PROGRAM) F-48 DOWN PAYMENT POSTING F-54 DOWN PAYMENT CLEARING F-44 ACCOUNT CLEARING VENDOR STATEMENT OF ACCOUNT
4 of 33
7/2/2012
ASSIGN PROGRAMS FOR CORRESPONDENCE REQUEST FOR CORRESPONDENCE MAINTAIN STATEMENT CREDIT MEMOS OBA7 DEFINE DOCUMENT TYPES F-41 VENDOR CREDIT MEMO POSTING TERMS OF PAYMENT OBB8 MAINTAIN TERMS OF PAYMENT OBXU DEFINE ACCOUNTS FOR CASH DISCOUNTS TAKEN EXTENDED WITHHOLDING TAX IMG CHECK WITHHOLDING TAX COUNTRIES (IMG>FA>FAGS>WHT>EWHT>BASIC SETGS>CHCK WHT COUNTRIES) IMG DEFINE WITHHOLDING TAX TYPE FOR INVOICE POSTING (IMG>FA>FAGS>WHT>EWHT>CALCULATION>WHT TYPE) IMG DEFINE WITHHOLDING TAX TYPE FOR PAYMENT POSTING (IMG>FA>FAGS>WHT>EWHT>CALCULATION>WHT TYPE) IMG DEFINE WITHHOLDING TAX CODES (IMG>FA>FAGS>WHT>EWHT>CALCULATION>WHT CODES) IMG DEFINE FORMULAS FOR CALCULATING WITHHOLDING TAX (IMG>FA>FAGS>WHT>EWHT>CALCULATION>WHT CODES) IMG ASSIGN WITHHOLDING TAX TYPES TO COMPANY CODE (IMG>FA>FAGS>WHT>EWHT>COMPANY CODE) IMG ACTIVATE EXTENDED WITHHOLDING TAX (IMG>FA>FAGS>WHT>EWHT>COMPANY CODE) OBWW DEFINE ACCOUNTS FOR WITHHOLDING TAX TO BE PAID OVER XK02 ASSIGNMENT OF WITHHOLDING TAX CODES IN VENDOR MASTER AUTOMATIC PAYMENT PROGRAM (FBZP) OBVCU PAYMENT METHODS IN COUNTRY OBVU PAYMENT METHODS IN COUNTRY CODE OBVU ALL COMPANY CODES OBVU PAYING COMPANY CODE FI12 CREATE HOUSE BANKS OBVCU BANK DETERMINATION (RANKING ORDER, BANK ACCOUNTS, AVAILABLE AMOUNTS, VALUE DATE) FCHI CREATION OF CHECK LOTS (SEQUENTIAL CHECKS) F110 PAYMENT PROGRAM RUN (PARAMETERS, ADDITIONAL LOG, SCHEDULE PROPOSAL, EDIT PROPOSAL, PRINTOUT/DATA MEDIUM, MAINTAIN VARIANT, PRINT CONTROL, PAYMENT RUN, SCHEDULE PRINT, OUTPUT CONTROLLER) CONFIGURING FAST ENTRY SCREEN FOR INCOMING INVOICES O7E5 DEFINE SCREEN TEMPLATES FOR INCOMING ITEMS FB00 ATTACH THE SCREEN TEMPLATE IN F-43 ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE OBD2 DEFINE CUSTOMER ACCOUNT GROUPS XDN1 CREATE NUMBER RANGES FOR CUSTOMER ACCOUNTS OBAR ASSIGN NUMBER RANGES TO CUSTOMER ACCOUT GROUPS
OB78 FB12 F.64
5 of 33
7/2/2012
CREATE RECONCILIATION ACCOUNT SUNDRY DEBTORS CREATE CUSTOMER MASTER DOCUMENT TYPES AND NUMBER RANGES SALE INVOICE POSTING CUSTOMER ACCOUNT DISPLAY CUSTOMER ACCOUNT DISPLAY INCOMING PAYMENT POSTING WITH CLEARING PAYMENT DIFFERENCES, TERMS OF PAYMENT & DISCOUNTS IMG DEFINE REASON CODES FOR PAYMENT DIFFERENCES (IMG>FA>AP&AR>BT>INCOMING PMTS>IP GLOBAL SETTINGS) OBB8 MAINTAIN TERMS OF PAYMENT OBXT DEFINE ACCOUNTS FOR CASH DISCOUNTS GRANTED OBXL DEFINE ACCOUNTS FOR OVER PAYMENTS/UNDER PAYMENTS OB00 DEFINE ACCOUNTS FOR ROUNDING DIFFERENCES DOWN PAYMENTS FROM CUSTOMERS (SPL GL INDICATOR: A) FS00 CREATE SPECIAL GL ACCOUNT ADVANCES FROM CUSTOMERS OBXR DEFINE ALT RECONCILIATION A/C FOR CUSTOMER DOWN PMTS (LINKING SUNDRY DEBTORS & ADVANCES FROM CUSTOMERS) F-29 CUSTOMER DOWN PAYMENT POSTING F-39 DOWN PAYMENT CLEARING F-32 ACCOUNT CLEAR BILL OF EXCHANGE TRANSACTIONS (SPL GL INDICATOR: W) FS00 CREATE GL ACCOUNTS SUNDRY DEBTORS BILL OF EXCHANGE & BANK BILL DISCOUNTING OBYN DEFINE ALT RECONCILIATION A/C FOR B/E RECEIVABLE (LINKING SUNDRY DEBTORS & S/DEBTORS BILL OF EXCHANGE) OBYK DEFINE BANK SUB ACCOUNTS (LINKING BANK CURRENT A/C, SUNDRY DEBTORS A/C AND BANK BILL DISCOUNTING A/C) OBXK DEFINE ACCOUNTS FOR BANK CHARGES F-36 POSTING BILL OF EXCHANGE RECEIPT F-33 BILL DISCOUNTING WITH BANK S_ALR_87012213 BILL OF EXCHANGE MANAGEMENT (TO SEE CUSTOMER WISE, DUE DATE WISE OUTSTANDINGS) FBL3N BANK WISE OUTSTANDINGS F-20 REVERSE CONTINGENT LIABILITY DUNNING OB61 DEFINE DUNNING AREAS FBMP DEFINE DUNNING PROCEDURE XD02 ASSIGN DUNNING PROCEDURE IN CUSTOMER MASTER F150 DUNNING RUN TAX ON SALES/PURCHASES OBQ3 DEFINE PROCEDURES IMG ASSIGN COUNTRY TO CALCULATION PROCEDURE (IMG>FA>FAGS>TAX ON SALES/PURCHASES>BASIC SETTINGS) FTXP DEFINE TAX CODES FOR SALES AND PURCHASES FS00 CREATE GL ACCOUNT SALES TAX PAYABLE OB40 DEFINE TAX ACCOUNTS
FS00 XD01 OBA7 F-22 FBL5N FD10N F-28
6 of 33
7/2/2012
XD02 FS00
OB59 OB09 ? ASSET EC08 OADB FTXP OBCL OAOB IMG IMG AS08 OAOA FS00
