Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Materi Determinasi Seks Tambahan
Uploaded by
wulandewi15120 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
50 views13 pagesmateri kuliah medical genetic determinasi seks tambahan
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentmateri kuliah medical genetic determinasi seks tambahan
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
50 views13 pagesMateri Determinasi Seks Tambahan
Uploaded by
wulandewi1512materi kuliah medical genetic determinasi seks tambahan
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 13
Materi determinasi seks
tambahan
RETNO DWI W.
2007
True hermaphroditism
Internal genital development:
Wolffian: on the side that has a testis or mostly testicular tissue, you
might get parts of the sperm transport system (such as
epididymis or vas deferens, etc.). On the side that has an ovary
or mostly ovarian tissue you might get apoptosis of the
wolffian duct.
Mullerian: on the side that has a testis or mostly testicular tissue,
you might get apoptosis and thus NO mullerian derivatives. On
the side that has an ovary or mostly ovarian tissue you might
not get MIS and thus the duct becomes am oviduct,
deformed uterus, and upper vagina.
External genital development:
Depending on the amount of testosterone that reaches the external
genital rudiments, you will either get a normal female vulva (virtually
no testosterone reaching this region) or more likely an ambiguous
external genitalia consisting of penis and split or bifid scrotum with a
vaginal opening between the two parts of the open scrotum.
5-alpha reductase deficiency [also known as
pseudovaginal perineoscrotal hypospadias syndrome or
PPHS] This is a male pseudohermaphrodite
In this condition the individuals are 46,XY.
They have a gene mutation that does not
permit the conversion of testosterone to
dihydrotestosterone in target tissue. Their
testes produce normal amounts of MIS
and testosterone which otherwise function
normally.
Gonads: testes
Internal genitalia; MIS is OK and testosterone is
OK so
Wolffian ducts form sperm transport system
Mullerian ducts undergo apoptosis
External genitalia form what looks like a vulva
but not quite right
Genital tubercle is a clitoris
Genital folds form labia minora-like structures
Genital swellings form labia majora like
structures.
Additional features: If raised as a female (despite the
absence of a vagina) these individuals at puberty will
respond to testosterone and grow a beard, deepen the
voice, and become muscular. There may a slight
enlargement of the clitoris. If detected early the testes
can be removed (they are internal) to prevent possible
gonadoblastoma and thus the pubertal changes will not
go in a male direction. To have intercourse these
individuals would need surgery to construct a vagina
passage. The lower vagina is either absent or very short.
Kasus DEFISIENSI 5 ALPHA REDUCTASE
Seorang wanita menjalani pemeriksaan USG rutin
pada kehamilan anak ke dua pada usia kehamilan
12, 20 dan 34 minggu.
Anak pertamanya lahir dengan hypospadia.
Kemudian wanita ini menikah lagi dengan
sepupunya dan mengalami keguguran. Tidak ada
kelainan kongenital dalam keluarganya. Hasil
pemeriksaan USG menunjukkan pertumbuhan
dan morfologi bayi normal.
Jenis kelamin bayi adalah wanita. Tetapi hasil USG
pada genitalia eksterna menunjukkan pembesaran
labia majora, tidak terlihat adanya labia minora,
clitoris, penis maupun testis.
Bayi lahir di usia kehamilan 40
minggu, fenotip wanita normal
dan tidak ada pembesaran
clitoris, tetapi dokter mendeteksi
adanya 2 gonad di canalis
inquinalis
Hasil analisa kromosom
menunjukkan karyotype bayi 46,
XY.
Fenotip bayi tidak membingungkan (ambigua),
dan pemeriksaan menunjukkan tingginya ratio
testosteron terhadap DHT, evaluasi USG
menunjukkan tidak ada uterus, ovarium,
tetapi ada vaginal pouch, maka Dx adalah :
defisiensi 5-alpha reductase yang
menyebabkan male pseudohermaphroditism.
Bayi ini homozigot dan ke dua orang tuanya
heterozigot.
