Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eeb 2
Uploaded by
karmayagnaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Eeb 2
Uploaded by
karmayagnaCopyright:
Available Formats
ECONOMIC
ENVIRONMENT
OF
BUSINESS
2011 02
BRAIN TEASER
HOW MANY SQUARES?
1 INTRODUCTION
The Behavior of an Enterprise in an Economic
Environment.
FOCUS Macro-economic Environment
The Business Sector depends on
- The Household Sector
- The Capital Market Sector
- The Government Sector
- The External Sector
Individually Companies can do little
Collectively they can Influence the Policies
CII Confederation of Indian Industry
FICCI Federation of Indian Chamber of Commerce
and Industry
ASSOCHAM Associated Chambers of Commerce and
Industry of India
They extract Tax Concessions and Subsidies from
the Government
Economic Laws in Favor of the Industry
2 ECONOMIC SYSTEM
The Sum Total of the Devices by which the
Preference among Alternative Purposes of
Economic Activity is determined and by which
Individual Activities are Coordinated for the
Achievement of these Purposes.
2.1 CAPITALISM
A Mixed Economic System in which the Private and
the Public Sectors coexist side by side.
Is Capitalism a fully Competitive Economic System?
2.2 SOCIALISM
The Responsibility of taking all Decisions Related
to Production and Economic Development lies with the
State.
- Apart from Labor all other means of Production
are owned by the State.
- Objective is Social Welfare and no Private Profit
- State Controls Production Pattern, Quantities and
Distribution.
3 MACRO-ECONOMIC SCENARIO
3.1 HIGH RATE OF GROWTH
Sales of Consumer and Consumer Durables Increase
3.2 INFLATION
Rise in General Level of Prices
Decrease in Demand
Consumer defers Purchase
3.3 HIGH RATES OF SAVINGS AND INVESTMENT
High Savings result in Higher Investment
Savings in the Bank
Investment either Internal or Foreign
3.4 FISCAL IMBALANCE
Government Funds
Income and Expenditure
What are the Funds used for?
3.5 BALANCE OF PAYMENT DEFECITS
Shortage of Foreign Exchange
Forces Restrictions on Imports
Protection of Domestic Industries
India example : Coco Cola, IBM
4 PROSPERITY, RECESSION & STAGFLATION
4.1 PROSPERITY
Supply and Demand High
Income High; Basic Needs Increase
Generates Competition
4.2 RECESSION
Crash in the Stock Market
Prices fall
Consumer Goods Sales are Maintained
4.3 DEPRESSION
Long Period of Recession results in Depression
US example
4.4 STAGFLATION
Result of Wrong Government Policies
Inadequate Growth; Inflation; Unemployment
5 FINANCIAL SYSTEMS
Basic Function: Accelerate Business Growth
Collection of Savings
Investment Transfer to Business Enterprises
Capital Formation
Households are Net Savers
Business Firms are Net Investors
There are 2 Markets
1 Money Market
Organized Sector and Unorganized Sector
2 Capital Market
Long-term Funding
IFCI, IDBI, SFC, SIDC, LIC, GIC
6 ECONOMIC POLICIES
6.1 INDUSTRIAL POLICY
Government allocated Capital to Industries
INDIA since 1956 Public and Private Sector
1973 Concession to Private Sector and Foreign
Multinationals
1980 Liberalization
Govt. Delicensed 28 Industry Categories
1991 New Industrial Policy
Deregulated the Indian Economy
6.2 TRADE POLICY
1 Outward Oriented
No discrimination in Domestic Markets
and Exports
2 Inward Oriented
Domestic Focus Only
India, since 1951 followed a Domestic Policy
1992 the Policy Changed
6.3 MONETARY POLICY
RBI
6.4 FISCAL POLICY
Provide a Stable Background for the Industry
For meeting Non-developmental Expenditures
Taxation for Public Expenditures
THANK YOU
You might also like
