Professional Documents
Culture Documents
APP RADIOLOGI Baru
Uploaded by
azzahramaris0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views14 pagesDokumen tersebut membahas tentang apendiks dan apendisitis. Apendiks adalah organ berbentuk tabung sepanjang sekitar 10 cm yang berpangkal di caecum. Apendisitis adalah peradangan yang terjadi pada apendiks yang merupakan penyebab abdomen akut paling sering. Bakteri Escherichia coli sering menjadi penyebab infeksi apendisitis.
Original Description:
Original Title
APP RADIOLOGI baru.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDokumen tersebut membahas tentang apendiks dan apendisitis. Apendiks adalah organ berbentuk tabung sepanjang sekitar 10 cm yang berpangkal di caecum. Apendisitis adalah peradangan yang terjadi pada apendiks yang merupakan penyebab abdomen akut paling sering. Bakteri Escherichia coli sering menjadi penyebab infeksi apendisitis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views14 pagesAPP RADIOLOGI Baru
Uploaded by
azzahramarisDokumen tersebut membahas tentang apendiks dan apendisitis. Apendiks adalah organ berbentuk tabung sepanjang sekitar 10 cm yang berpangkal di caecum. Apendisitis adalah peradangan yang terjadi pada apendiks yang merupakan penyebab abdomen akut paling sering. Bakteri Escherichia coli sering menjadi penyebab infeksi apendisitis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
Pembimbing
Dr. Rachmat M., Sp.Rad
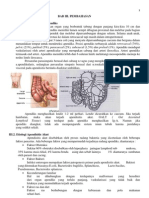
Apendiks : organ berbentuk tabung, panjangnya kira-kira
10cm (kisaran 3-15cm) (2,5-225cm), dan berpangkal di
caecum. Lumennya sempit di bagian proksimal dan melebar di
bagian distal. Diameter appendiks 6mm.
Appendicitis : peradangan yang terjadi pada
Appendix vermicularis, dan merupakan penyebab abdomen
akut yang paling sering.
Sjamsuhidajat r, De Jong W. Buku Ajar Ilmu Bedah. Edisi 2. Jakarta : EGC,2003
Posisi appendix:
a. Pelvic
b. Retrocecal
c. Preilieal
d. Postileal (retroileal)
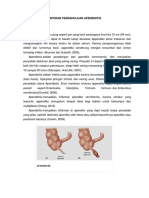
Obstruksi pada lumen appendix kongseti vaskuler
iskemik nekrosis terjadi infeksi.
Penyebab obstruksi yang paling sering adalah fecolith.
Penyebab lain dari obstruksi appendiks meliputi:
Hiperplasia folikel lymphoid
Carcinoid atau tumor lainnya
Benda asing (pin, biji-bijian)
Kadang parasit
Bakteri aerob fakultatif Bakteri anaerob
Escherichia coli
Viridans streptococci
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Enterococcus
Bacteroides fragilis
Peptostreptococcus micros
Bilophila species
Lactobacillus species
Patomekanisme
Syarat foto :
Identitas
Diafragma sampai
simpisis harus tampak
Tampak peritoneal fat
line tidak boleh
terpotong
Tampak muskulus
psoas
Identitas : Ny. Ela
Monika /PR/25thn
Marker : R
Tanggal : 20 Juni 2013
Posisi : AP , Oblik
Telah dilakukan
pemeriksaan
Apendikogram :
-Tampak kontras mengisi
kolon asenden dan caecum
-Kontras tidak sampai
distal
- tampak kontras mengisi
apendix dan ada tanda-
tanda perlengketan
- lumen apendix tidak rata
-Kaliber appendiks 1 cm
-Tampak udara pada ileum
Kesan : apendiksitis
Saran : Ct-Scan
aperistaltic, noncompressible, dilated appendix (
>6mm outer diameter)
distinct appendiceal wall layers
target appearance (axial section)
appendicolith
periappendiceal fluid collection
echogenic prominent pericaecal fat
confirming that the structure visualised is the
appendix is clearly essential and requires
demonstration of it being blind ending and
arising from the base of the caecum
Pembengkakkan appendiks
dengan bayangan echogenic
didalamnya (diameter > 6 mm)
Normal appendix. Contrast is seen
filling a normal appearing appendix
(arrows) demonstrating a thin wall.
Appendicitis with appendicolith.
An enlarged appendix (solid arrows)
is seen with an appendicolith
(dashed arrows) at the base.
Appendicitis. The appendix (solid
arrows) is abnormally dilated and
demonstrates a thickened
enhancing wall and no filling with
contrast.