Meskipun staff medis telah memberikan penjelasan
adanya virilisasi pada anak-anak dengan kelainan
semacam ini setelah puber, dan adanya
kemungkinan imprinting of fetal androgen on fetal
brain yang akan memberikan identifikasi seksual
pria, orang tua bayi tsb memutuskan untuk
membesarkan
anaknya
sebagai
perempuan,
dengan berbagai alasan antara lain keinginan
untuk memiliki anak perempuan, tidak ada
ambiguitas seksual saat lahir dan phallus yg tidak
berkembang (panjang 1 cm) setelah usia 3 tahun dan ketika usia 3,5 tahun, akan dilakukan operasi
pengambilan gonad.
Congenital insensitivity to androgen syndrome or CIAS
[formerly called testicular feminization] This is a male
pseudohermaphrodite
In this condition a gene on the X is
involved in forming receptors to
testosterone. These are absent in most or
all of the target tissue when that gene is
mutated. They are of karyotype 46,XY and
should not be confused with 46,XY sex
reversal which has a different mechanism
and outcome. In CIAS the SRY gene
function is normal and testes form and
produce both testosterone and MIS.
Gonads: testes
Internal genitalia: no receptors to testosterone and thus it
acts as if no testosterone is present; MIS function is
perfectly OK.
Wolffian ducts may not respond to testosterone if
receptors are absent and thus no sperm transport
system
Mullerian ducts: will undergo apoptosis in presence of
MIS
External genitalia: no receptors to testosterone so its as
if there were no testosterone present, hence.
Genital tubercle forms clitoris; genital folds form labia
minora; and genital swellings form labia majora.
Additional features: These are female at birth and look
like baby infant girls; they are raised as females and
respond to life as females. They lack a uterus, oviducts,
and upper vagina hence their lower vagina (urethal in
origin) is short and surgical correction may be needed for
normal sexual intercourse. They develop normal sized
breasts at puberty but do not develop public or axillary
hair. They lack a menarche, of course, because they
have testes, not ovaries. The internal testes are removed
once the condition is diagnosed because internal testes
lead to gonadoblastoma a potentially lethal cancer.
These females have normal male levels of testosterone.
They cannot become mothers by IVF because they lack
a uterus.
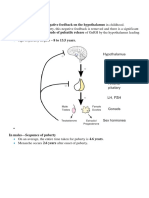
XY female
In XY humans, mutations of SRY cause male-to-female sex reversal. Sex
reversal in XY females results from the failure of the indifferent gonad to
develop into a testis.
At birth, the patients with this type of gonadal dysgenesis appear to be
normal females; however, they do not develop secondary sexual
characteristics at puberty, have amenorrhea and streak gonads. Phenotypic
abnormalities in these patients could be diverse and heterogeneous
depending on the precise moment of testicular degeneration and if both
testicular compartments are totally or partially affected. Thus, the phenotype
of an individual with an SRY mutation is either XY-female or normal fertile
male. Intersex individuals do not have SRY mutations.
Mutations in the SRY gene have been found to account for approximately
15% of cases with male to female sex reversal. To date, about 46 mutations
have been identified within the open reading frame of the SRY gene.6
Primarily, these mutations are within the HMG box, thus highlighting the
critical role of this domain, and only 10 mutations outside the HMG box
have been reported so far to the best of our knowledge
http://www.nature.com/ejhg/journal/v15/n1/full/5201719a.html
You might also like
- Identification and Management of Ambiguous GenitaliaDocument31 pagesIdentification and Management of Ambiguous Genitaliateslimolakunleraji100% (1)
- Ambiguous GenitaliaDocument24 pagesAmbiguous GenitaliaYolanda SamsudinNo ratings yet
- Intersex by AHMED ABDULWAHABDocument16 pagesIntersex by AHMED ABDULWAHABAbdullah Al AminNo ratings yet
