Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Inflammation Plenary
Uploaded by
pazucenaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Inflammation Plenary
Uploaded by
pazucenaCopyright:
Available Formats
Inflammation
ACUTE INFLAMMATION
Case 1
Case 1
An 18-year old male presented with abdominal
pain of one day duration, initially felt at the
epigastric area and became localized at the right
lower quadrant. There was associated
intermittent cramping and one episode of
vomiting.
Case 1
On admission, the temperature was 39.0
o
C,
pulse rate was 104 per minute. There was
tenderness and muscle guarding over the right
lower quadrant. The WBC count was 15 x 10
9
/L.
An appendectomy was performed.
Gross Findings
Gross Findings
The appendix was enlarged, indurated and
covered with a fibrinopurulent exudate. Cut
section showed softish wall with fecaloid and
purulent material filling its lumen.
Microscopic Findings
Questions
What is the histologic criterion for the diagnosis
of acute appendicitis?
What are the complications of appendicitis?
ACUTE INFLAMMATION
Case 2
Case 2
A middle-aged male, known alcoholic, was
admitted for difficulty in breathing and high
grade fever. He had been having cough,
productive of purulent sputum for the past five
days.
Case 2
One week prior to admission, the patient was
allegedly found sprawled in front of their house
with vomitus all over his upper garments. The
patient died on the tenth hospital day.
Gross Findings
Postmortem examination of both lungs showed
patchy areas of consolidation, with small
pockets of suppurative exudate within the right
lung.
Microscopic Findings
Microscopic Findings
Questions
What are the possible outcomes of
bronchopneumonia? What in the history point
to an acute inflammatory condition?
What are the histologic features seen on the
slide that point to an acute inflammatory
process?
ACUTE INFLAMMATION
Case 3
Case 3
A 50-year old female, obese, and multiparous
was admitted for recurrent right hypochondriac
and epigastric pain, sometimes associated with
low grade fever of the last two years. The pain
was noted especially after a heavy meal rich in
fat.
Case 3
Physical examination revealed slight tenderness
and muscle guarding over the right
hypochondrium. A cholecystogram reveal
rounded filling defects in the gallbladder. A
cholecystectomy was performed.
Gross Findings
Gross Findings
The gallbladder retained its normal pear shaped
configuration, but there was remnants of fibrous
adhesions on the serosal surface. The wall was
thickened. Several ovoid jet black calculi with
granular sufaces and brownish yellow cores were
found in the lumen. The mucosal surface was highly
trabeculated.
Microscopic Findings
Questions
What in the histology points to a chronic
inflammatory process?
What are the diseases where the presence of
lymphocytes connotes an acute inflammation?
ACUTE INFLAMMATION
Case 4
Case 4
A 40-year old male bank executive had been
having recurrent epigastric burning for several
months. Initial gastroscopy showed an ulcer at
the gastric antrum on the lesser curvature. He
was given medications of three weeks.
Case 4
There was no relief of symptoms and repeat
gastroscopy showed no reduction in the size of
the ulcer. Antrectomy with gastroduodenal
anastomosis was performed.
Gross Findings
Gross Findings
The antrectomy specimen showed a well
demarcated, oval shaped ulcer measuring 2.5
cm in its main diameter, with smooth slightly
rolled margin and clear base. The mucosa
immediately surrounding the ulcer is somewhat
edematous.
Microscopic Findings
Questions
What are the layers of a peptic ulcer?
What in the histology points o a chronic
inflammatory process?
What is the role of Helicobacter pylori in the
pathogenesis of gastric ulcer?
ACUTE INFLAMMATION
Case 5
Case 5
A 10-year-old boy was described by his mother
as having been sickly for the last two years, with
recurrent cough and low grade afternoon fever.
Several physicians had treated him either as a
case of simple upper respiratory infection or
pulmonary tuberculosis. Significant in the
history was that an aunt who took care of the
child in the past had at least two episodes of
frank hemoptysis during the past year.
Case 5
A few weeks prior to admission, the patient
became apathetic and less active. Shortly
thereafter, the cough became more distressing
and occasionally productive of blood-streaked
sputum. High fever and labored breathing
ensued. On admission, the child was cyanotic
and he died an hour later.
Gross Findings
Post mortem examination showed that the lungs
were almost completely consolidated by
fibrocaseous lesions which included numerous
tiny grayish nodules and small cavitation. The
regional lymph nodes were enlarged and matted
together, cut section showed caseation necrosis.
Microscopic Findings
Questions
What is a granuloma?
Give other disease entities that cause
granulomatous inflammation.