Perforated appendicitis. The
appendix (solid arrows) is
abnormally dilated with a thickened
enhancing wall. Small pockets of
extraluminal air (dashed arrows)
indicate perforation.
contrast-enhanced,
fat-suppressed, T1-
weighted, spin-echo
coronal magnetic
resonance image. A
markedly enhanced
and thickened inflamed
appendix (arrows) with
pericecal enhancement
due to the extent of
inflammation is shown.
Terima kasih
You might also like
- DIAGNOSIS CEPAT APPENDISITISDocument33 pagesDIAGNOSIS CEPAT APPENDISITISriza21No ratings yet
- RADIOLOGI EMERGENSI PELVISDocument33 pagesRADIOLOGI EMERGENSI PELVISferawati dakioNo ratings yet
- APPENDISITISDocument46 pagesAPPENDISITISUmam Junior100% (1)
- APENDIKSDocument46 pagesAPENDIKSIndahK.WardhaniPutri100% (2)
- LP Apendisitis GadarDocument16 pagesLP Apendisitis GadarElis MaemunahNo ratings yet
- APENDISITIS LAPORANDocument18 pagesAPENDISITIS LAPORANNopaRaskaNo ratings yet
- LAPORAN PENDAHULUAN APENDISITIS PERFORASIDocument21 pagesLAPORAN PENDAHULUAN APENDISITIS PERFORASIInda RumapassalNo ratings yet
- APENDISITISDocument51 pagesAPENDISITISNico AfituNo ratings yet
- LP ApendisitisDocument11 pagesLP ApendisitisMira RencaNo ratings yet
- Laporan Pendahuluan - ApendiksDocument27 pagesLaporan Pendahuluan - Apendiksviana mertiNo ratings yet
- APENDISITIS AKUTDocument6 pagesAPENDISITIS AKUTAang Syamsul BachriNo ratings yet
- APENDISITISDocument15 pagesAPENDISITISKarang SsiNo ratings yet
- Appendisitis AkutDocument17 pagesAppendisitis AkutMuhammad Diko PrakosoNo ratings yet
- LP Apendiktomi Lisna Shopiyah 201FK04082Document27 pagesLP Apendiktomi Lisna Shopiyah 201FK04082lisnashopiyahNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis dalamDocument5 pagesAppendicitis dalamEsha PerdanaNo ratings yet
- ANATOMI DAN FISIOLOGI APENDISDocument6 pagesANATOMI DAN FISIOLOGI APENDISMartonggoNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis Akut RadiologiDocument67 pagesAppendicitis Akut RadiologiAnonymous 2CvtIRVNo ratings yet
- Nopriyanto M10 LP Dan Askep ApendiksitisDocument25 pagesNopriyanto M10 LP Dan Askep ApendiksitisARA YOUTUBNo ratings yet
- LP Apendisitis K.6Document18 pagesLP Apendisitis K.6Nurul Zeika WahdaniyaNo ratings yet
- Paper Anastesi RA-SAB Pada AppendicitisDocument31 pagesPaper Anastesi RA-SAB Pada AppendicitisraniaboloyNo ratings yet
- Laporan Pendahuluan APENDISITISDocument16 pagesLaporan Pendahuluan APENDISITISIrnayanti MamiDgSiameNo ratings yet
- Laporan Pendahuluan Apendicitis Dan LaparatomiDocument38 pagesLaporan Pendahuluan Apendicitis Dan LaparatomiJayanti Indrayani100% (1)
- APENDIKSITISDocument12 pagesAPENDIKSITISkoko senoajiNo ratings yet
- Laporan Pendahuluan ApendisitisDocument20 pagesLaporan Pendahuluan ApendisitisPutri BullahNo ratings yet
- APPENDISITISDocument47 pagesAPPENDISITISArda Putri Kurniati100% (1)
- Laporan Pendahuluan ApendisitisDocument22 pagesLaporan Pendahuluan Apendisitishidayatul umrohNo ratings yet
- LP ApendisitisDocument15 pagesLP ApendisitisdebbyNo ratings yet
- LP ApendisitisDocument23 pagesLP Apendisitisfahmi ristayaniNo ratings yet
- Laporan Pendahuluan ApendikDocument20 pagesLaporan Pendahuluan Apendikzaenal ahsanudinNo ratings yet
- LP ApendiktomiDocument18 pagesLP Apendiktomidewi100% (1)
- LP AppendixDocument25 pagesLP AppendixAdellia LaudiiaNo ratings yet
- Laporan Pendahuluan ApendisitisDocument18 pagesLaporan Pendahuluan Apendisitisarya jayaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial App Akut Irvan R LohoDocument40 pagesTutorial App Akut Irvan R Lohoeruza hiwatariNo ratings yet
- LP Ibs AppendicitisDocument23 pagesLP Ibs AppendicitisFijar KaliwantonoNo ratings yet
- LAPORAN APENDISITISDocument33 pagesLAPORAN APENDISITISmufidatul husnaNo ratings yet
- Anatomi ApendikDocument45 pagesAnatomi Apendikyoe_999No ratings yet
- APENDISITIS AkutDocument34 pagesAPENDISITIS AkutAndreas Tedi Karo-Karo100% (1)
- APENDISITISDocument20 pagesAPENDISITISRizkyGandaPrayogiNo ratings yet
- APENDISITIS AKUTDocument20 pagesAPENDISITIS AKUTainngoa douNo ratings yet
- Referat Abses Apendiks Rima FixDocument22 pagesReferat Abses Apendiks Rima FixRima Aprilia Kartika AbsariNo ratings yet
- APENDISITIS AKUTDocument35 pagesAPENDISITIS AKUTRizka ZahroNo ratings yet
- LP ApendicDocument10 pagesLP Apendicindri anitaNo ratings yet
- AppendicitisDocument3 pagesAppendicitisArga GabrielNo ratings yet
- LP App LaparatomyDocument12 pagesLP App Laparatomykelvin vinaNo ratings yet
- APENDIKTOMIS SEBAGAI PENANGANAN APENDISITISDocument9 pagesAPENDIKTOMIS SEBAGAI PENANGANAN APENDISITISLinda Nur halisyahNo ratings yet
- Laporan Pendahuluan App Okfana 034Document17 pagesLaporan Pendahuluan App Okfana 034Okfana AbeliaNo ratings yet
- Laporan Pendahuluan ApendisitisDocument27 pagesLaporan Pendahuluan ApendisitisNigmah NajmNo ratings yet
- Apendisitis - TeoriDocument4 pagesApendisitis - TeoriSayyid FadhlyNo ratings yet
- LP Post Op ApendiktomiDocument11 pagesLP Post Op ApendiktomiEka Indah AditiaNo ratings yet
- LP AppendicitisDocument17 pagesLP AppendicitisGek LiaNo ratings yet
- Laporan Pendahuluan ApendisitisDocument13 pagesLaporan Pendahuluan ApendisitisMelani NursyifaNo ratings yet
- DETEKSI DINI APENDISITISDocument21 pagesDETEKSI DINI APENDISITISDwipaya YantiNo ratings yet
- LAPORAN APENDIKSITISDocument10 pagesLAPORAN APENDIKSITISari100% (2)
- Sak ApendisitisDocument8 pagesSak ApendisitisFirdaus 16No ratings yet
- Laporan Pendahuluan ApendisitisDocument24 pagesLaporan Pendahuluan ApendisitisNadya RatihNo ratings yet
- Laporan Pendahuluan ApendisitisDocument18 pagesLaporan Pendahuluan ApendisitisDesi NataliaNo ratings yet
- LP Apendisitis Muthia Debby - CompressDocument15 pagesLP Apendisitis Muthia Debby - CompressTara Mune16No ratings yet
- LP AppDocument14 pagesLP Appmimin verianaNo ratings yet
- Dermatitis VenenataDocument12 pagesDermatitis VenenataazzahramarisNo ratings yet
- Dermatitis VenenataDocument12 pagesDermatitis VenenataazzahramarisNo ratings yet
- Dermatitis VenenataDocument12 pagesDermatitis VenenataazzahramarisNo ratings yet
- Anatomi HidungDocument16 pagesAnatomi HidungazzahramarisNo ratings yet
- Dermatitis VenenataDocument12 pagesDermatitis VenenataazzahramarisNo ratings yet
- APP RADIOLOGI BaruDocument14 pagesAPP RADIOLOGI BaruazzahramarisNo ratings yet
- OsteochondromaDocument4 pagesOsteochondromaazzahramarisNo ratings yet
- TUMOR Urin FixDocument10 pagesTUMOR Urin FixazzahramarisNo ratings yet
- APP RADIOLOGI BaruDocument14 pagesAPP RADIOLOGI BaruazzahramarisNo ratings yet
- Ekspertise VERTEBRADocument2 pagesEkspertise VERTEBRAazzahramarisNo ratings yet