- Puberty hormone changes lead to reproductive organ developmentDocument3 pagesPuberty hormone changes lead to reproductive organ developmentSteff ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Sexdifferentiation1 151124152908 Lva1 App6891Document17 pagesSexdifferentiation1 151124152908 Lva1 App6891BeatrizEguilosAspirasNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Sexual DevelopmentDocument48 pagesDisorders of Sexual DevelopmentTofitofi TofiNo ratings yet
- Causes and Types of Amenorrhea ExplainedDocument73 pagesCauses and Types of Amenorrhea ExplainedgvfhgNo ratings yet
- Developmental Biology XL 138: Week 10Document61 pagesDevelopmental Biology XL 138: Week 10Soji AdimulaNo ratings yet
- Ambiguous Fonda Full Icomesh3Document20 pagesAmbiguous Fonda Full Icomesh3share fosNo ratings yet
- Sex Determination in MammalsDocument33 pagesSex Determination in MammalsBinita SedhaiNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Genital Tract DevDocument77 pagesAbnormal Genital Tract Dev2012100% (2)
- Intersex & Ambigous Genitalia Pediatric UrologyDocument26 pagesIntersex & Ambigous Genitalia Pediatric Urologyhayssam rashwanNo ratings yet
- Adolescent Gynecology MalformationsDocument14 pagesAdolescent Gynecology Malformationsvu hong chienNo ratings yet
- Reproductive PathologyDocument37 pagesReproductive PathologyKreshna MedhaNo ratings yet
- Ambiguous Genitalia2Document27 pagesAmbiguous Genitalia2Islam AminNo ratings yet
- Embryology of Genital System DevelopmentDocument10 pagesEmbryology of Genital System DevelopmentMelissa Aina Mohd YusofNo ratings yet
- Sexual DisordersDocument19 pagesSexual DisordersRealyn ZambasNo ratings yet
- Reproduction TranscriptionDocument21 pagesReproduction TranscriptionmarthafaragNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Development of Female Genital TractDocument69 pagesAbnormal Development of Female Genital TractJerry CreedNo ratings yet
- Primary AmenorrheaDocument33 pagesPrimary AmenorrheaZaraNo ratings yet
- Intersex & Ambigous GenitaliaDocument46 pagesIntersex & Ambigous Genitaliahayssam rashwanNo ratings yet
- Developmental Genetics and EmbryogenesisDocument18 pagesDevelopmental Genetics and Embryogenesisyuyu tuptupNo ratings yet
- Gender Identity Disorder Not Otherwise SpecifiedDocument4 pagesGender Identity Disorder Not Otherwise SpecifiedJona AddatuNo ratings yet
- Understanding Human Sexuality 13Th Edition Hyde Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesUnderstanding Human Sexuality 13Th Edition Hyde Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFcharlotte.gammon593100% (11)
- Understanding Human Sexuality 13th Edition Hyde Solutions Manual 1Document21 pagesUnderstanding Human Sexuality 13th Edition Hyde Solutions Manual 1Larry Kershaw100% (39)
- I. The BiologyDocument7 pagesI. The BiologyOffice AcadNo ratings yet
- Disorder of Determination and Sex DifferentiationDocument62 pagesDisorder of Determination and Sex DifferentiationSYAFIRA INAYAHNo ratings yet
- Local Media4503207032826047248Document19 pagesLocal Media4503207032826047248Mazu RutheraNo ratings yet
- Rimary Menorrhea: By: Zaineb Talib Nimaa Zahra Ali Hasoon Zina Safaa AldienDocument28 pagesRimary Menorrhea: By: Zaineb Talib Nimaa Zahra Ali Hasoon Zina Safaa AldienZaineb TalibNo ratings yet
- INFERTILITY Obg SeminarDocument19 pagesINFERTILITY Obg SeminarDelphy Varghese100% (2)
- INFERTILITY Obg SeminarDocument19 pagesINFERTILITY Obg SeminarDelphy VargheseNo ratings yet
- Sexual Growth and Development-Reproduction 2021Document79 pagesSexual Growth and Development-Reproduction 2021Elijah Kihiu18No ratings yet
- Pre-Natal: Development of Sex: Prepared By: Carla Marie Engaling Bsed Sciences 2BDocument17 pagesPre-Natal: Development of Sex: Prepared By: Carla Marie Engaling Bsed Sciences 2BAlquien Engaling CapuyanNo ratings yet
- Sexuality and IntersexualityDocument23 pagesSexuality and IntersexualityManu BharadwazNo ratings yet