ACUTE INFLAMMATION
Case 6
Case 6
A 25-year old female underwent excision of a 1-cm
in diameter, firm, movable, non-tender, ill-defined
left breast mass. Four months before, she had
previously undergone excision of a benign breast
mass in the same area. The case was diagnosed as
suture granuloma.
Microscopic Examination
Questions
What are the two types of granuloma based on
inciting agent?
ACUTE INFLAMMATION
Case 7
Case 7
A 49-year old male complained of a polypoid,
ulcerated and bleeding mass on the left
forefinger. This mass started as a wound which
he got while doing carpentry work at home.
Grossly, the mass was elevated, and ulcerated
with a hemorrhagic base. Histologic sections
showed granulation tissue.
Microscopic Findings
Microscopic Findings
Questions
What is neovascularization? What factors induce
it?
What are the components of the repair process
of tissues subjected to chronic inflammation?
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- AJSS Psychology RevDocument40 pagesAJSS Psychology RevpazucenaNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Growing Up in Filipino FamiliesDocument2 pagesGrowing Up in Filipino FamiliespazucenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter10 12 MemoDocument2 pagesChapter10 12 MemopazucenaNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Organization of Muscle FiberDocument1 pageOrganization of Muscle FiberpazucenaNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- AJSSFinals - PsychologyDocument38 pagesAJSSFinals - PsychologypazucenaNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Harrison SLEDocument11 pagesHarrison SLEpazucenaNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Growing Up in Filipino FamiliesDocument2 pagesGrowing Up in Filipino FamiliespazucenaNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Ajss Psychology Rev - Answer SheetDocument59 pagesAjss Psychology Rev - Answer SheetpazucenaNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Books For Learning Unit 3Document2 pagesBooks For Learning Unit 3pazucenaNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Cook Time: 1 Hour, 10 Minutes Total Time: 1 Hour, 10 MinutesDocument2 pagesCook Time: 1 Hour, 10 Minutes Total Time: 1 Hour, 10 MinutespazucenaNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Growing Up in Filipino FamiliesDocument2 pagesGrowing Up in Filipino FamiliespazucenaNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Solipsism FINALDocument9 pagesSolipsism FINALpazucena100% (1)
- AJSS Psychology RevDocument40 pagesAJSS Psychology RevpazucenaNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Kalusugan PangkalahatanDocument4 pagesKalusugan PangkalahatanpazucenaNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Social PsychologyDocument1 pageSocial PsychologypazucenaNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Reproductive Health Primer and Legal IssuesDocument83 pagesReproductive Health Primer and Legal IssueskasamahumanrightsNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- OS 203 06262013 Integumentary SystemDocument5 pagesOS 203 06262013 Integumentary SystempazucenaNo ratings yet
- Story PyramidDocument1 pageStory PyramidpazucenaNo ratings yet
- 793Document7 pages793pazucenaNo ratings yet
- Pigeon Hole PrincipleDocument13 pagesPigeon Hole Principleapi-184588206No ratings yet
- Social Psychology PSYC250Document21 pagesSocial Psychology PSYC250pazucenaNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Big Bang Theory and The Origin of EarthDocument8 pagesBig Bang Theory and The Origin of EarthpazucenaNo ratings yet
- SonnetDocument8 pagesSonnetpazucenaNo ratings yet
- Comb 1Document12 pagesComb 1pazucenaNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- PhiloDocument1 pagePhilopazucenaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document10 pagesLecture 5pazucenaNo ratings yet
- KierkegaardDocument7 pagesKierkegaardpazucenaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument4 pagesIntegumentary SystempazucenaNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- AristotleDocument8 pagesAristotlepazucenaNo ratings yet
- Psychogenic Non-Epileptic Seizures (PNES)Document19 pagesPsychogenic Non-Epileptic Seizures (PNES)adzhangNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Now 8Th Edition Brown Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument39 pagesNutrition Now 8Th Edition Brown Test Bank Full Chapter PDFdaviddulcieagt6100% (10)
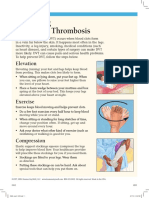
- Preventing Deep Vein Thrombosis: ElevationDocument2 pagesPreventing Deep Vein Thrombosis: ElevationTeuku Ilham AkbarNo ratings yet
- Hair Loss in CatsDocument6 pagesHair Loss in CatsGiulia Nădășan-CozmaNo ratings yet
- Heirs of Deauna vs. Fil-Star Maritime Corp.Document31 pagesHeirs of Deauna vs. Fil-Star Maritime Corp.Coleen ReyesNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Bell's PalsyDocument5 pagesTreatment of Bell's Palsymaryrose_jordanNo ratings yet
- David Neswald Report3!20!94Document3 pagesDavid Neswald Report3!20!94gwap360No ratings yet
- CYSTSDocument12 pagesCYSTSGowriNo ratings yet
- 2 Chapter20 Pregnant With Preexisting IllnessDocument80 pages2 Chapter20 Pregnant With Preexisting IllnessElgen B. AgravanteNo ratings yet
- SOP Akupresur MigrainDocument20 pagesSOP Akupresur MigrainrachelNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument42 pagesAcute Myocardial InfarctionAzra BalochNo ratings yet
- First Case Report of A Successfully Managed Severe COVID-19 Infectionin MalawiDocument4 pagesFirst Case Report of A Successfully Managed Severe COVID-19 Infectionin MalawiYoga PrabawaNo ratings yet
- Delirium: Annals of Internal MedicineDocument16 pagesDelirium: Annals of Internal Medicinemariell3193No ratings yet
- J.B. Family Case Presentation Group 1Document67 pagesJ.B. Family Case Presentation Group 1Jeno Luis AcubNo ratings yet
- New Guidelines For Potassium ReplacementDocument33 pagesNew Guidelines For Potassium ReplacementAnggry MambaitNo ratings yet
- SDCEP Drug Prescribing Ed 3 Update June 2021Document4 pagesSDCEP Drug Prescribing Ed 3 Update June 2021ABNo ratings yet
- Oncocytoma of The Nasal CavityDocument2 pagesOncocytoma of The Nasal CavityInes Camilla PutriNo ratings yet
- Streptokokni Toksični Šok SindromDocument6 pagesStreptokokni Toksični Šok SindromNandor SiliNo ratings yet
- First Degree BurnsDocument3 pagesFirst Degree BurnsbobboxNo ratings yet
- CE (Ra) F (P) PF1 (BHV AnG) PFA (NC BHV AP) PB (BHV AnG) PN (AnG)Document4 pagesCE (Ra) F (P) PF1 (BHV AnG) PFA (NC BHV AP) PB (BHV AnG) PN (AnG)anisaNo ratings yet
- Yellow Fever Vaccine:: What You Need To KnowDocument2 pagesYellow Fever Vaccine:: What You Need To Knowamal aldhafeeriNo ratings yet
- Alterations in Oxygenation 2Document18 pagesAlterations in Oxygenation 2alejandrino_leoaugustoNo ratings yet
- A Case Study in SchizophreniaDocument11 pagesA Case Study in SchizophreniaRamin ApparaoNo ratings yet
- FISDAP Operations Exam Questions and AnswersDocument9 pagesFISDAP Operations Exam Questions and Answersmtahir777945No ratings yet
- Laryngeal ObstructionDocument59 pagesLaryngeal ObstructionpravinNo ratings yet
- 4 Ingles Cuarto English Sickness ModuloDocument4 pages4 Ingles Cuarto English Sickness ModuloyeraldinNo ratings yet
- MALIGNANCYDocument47 pagesMALIGNANCYAsmi MohamedNo ratings yet
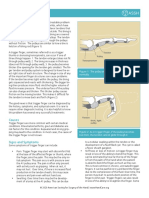
- Trigger FingerDocument2 pagesTrigger FingerTJPlayzNo ratings yet
- NephritisDocument21 pagesNephritisruchikaNo ratings yet
- Mini-OSCE Internal PicturesDocument108 pagesMini-OSCE Internal PicturesCheru TadesseNo ratings yet
- Peaceful Sleep Hypnosis: Meditate & RelaxFrom EverandPeaceful Sleep Hypnosis: Meditate & RelaxRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (142)
- Breaking the Habit of Being YourselfFrom EverandBreaking the Habit of Being YourselfRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1458)
- Summary of The 4-Hour Body: An Uncommon Guide to Rapid Fat-Loss, Incredible Sex, and Becoming Superhuman by Timothy FerrissFrom EverandSummary of The 4-Hour Body: An Uncommon Guide to Rapid Fat-Loss, Incredible Sex, and Becoming Superhuman by Timothy FerrissRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (81)
- How to Talk to Anyone: Learn the Secrets of Good Communication and the Little Tricks for Big Success in RelationshipFrom EverandHow to Talk to Anyone: Learn the Secrets of Good Communication and the Little Tricks for Big Success in RelationshipRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1135)
- Gut Health Hacks: 200 Ways to Balance Your Gut Microbiome and Improve Your Health!From EverandGut Health Hacks: 200 Ways to Balance Your Gut Microbiome and Improve Your Health!Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningFrom EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)