- Government Business InterfaceDocument14 pagesGovernment Business InterfaceManoj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Policy: Presentation OnDocument26 pagesIndustrial Policy: Presentation OnAshish PatelNo ratings yet
- Question Bank: Short Answer QuestionsDocument29 pagesQuestion Bank: Short Answer QuestionsPayal GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Handout - IndustryDocument13 pagesHandout - IndustryAnkit KumarNo ratings yet
- Disinvestment in IndiaDocument32 pagesDisinvestment in IndiaDixita ParmarNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics: Industrial Policies and the Growth of Private Sector Enterprises in IndiaDocument16 pagesManagerial Economics: Industrial Policies and the Growth of Private Sector Enterprises in IndiaSURAJ GADAVENo ratings yet
- Indian Economy 1950-1990Document16 pagesIndian Economy 1950-1990Chaitanya Sethi XI-BNo ratings yet
- Industrial Policy of IndiaDocument36 pagesIndustrial Policy of IndiaDikshaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledHarsh Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Government Schemes and Incentives For - pptx1Document26 pagesGovernment Schemes and Incentives For - pptx1Arjun VasudevNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Govt Support To SSIsDocument27 pagesClass 8 Govt Support To SSIsVamphyri VinNo ratings yet
- 4th Business Environment Notes Cover Economic, Fiscal & Trade PoliciesDocument38 pages4th Business Environment Notes Cover Economic, Fiscal & Trade PoliciesVikas jhaNo ratings yet
- Personnel ManagementDocument13 pagesPersonnel ManagementCaptainVipro YTNo ratings yet
- Nature of The Indian Economy: Before 2000Document13 pagesNature of The Indian Economy: Before 2000Dachu DarshanNo ratings yet
- 404 Ib Ie&td NotesDocument75 pages404 Ib Ie&td NotesDr. Rakesh BhatiNo ratings yet
- Global Recession: Fund (IMF) - It Considers A GlobalDocument12 pagesGlobal Recession: Fund (IMF) - It Considers A GlobalmodijiNo ratings yet
- Stages of InternationalizationDocument28 pagesStages of InternationalizationIshita KheriaNo ratings yet
- Economic Reforms: Immediate Causes That Led To The NepDocument13 pagesEconomic Reforms: Immediate Causes That Led To The NepJaganath RathNo ratings yet
- Vision IAS Mains Test 5 2021Document22 pagesVision IAS Mains Test 5 2021Amar GoswamiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Notes: Indian Economic Development 1950-1990Document10 pagesCBSE Class 11 Notes: Indian Economic Development 1950-1990ARNAVNo ratings yet
- New Economic Policy of 1991Document9 pagesNew Economic Policy of 1991Ka IfiNo ratings yet
- Strategy of Industrial Growth (1947-1990) &Document22 pagesStrategy of Industrial Growth (1947-1990) &Geeta GhaiNo ratings yet
- Industrial Policy of IndiaDocument19 pagesIndustrial Policy of IndiaMonisha PurwarNo ratings yet
- Indian Economy 1950-1990-1Document12 pagesIndian Economy 1950-1990-1akp200522No ratings yet
- CH 3 Liberalisation, Privatisation and Globalisation An AppraisalDocument6 pagesCH 3 Liberalisation, Privatisation and Globalisation An AppraisalDhruv SinghalNo ratings yet
- Industrial PolicyDocument47 pagesIndustrial Policyanuanuanu87No ratings yet
- Importance of Economic DevelopmentDocument7 pagesImportance of Economic DevelopmentORINDAY, Precious Pearl C.No ratings yet
- B.E 4 (Juhi Rajwani)Document7 pagesB.E 4 (Juhi Rajwani)Mukesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Indian Economy Assignment on Foreign Direct Investment PolicyDocument9 pagesIndian Economy Assignment on Foreign Direct Investment PolicyRatnesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Importance of Business EnvironmentDocument8 pagesImportance of Business EnvironmentRiskyeiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Economics: Appraisal of Indian Economic ReformsDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 11 Economics: Appraisal of Indian Economic ReformsAyush LohiyaNo ratings yet
- Upsc Preparation: Industrial PolicyDocument4 pagesUpsc Preparation: Industrial PolicyZankhana BhosleNo ratings yet
- ROLE OF INDUSTRYDocument38 pagesROLE OF INDUSTRYHetvi ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Overview & Profile - FinalDocument27 pagesChapter 1 Overview & Profile - FinalyezdianNo ratings yet
- Indian Economic EnvironmentDocument20 pagesIndian Economic EnvironmentSayak Goswami100% (2)
- Economy11 - 3 - Liberalisation Privatisation and GlobalisationDocument21 pagesEconomy11 - 3 - Liberalisation Privatisation and GlobalisationVishal KumarNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 24 Nov 2023Document2 pagesAdobe Scan 24 Nov 2023subuhana20067No ratings yet
- Liberalisation Policy: Vivekananda Institute of Professional Studies VsllsDocument11 pagesLiberalisation Policy: Vivekananda Institute of Professional Studies VsllsHardik SharmaNo ratings yet
- If - AssignDocument20 pagesIf - AssignSHIKHAR GOSWAMINo ratings yet
- Economic Reform ProgramsDocument8 pagesEconomic Reform Programsfyff536yydNo ratings yet
- India's Foreign TradeDocument8 pagesIndia's Foreign TradeSammir MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Government Policies For Business GrowthDocument19 pagesChapter 4 Government Policies For Business Growtharavindh chockalingamNo ratings yet
- BuluDocument20 pagesBulunarayanmeher07No ratings yet
- Indian Economy 1950Document17 pagesIndian Economy 1950sukh singhNo ratings yet
- Ed PPT (Dhwani, Ritika, Sanchit)Document14 pagesEd PPT (Dhwani, Ritika, Sanchit)2K19/BMBA/13 RITIKANo ratings yet
- Recent Development in Global Financial MarketDocument8 pagesRecent Development in Global Financial MarketBini MathewNo ratings yet
- Economics ProjectDocument16 pagesEconomics Projectshikhakhandelia199233% (6)
- Minor Project PresentationDocument35 pagesMinor Project PresentationNikitha GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Business Environment NotesDocument21 pagesBusiness Environment NotesAyush MundNo ratings yet
- New Economic Policy 1991Document12 pagesNew Economic Policy 1991AtinNo ratings yet
- Industrial PolicyDocument7 pagesIndustrial PolicynswgtstbifmkmpeccwNo ratings yet
- Ch2 Five Year PlansDocument9 pagesCh2 Five Year PlansShan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Economic Structure of IndiaDocument22 pagesEconomic Structure of IndiaShreedhar DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Regulatory Role of Government: Module-3Document49 pagesRegulatory Role of Government: Module-3khan28100% (1)
- What All Did Recession Ate?Document21 pagesWhat All Did Recession Ate?Kartik SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Maam Ella MidtermDocument13 pagesReviewer Maam Ella MidtermBianca MarieNo ratings yet
- Business EnvironmentDocument15 pagesBusiness EnvironmentSameer ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Business Environment: List of Public Sector Banks in India and Their HeadquartersDocument7 pagesBusiness Environment: List of Public Sector Banks in India and Their HeadquartersSouvik PurkayasthaNo ratings yet
- BhagavadGita theArtofLeadership OldTextNewContextDocument19 pagesBhagavadGita theArtofLeadership OldTextNewContextkarmayagnaNo ratings yet
- Beer Production ProcessDocument1 pageBeer Production ProcesskarmayagnaNo ratings yet
- Borders Crossed: Vibhishana in The Ramayana and Beyond: South Asia: Journal of South Asian StudiesDocument22 pagesBorders Crossed: Vibhishana in The Ramayana and Beyond: South Asia: Journal of South Asian StudieskarmayagnaNo ratings yet
- Spiritual Development Through The Chakra Progression: Jennifer Drapkin, Clayton Mcclintock, Elsa Lau, Lisa MillerDocument16 pagesSpiritual Development Through The Chakra Progression: Jennifer Drapkin, Clayton Mcclintock, Elsa Lau, Lisa MillerkarmayagnaNo ratings yet
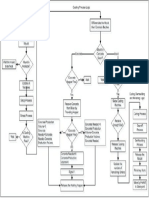
- Logical Flow Diagram of The Production Process OperationsDocument1 pageLogical Flow Diagram of The Production Process OperationskarmayagnaNo ratings yet
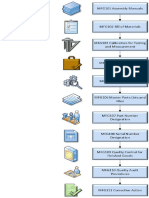
- Main Functions of The Operative Manufacturing Execution LevelDocument1 pageMain Functions of The Operative Manufacturing Execution LevelkarmayagnaNo ratings yet
- Ecommerce FlowchartDocument1 pageEcommerce FlowchartkarmayagnaNo ratings yet
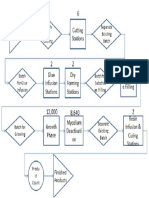
- Manufacturing Process MapDocument1 pageManufacturing Process MapkarmayagnaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing WorkflowDocument1 pageManufacturing WorkflowDidik HariadiNo ratings yet
- Flow Chart of The Manufacturing Process Used by Arena Software Numbers Indicating BatchDocument1 pageFlow Chart of The Manufacturing Process Used by Arena Software Numbers Indicating BatchkarmayagnaNo ratings yet
- Flowchart of The Industrial Process For The Manufacturing of Plastic Yogurt CupsDocument1 pageFlowchart of The Industrial Process For The Manufacturing of Plastic Yogurt CupskarmayagnaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing WorkflowDocument1 pageManufacturing WorkflowDidik HariadiNo ratings yet
- Logical Flow Diagram of The Production Process OperationsDocument1 pageLogical Flow Diagram of The Production Process OperationskarmayagnaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Process MapDocument1 pageManufacturing Process MapkarmayagnaNo ratings yet
- Logical Flow Diagram of The Production Process OperationsDocument1 pageLogical Flow Diagram of The Production Process OperationskarmayagnaNo ratings yet
- Flowchart of The Industrial Process For The Manufacturing of Plastic Yogurt CupsDocument1 pageFlowchart of The Industrial Process For The Manufacturing of Plastic Yogurt CupskarmayagnaNo ratings yet
- Services FlowchartDocument1 pageServices FlowchartLuis Fernando Sanchez TapiaNo ratings yet
- Beer Processing PFDDocument1 pageBeer Processing PFDkarmayagnaNo ratings yet
- Ecommerce FlowchartDocument1 pageEcommerce FlowchartkarmayagnaNo ratings yet
- Quality Control Process: Material SupplierDocument1 pageQuality Control Process: Material Supplieralva10 vaNo ratings yet
- Server WorkflowDocument1 pageServer WorkflowkarmayagnaNo ratings yet
- Order WorkflowDocument1 pageOrder WorkflowkarmayagnaNo ratings yet
- Order FlowchartDocument1 pageOrder FlowchartkarmayagnaNo ratings yet
- Intra Arterial ChemotherapyDocument6 pagesIntra Arterial ChemotherapykarmayagnaNo ratings yet
- Survival After Oral CancerDocument5 pagesSurvival After Oral CancerkarmayagnaNo ratings yet
- Statistical Study For Sonographic Differential Diagnosis ofDocument8 pagesStatistical Study For Sonographic Differential Diagnosis ofkarmayagnaNo ratings yet
- Oral CancerDocument5 pagesOral CancerkarmayagnaNo ratings yet
- Relationship of Tumor Thickness in Punch Biopsy and SubsequentDocument4 pagesRelationship of Tumor Thickness in Punch Biopsy and SubsequentkarmayagnaNo ratings yet
- Secondary Orbital MlanomasDocument5 pagesSecondary Orbital MlanomaskarmayagnaNo ratings yet
- Outcome of SQ .Cell CA of GingivaDocument5 pagesOutcome of SQ .Cell CA of GingivakarmayagnaNo ratings yet
- Purchase Order for PumpsDocument6 pagesPurchase Order for PumpsSuyog GawandeNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument10 pagesUntitledAshutosh SahooNo ratings yet
- SDM MergedDocument122 pagesSDM MergedAnjali BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Menyusun Laporan KeuanganDocument18 pagesMenyusun Laporan KeuanganAngelaNo ratings yet
- 20190212092028-DLT Application Process and Fee Structure PublicDocument8 pages20190212092028-DLT Application Process and Fee Structure PublicAbdullah MutaharNo ratings yet
- Accounting 202 Chapter 4 NotesDocument7 pagesAccounting 202 Chapter 4 NotesnitinNo ratings yet
- CVPCustomer Value Proposition AnalysisDocument4 pagesCVPCustomer Value Proposition AnalysisJessy WairiaNo ratings yet
- Press Release SampleDocument5 pagesPress Release Samplemadhusmita14No ratings yet
- Mustapha Hasni Hartmann Benz GMBHDocument3 pagesMustapha Hasni Hartmann Benz GMBHmustaphahasnieasygold24No ratings yet
- CH 18Document130 pagesCH 18Indah PNo ratings yet
- HRP SDocument44 pagesHRP SParshant GuptaNo ratings yet
- TATA S Digital ReshuffleDocument11 pagesTATA S Digital ReshuffleXama VariaNo ratings yet
- Project WorkDocument41 pagesProject WorkNaveed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-IntroductionDocument15 pagesLecture 1-IntroductionIbrahem Hani AlkhazalehNo ratings yet
- Confirmation Slip D10487DC15402: Audax Pink 5!Document2 pagesConfirmation Slip D10487DC15402: Audax Pink 5!shasiNo ratings yet
- Lightstone Equipment LTD Wanted To Expand Into New Brunswick andDocument1 pageLightstone Equipment LTD Wanted To Expand Into New Brunswick andHassan JanNo ratings yet
- Sba-Reaction Paper (Week 7)Document2 pagesSba-Reaction Paper (Week 7)Mary Joy SameonNo ratings yet
- Business Plan NG Mga POGIDocument12 pagesBusiness Plan NG Mga POGIJoshua BrazalNo ratings yet
- China's Crusade Against Its Tech FirmsDocument5 pagesChina's Crusade Against Its Tech FirmscoolNo ratings yet
- Past Papers Practice (ICAP QS) - H.O # 3Document5 pagesPast Papers Practice (ICAP QS) - H.O # 3Saif SiddNo ratings yet
- Tour 303 Module 1 Lesson 1Document13 pagesTour 303 Module 1 Lesson 1Aira MapuaNo ratings yet
- Part 1: Task Risk Assessment: A Description/labelled Sketch of The Location(s)Document8 pagesPart 1: Task Risk Assessment: A Description/labelled Sketch of The Location(s)samuelNo ratings yet
- Knott V Cottee (1852) 51 ER 705Document3 pagesKnott V Cottee (1852) 51 ER 705schoolemailsdumpNo ratings yet
- 291 A-Financial AccountDocument21 pages291 A-Financial AccountK GanesanNo ratings yet
- RBI Guidelines On Currency ManagementDocument16 pagesRBI Guidelines On Currency Managementeknath2000No ratings yet
- Ensuring Quality in Distribution of Medicinal ProductsDocument16 pagesEnsuring Quality in Distribution of Medicinal ProductsASHU PURINo ratings yet
- Alayu Source Project Performance The CasDocument56 pagesAlayu Source Project Performance The CasDuke GlobalNo ratings yet
- 5 Little Known Profitable BusinessesDocument34 pages5 Little Known Profitable BusinessesFidelisNo ratings yet
- Rimini Street Ebook 12 Clients Using BDRDocument16 pagesRimini Street Ebook 12 Clients Using BDREverson SAPNo ratings yet
- Enerveo Quality Policy CommitmentDocument1 pageEnerveo Quality Policy CommitmentJohn GeddesNo ratings yet