ASSIGN SALES TAX CODE IN CUSTOMER MASTER ASSIGN TAX CODES IN SALES GL ACCOUNT (* FOR ALL TAX CODES) OPEN ITEM VALUATION FOR VENDOR/CUSTOMER ACCOUNTS DEFINE VALUATION METHODS DEFINE ACCOUNTS FOR EXCHANGE RATE DIFFERENCE FOREX RUN ON CLOSING DATE MANAGEMENT COPY REFERENCE CHART OF DEPRECIATION/DEP AREAS DEFINE DEPRECIATION AREAS CREATE 0% TAX CODES FOR SALES AND PURCHASES ASSIGN TAX CODES FOR NON TAXABLE TRANSACTIONS ASSIGN CHART OF DEPRECIATION TO COMPANY CODE SPECIFY ACCOUNT DETERMINATION (NO SETTINGS REQD) (IMG>FA>AA>ORG STRUCTURE>ASSET CLASSES) CREATE SCREEN LAYOUT RULES (NO SETTINGS REQD) (IMG>FA>AA>ORG STRUCTURE>ASSET CLASSES) DEFINE NUMBER RANGE INTERVAL DEFINE ASSET CLASSES CREATION OF GL ACCOUNTS (LIKE LAND, BLDGS, PLANT & MACHINERY, FURNITURE&FIXTURES, VEHICLES, CAPITAL WORK IN PROGRESS, ACCUMULATED DEPN FOR EACH ASSET, ASSET SALE, PROFIT ON SALE OF ASSET, LOSS ON SALE OF ASSET, LOSS DUE TO SCRAPPING, DEPRECIATION ACCOUNT ETC.) DETERMINE DEPN AREAS IN ASSET CLASSES ASSIGN GL ACCOUNTS (INTEGRATION WITH GENL LEDGER) SPECIFY DOCUMENT TYPE FOR POSTING OF DEPRECIATION SPECIFY INTERVALS AND POSTING RULES SPECIFY ROUNDING OFF NET BLOCK AND/OR DEPRECIATION DEFINE SCREEN LAYOUT FOR ASSET MASTER DATA (IMG>FA>AA>MASTER DATA>SCREEN LAYOUT) DEFINE SCREEN LAYOUT FOR ASSET DEPRECIATION AREAS DEPRECIATION KEYS DEFINE BASE METHOD (ALWAYS SELECT 0014 FOR SLM) NO SETTINGS REQD (IMG>FA>AA>DEPN>VALUATION METHODS>DEPN KEY>CALCULATION METHODS) DEFINE DECLINING BALANCE METHOD (ALWAYS SELECT 001) NO SETTINGS REQD DEFINE MULTI LEVEL METHODS (FOR SLM & WDV) MAINTAIN PERIOD CONTROL METHODS MAINTAIN DEPRECIATION KEY (FOR SLM & WDV) TRANSACTIONS CREATE ASSET MASTER CREATE SUB ASSET MASTER ASSET PURCHASE POSTING (TRANSACTION TYPE 100 FOR EXTERNAL ACQUISITION TYPE)
OAYZ AO90 OBA7 OAYR OAYO IMG AO21 IMG
AFAMD AFAMS AFAMP AFAMA AS01 AS11 F-90
7 of 33
7/2/2012
F-90 SUB ASSET PURCHASE POSTING AW01N ASSET EXPLORER S_ALR_87011965 ASSET BALANCES BY BUSINESS AREA F-92 ASSET SALE (RETIREMENT WITH REVENUE) ABUMN ASSET TRANSFER (WITHIN COMPANY CODE) ABAVN ASSET SCRAPPING AFAB POSTING OF DEPRECIATION CAPITAL WORK IN PROGRESS SETTLEMENT OK07 DEFINE/ASSIGN SETTLEMENT PROFILE (CO ALLOCATION STRUCTURE) SNUM MAINTAIN NUMBER RANGES FOR SETTLEMENT DOCUMENTS (ASSIGN VBCF ELEMENT GROUP TO STD ACCOUNTING DOC) AIAB CAPITALIZE ASSETS UNDER CONSTRUCTION MM FI INTEGRATION OMSK DEFINE VALUATION CLASSES OBYC CONFIGURE AUTOMATIC POSTINGS SD FI INTEGRATION VKOA PREPARE REVENUE ACCOUNT DETERMINATION
8 of 33
7/2/2012
Company: Smallest organizational unit for which individual financial statements can be drawn up according to the relevant commercial law. A company can consist of one or more company codes. All company codes within a company must use the same transaction chart of accounts and the same fiscal year breakdown. The company code currencies, on the other hand, can be different. A company code has one local currency in which its transaction figures are recorded. Company Code: The smallest organizational unit for which a complete self-contained set of accounts can be drawn up for the purposes of external reporting. The process of external reporting involves recording all relevant transactions and generating all supporting documents required for financial statements (balance sheets, profit and loss statements and so on.) Business Area: Organizational unit of financial accounting that represents a separate area of operations or responsibilities within an organization and to which value changes recorded in Financial Accounting can be allocated. Business areas are used in external segment reporting (over and above company codes) based on the significant areas of operation (for example, product lines) of a business enterprise. A segment is an isolated area of activity. All essential balance sheet items, such as fixed assets, receivables, payables, and inventories, and all items of the profit and loss statement can be assigned directly to a business area. The balance sheet items for banks, capital, and taxes, however, cannot be directly assigned to business areas. They need to be assigned manually. This means that business area financial statements cannot be drawn up for commercial and tax law. Business area balance sheets and income statements are used only for internal reporting purposes. The system determines the appropriate business area from information such as the material, plant, or cost center we enter in a business transaction like a goods movement. Assignments we make (between cost centers and business areas for example) or the combination of information we specify (a plant and a particular division for example) are the basis on which the system determines the appropriate business area.
9 of 33
7/2/2012
Variant Principle: The variant principle is a three step method used in R/3 to assign special properties to one or more R/3 objects. The three steps are: 1. Define the variant, 2. Populate the variant with values, 3. Assign the variant to R/3 objects. The principle is used for Field status, Posting periods, fiscal years etc. Fiscal year variant: To separate business transactions into different periods, a fiscal year with posting periods has to be defined. The fiscal year is defined as a variant which is assigned to the company code. The fiscal year variant specifies the number of posting periods and special periods in a fiscal year and how the system is to determine the assigned posting periods. Types of Fiscal Years: 1. Year Dependent: Periods can vary from year to year. A fiscal year variant has to be defined as year dependent if the start and the end date of the posting periods of some fiscal years are different from the dates of other fiscal years, or if some fiscal years shall use a different number of posting periods. Shortened Fiscal Year: A shortened fiscal year arises through a shift in the end of the fiscal year. The shortened fiscal year covers the period between the end of the last fiscal year in the old cycle and the beginning of the next fiscal year in the new cycle. Instances: Company changing the beginning of the fiscal year or if the company was sold. 2. Year independent (Fiscal Year same as Calendar Year & Fiscal Year not same as Calendar Year): If each fiscal year of a fiscal year variant uses the same number of periods, and the posting periods always start and end at the same day of the year, the variant is called year independent. If the fiscal year is defined as the calendar year, the posting periods are equal to the months of the year. Therefore a calendar year variant must have 12 posting periods. If the fiscal year differs from the calendar year, we must specify the number of posting periods we want to use & how
10 of 33
7/2/2012
the fiscal year is to be determined from the posting date. To do this, we specify the displacement for each period compared to the year of the posting date by using the annual displacement indicators -1, +1. Using these indicators, the system determines the fiscal year. Chart of Accounts: The chart of accounts is a variant which contains the structure and the basic information about general ledger accounts. Information to be given in Chart of Accounts: Maintenance Language, Length of GL Account Number, Manual or automatic creation of cost elements, Group chart of accounts etc. Operative Chart of Accounts: The operating chart of accounts contains the G/L accounts that you use for posting in your company code during daily activities. Financial Accounting and Controlling both use this chart of accounts. Country Specific Chart of Accounts: These are structured in accordance with legal requirements of the country in question Group Chart of Accounts: This is structured in accordance with requirements pertaining to Consolidation. The account group determines: The data that is relevant for the master record A number range from which numbers are selected for the master records. An account group must be assigned to each master record. Retained Earnings Account: The difference in Profit and Loss account is transferred to Reserves & Surplus Posting Period Variant: A variant which contains posting periods. A Posting Period is a period within a fiscal year for which transaction figures are updated. Every transaction that is posted is assigned to a particular posting period. The transaction figures are then updated for this period. During the time of the closing procedure, 2 period ranges have to be open at the same time. Open and Close Posting Periods: To define the periods those are open for postings.
11 of 33
7/2/2012
Document Type: Key that distinguishes the business transactions to be posted. The document type determines where the document is stored, as well as the account types to be posted. The Document Type controls the header which is valid for an entire document. Number Range: Defines the allowable range in which a document number must be positioned and cannot overlap. (Internal Numbering & External Numbering) Tolerances: Rules that define acceptable differences during Posting of transactions. Allowed Payment differences will be specified in Tolerance Group for GL Accounts. Tolerance Group for Employees is used to control the Upper Limits for Transactions & Allowed Payment Differences. Field Status Variant: The Field Status Variant contains various Field Status Groups. In a Field Status Group each field is defined whether it is Required, Optional or Suppressed. Master Data: The Data which remains unchanged for long periods of time and which is often referred to by other data. This data is called Master Data. Chart of Accounts segment: The COA contains basic information about the accounts. Information per account is bundled into what is called the COA segment. Contents: Account Group, P&L account type or Bal Sheet account type, Description of the account Short text as well as long text and Consolidation in COA like Trading partner and Group Account Number. Company Code Segment: Information in this segment is specific for this company code. This information controls entry of accounting documents and management of accounting data. Contents: Control Data, Bank/Interest, Information Tabs, under these we specify currency, tax, reconciliation account, sort key, field status group, house bank, interest calculation information etc., Reconciliation accounts (Sub ledger open item function):
12 of 33
7/2/2012
Are General Ledger accounts assigned partner master records to record all sub ledger. Any postings to the sub automatically update the balances of reconciliation accounts.
to the business transactions in the ledger accounts the assigned
Methods for creating GL Accounts: Manual: one step and two step Copying: Copy an individual GL account with reference to another GL account, Copy the entire company code segment, copy the entire chart of accounts segment. Data transfer: Upload a new chart of accounts from an external system e.g. flat file. Document: The R/3 system uses the document principle: Postings are always stored in document form. The document remains as a complete unit in the system until it is archived. A document is identified by the combination of Document number Company code Fiscal year The R/3 FI document consists of A document header (information which applies to the entire document & the important control key is document type for the header) 2 to 999 line items (information which is specific to that line item & the important control key is posting key for the line item). When a document is displayed, the first screen we see is an overview screen containing the most important information from the document header and the line items. We have a display line for each line item. We can decide what data is displayed in this line by specifying the line layout. We can define several variants for line layout. When displaying a document, we can switch between the variants. We can define our own variant by selecting from Current Display Variant. GL Account Blocking: Blocked for Creation Blocked for Posting Blocked for Planning
13 of 33
7/2/2012
Blocked for Posting (in Company Code) Hold Documents: (System will prompt for a temporary document number to be given by the user) We can enter incomplete documents by using the Hold function. If we do this, the system does not update any account balances. Sample Documents: Sample Document is a special type of reference document. Data from this document is used to create default entries on the accounting document entry screen. A sample document does not update transaction figures but merely serves as a data source for an accounting document. Steps: Creation of Number Range Group X2 and Numbers for Sample Document Template Creation of Sample Document Template Posting of Entries by using Sample Document as reference Recurring Documents: A periodical recurring posting made by the recurring entry program on the basis of recurring entry original document. The procedure is comparable with a standing order by which, banks are authorized to debit rent payments, payment contributions or loan repayments. Steps: Creation of Number Range Group X1 and Numbers for Recurring Document Template Creation of Recurring Document Template Posting of Documents by using Recurring Document Template by way of Batch Input Accrual/Deferral Documents: To ensure that expenses and incomes are posted to the correct period, we enter accrual/deferral documents. Accruals: An accrual is any expenditure before the closing key date which represents an expense for any period after this date. Deferral: Deferred income is any receipt before the closing key date which represents revenue for any period after this date. Steps:
14 of 33
7/2/2012
Creation of Reversal Reason which will allow reversing on any day Posting of Accrual/Deferral Document Reversal of Accrual/Deferral Document
Open item management: GL accounts should be administered with open item management when we need to check whether there is an offsetting posting for a given business transaction. Open and cleared items can be displayed separately, and therefore it is easy to see which business transactions still need to be cleared. Examples: GR/IR Clearing A/c., Cash Discount Clearing A/c., Bank Clearing A/cs. etc. Note: Reconciliation accounts are managed implicitly using Sub Ledger Open Item Function. Clearings: Full Payment Clearing Partial Payment Clearing Residual Clearing Document Reversal: Reversal of a posting by entering an identical amount to the opposite side of the account, thereby offsetting the original amount. Individual Reversal Reversal of Reversal Mass Reversal Cleared Item Reversal Accrual/Deferral Reversal
Currencies: In Financial Accounting, we have to specify for each of the company codes, in which currency ledgers should be managed. This currency is the national currency of the company code, that is, the local currency (or company code currency). From a company code view, all other currencies are then foreign currencies. The ledgers can be managed in two parallel currencies in addition to the local currency, for example, group currency or hard currency. Group currency is used in the consolidated financial statements. Hard Currency or
15 of 33
7/2/2012
Country-specific second currency is used in countries with high rates of inflation. Global company Currency: Currency used for an internal trading partner. Global company currency is defined when defining the company that is assigned to the company code. Exchange Rate Type: - Key used to define exchange rates in the system. For each currency pair we can define different exchange rates. The different exchange rates are used for the purposes of Valuation, Conversion, Translation, Planning etc. Standard Translation at Bank Buying rate G Type Standard Translation at Bank selling rate B Type Average rate M Type Historical exchange rate - 1003 Translation Ratio: The (consistent) relationship between the monetary units of two foreign currencies. Foreign Exchange Revaluation G Type Bank Buying Open Item Non Open Item B Type Bank Selling Open Item Non Open Item We can create different valuation methods for valuing foreign currency. For each valuation method, we have to define: Parameters for the valuation procedure Parameters for exchange rate determination Valuation Method: A unique key determining foreign currency valuation method. Interest Calculations S Type Balance Interest Calculation (for GL Accounts) o Is applied to the entire balance of a GL or Customer Account, applying a particular interest rate for a specified period of time P Type Item Interest Calculation (for Customers & Vendors) o Interest on arrears is applied to individual items in accounts receivable or accounts payable.
16 of 33
7/2/2012
A certain interest rate is applied to the items that are still open or unpaid at a specified date. Interest calculation configuration: Interest calculation Indicator o Interest calculation types set basic parameters used in calculation. To calculate interest for an account (GL, Customer, Vendor), the master data for that account must include the interest calculation indicator that applies. Each interest ID must be assigned an interest calculation type, indicating whether it is used for balance interest calculation or item interest calculation. General terms o General terms specify further parameters about how each interest calculation indicator works. o Here we specify interest calculation ID, interest calculation frequency, settlement day, calendar type (G type for rupee loans & F type for FC loans). Define reference interest rates o Define reference interest rate ID, effect from date and currency Time dependent terms o Time-based terms set validity dates and relationships to interest rates. Here we specify interest calculation ID, currency, valid from, sequence number(1&2 - credit interest balance interest calculation for 1 & debit interest balance interest calculation for 2), term and reference interest rate ID. Interest rates o Interest rates establish reference interest rates that interest calculations can be tied to. Here we specify Reference interest rate ID, valid from and interest rate. Account determination o Account determination establishes which accounts the results of an interest calculation will be posted to. Accounts Payable Reconciliation accounts:
17 of 33
7/2/2012
Reconciliation accounts are managed implicitly using Sub Ledger Open Item function. Posting Keys Vendor Debit: 25 Vendor Credit: 31 Document Types KR Vendor Invoice KZ Vendor Payment KA Vendor Document (Transfers/Reversals) AP (Vendor Accounts) is a Subsidiary Ledger of Sundry Creditors & Sundry Creditors is a Reconciliation Account under Current Liabilities. Steps: Creation of Vendor Account Groups like FI Vendors (Services), MM Vendors (Materials) and One-time Vendors with Reconciliation Account Field mandatory. Creation of Number Range Groups and Numbers for Vendors. Assignment of Number Range Group to Vendor Account Group Define Tolerance Groups for Vendors. Creation of Vendor Master. Document Types and Number Ranges for KR, KZ and KA. The Vendor Account Group controls The number ranges of the accounts, the status of the fields in the master record and whether the account is a one time vendor One-time Vendor: Vendors who have a business transaction only once are called one-time vendors. We create collective master record for one-time vendors. The complete details of the Vendor will be given at the time of Invoice Posting. (While creating the group a One-time Vendor Group should be selected.) Tolerances: Rules that define acceptable differences during posting Tolerance Groups for Vendors: The tolerances are used for differences in payment and residual items which can occur during payment settlement.
18 of 33
7/2/2012
We can specify the tolerances under one or more tolerance groups. Allocate a Tolerance Group to each Vendor via the master record. For each Tolerance Group we specify: 1. Tolerances upto which differences in payment are posted automatically to expense or revenue account when clearing open items. 2. The handling of the terms of payment for residual items, if they are to be posted during clearing. Employee Tolerances also can be specified. Employee Tolerance is used to control the Upper limits for posting procedures (Posting Authorizations) and Permitted Payment Differences. While clearing, the lower limit of the 2 will be taken. Vendor Master: The account group is entered on the initial create screen. In FI, once the vendor account is created, its account group cannot be changed. Give Reconciliation Account Number, Sort Key 012 Vendor Name, Payment Terms, Tolerance Group & Select Check Double Invoicing. Line item display and open item management are always preset to on for every vendor account. A complete Vendor Account consists of 3 segments 1. General Data at the client level 2. Company code segment and 3. Purchasing Organization segment General data consists Address, Control data, Payment transactions etc. The account number is assigned to the Vendor at the client level. This ensures that the account number for a Vendor is the same for all company codes and sales areas. Company data consists of Accounting information, Payment transactions, Correspondence, Insurance, Withholding tax etc. Note: If MM creates their segment of the master record and then FI creates their segments of the master record, there is the risk of creating incomplete or duplicate master records. To find and correct these incomplete accounts, we can run report RFKKAG00 and make the necessary corrections. Creation of duplicate accounts can be prevented by: Using the matchcode before creating a new account
19 of 33
7/2/2012
Switching on automatic duplication check
Important Fields Search Item: Should be filled with a short version of the vendor name according to company rules/desires. An additional search field also can be filled up. Group Key: Vendors who belong to one corporate group can be bundled together by a user-defined group key. This group key can be used for running reports, transaction processing or for matchcodes. Accounting clerk: The accounting clerks name has to be stored under an ID and this ID can be entered in the vendor master record of the account he or she is responsible for. The accounting clerks name is then printed on correspondence and this ID is used to sort dunning and payment proposal lists. Down Payments to Vendors Create Special GL Account Advance to Vendors (Reconciliation Account) under Current Assets Create Link between S/Creditors and Advance to Vendors (Special GL Indicator: A) Down Payment Posting Purchase Invoice Posting Transfer of Down Payment from Special GL to Normal item by clearing Special GL Account Clearing of Normal Item Extended Withholding Tax (TDS) In Accounts Payable, the vendor is the person subject to tax, and the company code is obligated to deduct withholding tax and pay this over to the tax authorities on their (the vendors) behalf. At the time of Invoice Posting Service Charges A/c. Dr. 100000 To Contractors A/c. 98000 To TDS A/c. 2000 At the time of Advance Payment Posting Contractors A/c. Dr. 100000 To Bank A/c. 98000 To TDS A/c. 2000 Terms of payment
20 of 33
7/2/2012
Terms of payment are conditions established between business partners to settle the payment of invoices. The conditions define the invoice payment, due date and the cash discount offered for early settlement of the invoice. Automatic Payment Program (FBZP) Every company needs some way to pay their vendors. The automatic payment program is a tool that will help users manage payables. Accounts payable invoices have to be paid on time to receive possible discounts. The settings are divided into the following categories: All company codes Inter-company payment relationships The company code(s) that process payments Cash discounts Tolerance days for payments The customer and vendor transactions to be processed Paying company codes Minimum amounts for incoming and outgoing payments Forms for payment advice and EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) Bill of Exchange parameters Payment methods / country Methods of payments such as Cheque, Bank Transfer etc. Define the basic requirements and specifications for each payment method Create a Cheque, bank transfer, bill of exchange, etc. Master record requirements, i.e. address required Document types for postings Print programs Permitted currencies Payment methods / company code Define for each payment method and company code Minimum and maximum payment amounts Whether payments abroad and foreign currencies are allowed Grouping options Bank optimization Forms for payment media Bank Determination These components need to be taken into consideration when selecting the paying house bank
21 of 33
7/2/2012
Ranking order (per pmt method, define, 1. which house bank should be considered for payment first, second, third, etc., 2. Currency, 3. Bill of exchange) Accounts & Amounts (per house bank and payment method combination, define, 1. The offset account to the subledger posting, 2. Clearing accounts for bills of exchange 3. The available amount of funds in each bank) Charges (Assess additional bank charges for incoming and outgoing payments, Used with bills of exchange, Additional automatic posting configuration) Value date (per house bank and payment method combination, value date is 1. Used with cash management and forecast 2. The number of days until value date plus the posting date)
Payment Run (F110) Parameters: In this step, the following questions are asked and answered Who is going to be paid? What payment methods will be used? When will they be paid? Which company codes will be considered? How are they going to be paid? Proposal: Once the parameters have been specified, the proposal run is scheduled and it produces a list of business partners and open invoices that are due for payment. Invoices can be blocked or unblocked for payment. Program: Once the payment list has been verified, the payment run is scheduled. A payment document is created and the general ledger and sub-ledger accounts are updated. Print: The accounting functions are completed and a separate print program is scheduled to generate the payment media. Accounts Receivable Posting Keys Customer Debit: 01 Customer Credit: 15 S/Debtors Bill of Exchange Debit: 09 S/Debtors Bill of Exchange Credit: 19 Document Types DR Customer Invoice DZ Customer Payment DA Customer Document (Transfers/Reversals)
22 of 33
7/2/2012
AR (Customer Accounts) is a Subsidiary Ledger & Sundry Debtors is a Reconciliation Account under Current Assets. Steps: Creation of Customer Account Groups like FI Customers and SD Customers with Reconciliation Account Field mandatory. Creation of Number Range Groups and Numbers for Customers. Assignment of Number Range Group to Customer Account Group. Creation of Customer Master. Document Types and Number Ranges for KR, KZ and KA. The Customer Account Group controls The number ranges of the accounts, the status of the fields in the master record and whether the account is a one time customer. Customer Master The account group is entered on the initial create screen. In FI, once the customer account is created, its account group cannot be changed. Select Company Code Data Button - Give Reconciliation Account Number, Sort Key 012 Vendor Name, Payment Terms, Tolerance Group & Select Check Double Invoicing. Line item display and open item management are always preset to on for every customer account. A complete Customer Account consists of 3 segments 1. General Data at the client level 2. Company code segment and 3. Sales Area segment General data consists Address, Control data, Payment transactions etc. The account number is assigned to the Customer at the client level. This ensures that the account number for a customer is the same for all company codes and sales areas. Company data consists Accounting information, Payment transactions, Correspondence, Insurance, Withholding tax etc.
23 of 33
7/2/2012
Note: If SD creates their segment of the master record and then FI creates their segments of the master record, there is the risk of creating incomplete or duplicate master records. To find and correct these incomplete accounts, we can run report RFDKAG00 and make the necessary corrections. Creation of duplicate accounts can be prevented by: Using the matchcode before creating a new account Switching on automatic duplication check Important Fields Search Item: Should be filled with a short version of the customer name according to company rules/desires. An additional search field also can be filled up. Group Key: Customers who belong to one corporate group can be bundled together by a user-defined group key. This group key can be used for running reports, transaction processing or for matchcodes. Accounting clerk: The accounting clerks name has to be stored under an ID and this ID can be entered in the customer master record of the account he or she is responsible for. The accounting clerks name is then printed on correspondence and this ID is used to sort dunning and payment proposal lists. Down Payments from Customers Create Special GL Account Advances from Customers (Reconciliation Account) under Current Liabilities Create Link between S/Debtors and Advances from Customers (Special GL Indicator: A) Down Payment Receipt Posting Sale Invoice Posting Transfer of Down Payment from Special GL to Normal item by clearing Special GL Account Clearing of Normal Item Bills of Exchange LC (Letter of Credit 30/60/90 days sight) Contingent Liability Bills Discounted with Bank W is the Special GL Indicator (W stands for Bill of Exchange Bankable) Bills of Exchange Transaction Normal Accounting SAP Accounting Customer A/c. Dr. Customer A/c. Dr. (S/Debtors Debit)
24 of 33
7/2/2012
To Sales A/c. Bill of Exchange Receipt No Entry
Discounting Bank A/c. Dr. Interest A/c. Dr. To Bill Discounting A/c. Reversal of Contingent Liability Bill Discounting A/c. Dr. To Customer A/c. Reports Customer wise, Due Date wise, Bill wise outside the system
To Sales A/c. Bill of Exchange Receipt Customer (W) A/c. Dr. (S/Drs. BExchnge A/c. Debit) To Customer A/c. (S/Drs. With clearing) Discounting Bank A/c. Dr. Interest A/c. Dr. To Bank Bill Discounting A/c. Reversal of Contingent Liability Bank Bill Discounting A/c. Dr. To Customer (W) A/c. (S/Drs. Bill of Exchange with clearing) Reports within the system Customer wise, Due Date wise, Bill wise within the system
Dunning System defined reminder letters Dunning Area: South, North, East, West Dunning Levels: 4 (Maximum levels 9) Dunning Frequency: 10/20/30 days Grace Period: 3/4/5 days The Dunning Program settings are divided into the following categories: Dunning Procedure o Define the key for the dunning procedure to be used o Give a description for the dunning procedure o Define dunning interval in days o Specify minimum days in arrears after which a dunning notice will be sent o Grace period per line item o Interest calculation indicator for calculation of dunning interest Dunning levels (Each item to be dunned gets a dunning level according to its days in arrears) o Define minimum number of days, referring to the due date of net payment, to reach a certain dunning level o Define whether interest is to be calculated o Define print parameters
25 of 33
7/2/2012
Charges o Define dunning charges, depending on the dunning level o Dunning charges can be either a fixed amount or a percentage of the dunned amount o A minimum amount for the dunning charges can be set Minimum amounts o Define minimum amount or percentage of the overdue items to reach a dunning level o Minimum amount to be reached in order to calculate interest per dunning level Dunning texts o Define the name of the form that will be used at each dunning level Environment o Company code data o Sort fields o Sender details o Dunning areas o Dunning keys (A dunning key determines that the line item can only be dunned with restrictions or is to be displayed separately on the dunning notice. By assigning dunning keys to certain items we can prevent these items from exceeding a certain dunning level.) o Dunning block reasons ( A dunning block prevents accounts and items to be dunned) o Interest o Dunning grouping
Steps in Dunning Run Maintain Parameters (specify the accounts and documents that are to be considered in the dunning run) Proposal Run Editing Proposal Printing Dunning Notices Sales Tax Input Tax or Purchase Tax Base 100 2% Tax 2 ---Inventory RM 102 ----
26 of 33
7/2/2012
Output Tax or Sales Tax Base Price 100 Sales Account 4% ST 4 ST Payable Account ---104 ---Assets Subsidiary Ledger Chart of Depreciation Copy Germany Chart of Depreciation Depreciation Areas Book, Tax, Consolidated and Costing Depreciation Methods Straight Line Method and Written Down Value Method Depreciation Keys Rate + Method 5% SLM, 5%WDV etc. Rules: Sub Asset Master is to be created WRT Main Asset Master Main Asset Master is to be created WRT Asset Class In Asset Class we mention Account Determination For Account Determination we assign Accounts on the basis of Transaction like Purchase, Sale, Profit, Loss, Scrapping, Depreciation, Accumulated Depreciation etc. Transaction Account Asset Class Determination Land Free Hold Land Lease Hold Land Factory Buildings Non Factory Bldgs. Department A Department B Department C Furniture & Fixtures Office Equipment Asset Masters Sub Asset Masters
Purchase, Buildings Sale, Profit, Loss, Scrapping, Depreciation, Plant & Accumulated Machinery Depreciation etc. Furniture & Fixtures
Machine No.1
Motor
27 of 33
7/2/2012
Vehicles
Capital Work in Progress
Indigenous Vehicles Imported Vehicles Expansion 1 Expansion 2 Expansion 3
System defined Account Determinations and Screen Layout Rules: Description Screen Account Layout Determination Rule Real Estate and Similar Rights 10000 1000 Buildings 11000 1100 Machinery and Equipment 20000 2000 Furniture & Fixtures 30000 3000 Vehicles 31000 3100 Hardware (IT) 32000 3200 Down Payments paid and Assets under 40000 4000 Construction Low Value Assets 50000 5000 Leasing 60000 6000 Objects of Art 80000 8000 Depreciation Keys Define Base Method (SLM 0014) Define Declining Balance Method (WDV 001) Define Multi Level Method Define Period Control Method Define Depreciation Key Financial Statement Version (FSV) Summary, Schedules and Accounts We define a financial statement version in 2 steps: 1. Enter in the directory of financial statement versions 2. Define hierarchy levels and assign accounts Each version must have the following special items: 1. Assets 2. Liabilities 3. Profit 4. Loss 5. Profit and Loss results 6. Accounts not assigned
28 of 33
7/2/2012
The ABAP/4 program RFBILA00 calculates the balance sheet profit/loss from the assets and liabilities totals and enters the result in the Balance sheet results profit/loss item. The profit and loss statement results are determined from all accounts not assigned to either assets or liabilities, and are entered in the proper item. A financial statement version consists of a maximum of 10 hierarchy levels o Assign items to each level. The system calculates a total/subtotal for each item which is then displayed when the program is run. o Assign texts to each item. o Assign the accounts whose balance and account name are to be listed to the lowest levels.
Closing Procedure
Month-end closing activities (Preparatory activities) HR Payroll posting MM Maintain GR/IR clearing account Material valuations Close material ledger Close material master SD - Goods issues/invoices (Verify that all postings for the period have been generated) FI Accrual/Deferral postings Recurring Entries Depreciation posting Interest AuC settlement Close old period & open new period CO - Cost Centers: - Imputed costs, Distribution and assessment, indirect activity allocation, Calculate actual activity prices and update allocations Internal Orders: - Overheads - Settlement (For external settlement to AA or FI, reopen appropriate GL A/cs) Production orders: - Overheads - WIP calculation - Variance calculation - Settlement Profitability Analysis: - Cost center assessments
29 of 33
7/2/2012
- Activity based costing - Allocations Lock old posting period for Controlling transactions Month-end closing activities (Financial closing) FI - Re-open periods for adjustments CO/FI reconciliation postings (Cross-company code, cross-business area and cross-functional area flows within CO are posted to FI) Foreign currency open item valuation Accounting > Financial Accounting > Accounts receivable > Periodic Processing > Closing > Valuate > Valuation of Open Items in Foreign Currency Foreign currency balance sheet account valuation Accounting > Financial Accounting > GL Accounts > Periodic Processing > Closing > Valuate > Valuation of Open Items in Foreign Currency FI/PCA Balance sheet adjustment FI/CO-PA Profit and loss adjustment Final closing of posting periods Final Reporting: - Compact document journal - Financial statements - Taxes on sales/purchases - Balance audit trial Year-end closing activities (Preparatory activities) In addition to the regular month-end closing activities for the final period of the fiscal year to be closed, the activities to be performed for year-end closing process include: MM - Physical inventory procedure (Year-end or as required) Inventory valuations lowest value determination, LIFO, FIFO (After closing the postings in MM for the fiscal year) CO - PP Material valuation from new material cost estimates FI - FI - Open new fiscal year AR/AP Balance confirmations AA Fiscal year change FI Balance carryforward AA Valuations & Capital investment subsidies (after AA postings completed for fiscal year) AA Year-end closing AR/AP Close fiscal year Year-end closing activities (Financial closing)
30 of 33
7/2/2012
FI - Analyze GR/IR postings Regroup receivables/payables General adjustments Final fiscal year closing GL Account balances old fiscal year to new fiscal year (Reconcile carry forward balances with prior year final balances) FI/CO/AA Final reporting (same as monthly + Account balances year-end) AA Asset history sheet Accumulated balance audit trial
Cross Company Code Transactions
A cross company code transaction involves 2 or more company codes in one business transaction. For a cross company code transaction, the system will post a separate document in each of the company codes involved. Examples for cross company code transactions are: One company code makes purchases for other company codes (Central Procurement) One company code pays for other company codes (Central Payment) One company code sells goods to other company code Steps: Create Clearing Accounts in each of the company codes. The Clearing Accounts may be GL Accounts, Customer or Vendor Accounts. Configure the Automatic Postings for Cross Company Code Transactions by assigning Clearing Accounts for both the company codes. Creation of Clearing Accounts in both (FS00) In Company Code # 1 Account Current Assets Group Balance Sheet Account Short Text Clearing with CC2 Long Text Clearing with Company Code 2 the Company Codes In Company Code # 2 Current Liabilities Balance Sheet Account Clearing with CC1 Clearing with Company Code 1
31 of 33
7/2/2012
Account Currency
INR Only Bal in Local Currency Line Item Display 001 G001 Post Automatically Only
INR Only Bal in Local Currency Line Item Display 001 G001 Post Automatically Only
Sort Key Field Status Group
Cash Journal
The Cash Journal is a Bank Accounting subledger for the management of cash in a business. It can be used independently of other posting transactions. Cash journal entries are saved locally in the cash journal subledger. All balances are automatically calculated and displayed. The cash journal entries saved are posted to the GL.
Integration
MM FI Integration
Material Types ROH Raw Material ERSA Stores & Spares VERP Packaging Material FERT Finished Goods HALB Semi Finished Goods HAWA Traded Goods DIEN Services Views Basic View, Purchase View, Production View, Sales View, Quality View, Accounting View, Costing View, MRP View, Plant View etc. Creation of Material Master (MM01) Logistics > Material Management > Material Master > Material > Create General > Immediately Accounting Views (MM03)
32 of 33
7/2/2012
Fields: 1) Valuation Category 2) Valuation Class 3) Price Control Valuation Category: Batch Classification & Average Valuation Class: For Raw Material Indigenous and Imported Rules: The Material Master is to be created wrt Material Type In the Material Master we assign the Valuation Class For Valuation Class we assign the GL Masters based on the type of Transaction Price Control SPRO > Material Management > Define Price Control for S Standard Price, will V Moving Average, will Goods
> Valuation & Account Assignment Material Types be used for Finished Goods be used for other than Finished
MM FLOW
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Purchase Requisition No FI Entry Enquiry, Quotation and Price Comparison No FI Entry Purchase Order No FI Entry Purchase Order Release Procedure No FI Entry Goods Receipt (Will be taken wrt PO) Inventory RM Local A/c. Dr (BS CA) BSX To GR/IR Clearing A/c. (BS CL) WRX 6. Invoice Verification GR/IR Clearing A/c. Dr (BS CL) WRX To Vendor A/c. (BS CL) P.O. 7. Consumption RM Consumption Local A/c. Dr (P&L Dr) GBB-VBR To Inventory RM Local A/c. (BS CA) BSX 8. Production Receipt Inventory FG A/c. Dr (BS CA) BSX To Increase/Decrease in Stocks FG (P&L Cr) GBBZOB 9. FG Delivery Increase/Decrease in Stocks FG Dr (P&L Cr) GBBVAX To Inventory FG (BS CA) BSX 10. Billing SD Area FI MM Integration Settings (OBYC) SPRO > Material Management > Valuation and Account Assignment > Account Determination > Account Determination without Wizard > Configure Automatic Postings (OMWB)
33 of 33
7/2/2012
Cancel the existing Plant Select Account Assignment Button (OBYC)
SD FI Integration
SD FLOW
1. Enquiry/Quotation No FI Entry 2. Sales Order No FI Entry 3. Delivery Without PGI & With PGI Increase/Decrease in Stocks A/c. Dr To Inventory FG BSX 4. Billing Party A/c. Dr SO Commission A/c. Dr ERS To Sales Export A/c. To Freight Collection A/c. Pricing Procedure VK11 Material ERS Region to Region ERL Tax Code ERF GBB VAX
ERL ERF
Condition Type: KOFI
SD FI Integration (VKOA) SPRO > Financial Accounting > General Ledger Accounting > Business Transactions > Integration > Sales and Distribution > Prepare Revenue Account Determination Double Click 003 Material Group Account Key Application Area: V Sales/Distribution Condition Type: KOFI Account Assignment Goods Account Key Trading Goods ERL Revenue Finished Goods ERS Sales Deductions Services ERF Freight Revenue
You might also like
- Sap Fico Interview Questions AnswersDocument72 pagesSap Fico Interview Questions AnswersRavi TejaNo ratings yet
- Sap Fico Interview Questions AnswersDocument72 pagesSap Fico Interview Questions AnswersRavi TejaNo ratings yet
- Posting Key To Be Used For Particular Transaction by SAPDocument2 pagesPosting Key To Be Used For Particular Transaction by SAPranjitkusahuNo ratings yet
- Global Rollout With A TemplateDocument3 pagesGlobal Rollout With A TemplateranjitkusahuNo ratings yet
- MarketingDocument4 pagesMarketingranjitkusahuNo ratings yet
- Activating CIN Details in Vendor MasterDocument9 pagesActivating CIN Details in Vendor Masterabhisek_jajooNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5782)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Math 8 1 - 31Document29 pagesMath 8 1 - 31Emvie Loyd Pagunsan-ItableNo ratings yet
- TAFC R10 SP54 Release NotesDocument10 pagesTAFC R10 SP54 Release NotesBejace NyachhyonNo ratings yet
- List/Status of 655 Projects Upto 5.00 MW Capacity As On TodayDocument45 pagesList/Status of 655 Projects Upto 5.00 MW Capacity As On Todayganvaqqqzz21No ratings yet
- Unitrain I Overview enDocument1 pageUnitrain I Overview enDragoi MihaiNo ratings yet
- Misbehaviour - Nges Rgyur - I PDFDocument32 pagesMisbehaviour - Nges Rgyur - I PDFozergyalmoNo ratings yet
- Activity Codes - Jun 2011 - v4Document2 pagesActivity Codes - Jun 2011 - v4Venugopal HariharanNo ratings yet
- Marylebone Construction UpdateDocument2 pagesMarylebone Construction UpdatePedro SousaNo ratings yet
- 14 Worst Breakfast FoodsDocument31 pages14 Worst Breakfast Foodscora4eva5699100% (1)
- MadBeard Fillable Character Sheet v1.12Document4 pagesMadBeard Fillable Character Sheet v1.12DiononNo ratings yet
- Hbo Chapter 6 Theories of MotivationDocument29 pagesHbo Chapter 6 Theories of MotivationJannelle SalacNo ratings yet
- Accounting What The Numbers Mean 11th Edition Marshall Solutions Manual 1Document36 pagesAccounting What The Numbers Mean 11th Edition Marshall Solutions Manual 1amandawilkinsijckmdtxez100% (23)
- Bondor MultiDocument8 pagesBondor MultiPria UtamaNo ratings yet
- The Hittite Name For GarlicDocument5 pagesThe Hittite Name For GarlictarnawtNo ratings yet
- ScriptsDocument6 pagesScriptsDx CatNo ratings yet
- Indian Wall Paintings - Analysis of Materials and TechniquesDocument7 pagesIndian Wall Paintings - Analysis of Materials and Techniquesshu_sNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Admission & Discharge Dip NursingDocument7 pagesMental Health Admission & Discharge Dip NursingMuranatu CynthiaNo ratings yet
- The Wavy Tunnel: Trade Management Jody SamuelsDocument40 pagesThe Wavy Tunnel: Trade Management Jody SamuelsPeter Nguyen100% (1)
- Sample Detailed EvaluationDocument5 pagesSample Detailed Evaluationits4krishna3776No ratings yet
- The Political Philosophy of Giorgio Agamben A Critical EvaluationDocument20 pagesThe Political Philosophy of Giorgio Agamben A Critical EvaluationLEANo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae (October 31, 2011)Document5 pagesCurriculum Vitae (October 31, 2011)Alvin Ringgo C. Reyes100% (1)
- ZZXCDocument2 pagesZZXCKrisleen AbrenicaNo ratings yet
- Court Reviews Liability of Staffing Agency for Damages Caused by Employee StrikeDocument5 pagesCourt Reviews Liability of Staffing Agency for Damages Caused by Employee StrikeDenzhu MarcuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15-Writing3 (Thesis Sentence)Document7 pagesChapter 15-Writing3 (Thesis Sentence)Dehan Rakka GusthiraNo ratings yet
- HM5 - ScriptDocument4 pagesHM5 - ScriptCamilleTizonNo ratings yet
- FI - Primeiro Kfir 1975 - 1254 PDFDocument1 pageFI - Primeiro Kfir 1975 - 1254 PDFguilhermeNo ratings yet
- Invoice Inv0006: Er. Mohamed Irshadh P MDocument1 pageInvoice Inv0006: Er. Mohamed Irshadh P Mmanoj100% (1)
- Dead Can Dance - How Fortunate The Man With None LyricsDocument3 pagesDead Can Dance - How Fortunate The Man With None LyricstheourgikonNo ratings yet
- Rock Art and Metal TradeDocument22 pagesRock Art and Metal TradeKavu RI100% (1)
- Adjusted School Reading Program of Buneg EsDocument7 pagesAdjusted School Reading Program of Buneg EsGener Taña AntonioNo ratings yet
- E2415 PDFDocument4 pagesE2415 PDFdannychacon27No ratings yet