- Male vs Female Sex DifferentiationDocument9 pagesMale vs Female Sex DifferentiationAKHIRUL SIREGARNo ratings yet
- L22 PDFDocument39 pagesL22 PDFMiles HuiNo ratings yet
- Fertilitas Dan Infertilitas: BY Tettisolehati, S.KP., M.KepDocument32 pagesFertilitas Dan Infertilitas: BY Tettisolehati, S.KP., M.KepAny AndrianiNo ratings yet
- Swyer Syndrome: Genetics Home ReferenceDocument7 pagesSwyer Syndrome: Genetics Home ReferenceCarl Lawrence R. CarpioNo ratings yet
- Barr Body and HermaphroditismDocument41 pagesBarr Body and HermaphroditismTamjid KhanNo ratings yet
- Congenetal Anorchia: Name: Vishnu Sabu GROUP: M1853Document9 pagesCongenetal Anorchia: Name: Vishnu Sabu GROUP: M1853mihaella_litovcencoNo ratings yet
- Development of Reproductive SystemDocument27 pagesDevelopment of Reproductive Systemwmdpr4x64fNo ratings yet
- Refer atDocument28 pagesRefer atrianiastariNo ratings yet
- Embryology GenitalDocument53 pagesEmbryology GenitalDhonat Flash100% (1)
- CC22Document20 pagesCC22Kathlyn Abby HaliliNo ratings yet
- SexualityDocument64 pagesSexualityjmclacasNo ratings yet
- Embryo Finals 1Document4 pagesEmbryo Finals 1VenzNo ratings yet
- Infertility To ShowDocument29 pagesInfertility To ShowRaven Renz OngNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System - SlidesDocument141 pagesFemale Reproductive System - SlidesKennedy KaguchiaNo ratings yet
- Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome (AIS)Document19 pagesAndrogen Insensitivity Syndrome (AIS)arief206_eighteenNo ratings yet
- Sex: The Biological CategoryDocument25 pagesSex: The Biological CategoryNoelle Leslie Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 1 - Nusratuddin Abdullah - How To Define Disorder Sexual Development Wide ScreenDocument44 pages1 - Nusratuddin Abdullah - How To Define Disorder Sexual Development Wide ScreenKie Amelia SuwantoNo ratings yet
- Dian Ais EditDocument41 pagesDian Ais EditDian SiregarNo ratings yet
- Embryonic Development of Male and Female Reproductive SystemsDocument14 pagesEmbryonic Development of Male and Female Reproductive SystemsDiana Jangmi MerhanNo ratings yet
- Sexual Development & Differentiation: Sex and GenderDocument10 pagesSexual Development & Differentiation: Sex and GenderDeboprasad DasNo ratings yet
- Female Genital Tract Development and AbnormalitiesDocument37 pagesFemale Genital Tract Development and AbnormalitiesClintonNo ratings yet
- Measures of Man Exam 2 Study Guide: Sex, Gender, IntersexDocument5 pagesMeasures of Man Exam 2 Study Guide: Sex, Gender, IntersexKennon RudeNo ratings yet
- L1 General Intro To Reprod PhysiolDocument20 pagesL1 General Intro To Reprod PhysiolMoses AjiwekaNo ratings yet
- Fertility and Infertility Factors in Men and WomenDocument32 pagesFertility and Infertility Factors in Men and WomenWindy Shintia FandinyNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Sexual Differentiation: A Amirhakimi, MD Pediatric Endocrinologist Shiraz University of Medical SciencesDocument30 pagesDisorders of Sexual Differentiation: A Amirhakimi, MD Pediatric Endocrinologist Shiraz University of Medical SciencesTitus RheinhardoNo ratings yet
- Sex Ed Uncensored - Sexual Identity: Mind Blowing Sex Sh8t!!! for Young AdultsFrom EverandSex Ed Uncensored - Sexual Identity: Mind Blowing Sex Sh8t!!! for Young AdultsNo ratings yet
- Cover Lapsus BedahDocument1 pageCover Lapsus BedahWiwit WuLandariNo ratings yet
- AnaphylaxisDocument12 pagesAnaphylaxisIkhza PandawaNo ratings yet
- Contoh Surat UndanganDocument7 pagesContoh Surat UndanganFaisallrizzaNo ratings yet
- POLISITEMIADocument8 pagesPOLISITEMIAWiwit WuLandariNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument8 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic FeverzunianggraeniNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument8 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic FeverzunianggraeniNo ratings yet