Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A2 ch11 04
Uploaded by
AmalAbdlFattahOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A2 ch11 04
Uploaded by
AmalAbdlFattahCopyright:
Available Formats
11-4Sum
11-4
Sumand
andDifference
DifferenceIdentities
Identities
Warm Up
Lesson Presentation
Lesson Quiz
HoltMcDougal
Algebra 2Algebra 2
Holt
11-4 Sum and Difference Identities
Warm Up
Find each product, if possible.
1. AB
Holt McDougal Algebra 2
2. BA
11-4 Sum and Difference Identities
Objectives
Evaluate trigonometric expressions by
using sum and difference identities.
Use matrix multiplication with sum and
difference identities to perform
rotations.
Holt McDougal Algebra 2
11-4 Sum and Difference Identities
Vocabulary
rotation matrix
Holt McDougal Algebra 2
11-4 Sum and Difference Identities
Matrix multiplication and sum and difference
identities are tools to find the coordinates of
points rotated about the origin on a plane.
Holt McDougal Algebra 2
11-4 Sum and Difference Identities
Holt McDougal Algebra 2
11-4 Sum and Difference Identities
Example 1A: Evaluating Expressions with Sum and
Difference Identities
Find the exact value of cos 15.
Write 15 as the difference
45 30 because
cos 15 = cos (45 30)
trigonometric values of
45 and 30 are known.
Apply the identity for cos (A B).
= cos 45 cos 30 + sin 45 sin 30
Evaluate.
Simplify.
Holt McDougal Algebra 2
11-4 Sum and Difference Identities
Example 1B: Proving Evaluating Expressions with
Sum and Difference Identities
Find the exact value of
.
Write
as the sum of
Apply the identity for
tan (A + B).
Holt McDougal Algebra 2
11-4 Sum and Difference Identities
Example 1B Continued
Evaluate.
Simplify.
Holt McDougal Algebra 2
11-4 Sum and Difference Identities
Check It Out! Example 1a
Find the exact value of tan 105.
tan 105= tan(60 + 45)
Write 105 as the sum of
60 + 45 because
trigonometric values of
60 and 45 are known.
Apply the identity for
tan (A + B).
Holt McDougal Algebra 2
11-4 Sum and Difference Identities
Check It Out! Example 1a Continued
Evaluate.
=
Simplify.
Holt McDougal Algebra 2
11-4 Sum and Difference Identities
Check It Out! Example 1b
Find the exact value of each expression.
Write
as the sum of
because
trigonometric values of
and
are known.
Apply the identity for
sin (A B).
Holt McDougal Algebra 2
11-4 Sum and Difference Identities
Check It Out! Example 1b Continued
Find the exact value of each expression.
Evaluate.
Simplify.
Holt McDougal Algebra 2
11-4 Sum and Difference Identities
Shifting the cosine function right radians is
equivalent to reflecting it across the x-axis. A proof
of this is shown in Example 2 by using a difference
identity.
Holt McDougal Algebra 2
11-4 Sum and Difference Identities
Example 2: Proving Identities with Sum and
Difference Identities
Prove the identity tan
tan
Choose the left-hand side to
modify.
Apply the identity for tan (A + B).
Evaluate.
Simplify.
Holt McDougal Algebra 2
11-4 Sum and Difference Identities
Check It Out! Example 2
Prove the identity
.
Apply the identity for
cos A + B.
Evaluate.
= sin x
Holt McDougal Algebra 2
Simplify.
11-4 Sum and Difference Identities
Example 3: Using the Pythagorean Theorem with
Sum and Difference Identities
Find cos (A B) if sin A = with 0 < A < and
if tan B =
with 0 < B <
Step 1 Find cos A, cos B, and sin B.
Use reference angles and the ratio
definitions sin A = and tan B = Draw a
triangle in the appropriate quadrant and
label x, y, and r for each angle.
Holt McDougal Algebra 2
11-4 Sum and Difference Identities
Example 3 Continued
In Quadrant l (Ql),
0 < A < 90 and
sin A = .
r=3
A
x
Holt McDougal Algebra 2
In Quadrant l (Ql),
0< B < 90 and tan B =
r
y=1
B
x=4
y=3
11-4 Sum and Difference Identities
Example 3 Continued
r=3
A
r
y=1
y=3
B
x=4
x2 + 12 = 32
32 + 42 = r2
Thus, cos A =
Thus, cos B =
and sin A =
and sin B =
Holt McDougal Algebra 2
11-4 Sum and Difference Identities
Example 3 Continued
Step 2 Use the angle-difference identity to find
cos (A B).
cos (A B) = cosAcosB + sinA sinB
Apply the identity for
cos (A B).
Substitute
for
cos A, for cos
B, and
cos(A B) =
Holt McDougal Algebra 2
Simplify.
for sin B.
11-4 Sum and Difference Identities
Check It Out! Example 3
Find sin (A B) if sinA = with 90 < A < 180
and if cosB = with 0 < B < 90.
In Quadrant ll (Ql),
90< A < 180 and
sin A = .
In Quadrant l (Ql),
0< B < 90 and cos B =
r=5
y=4
r=5
A
x
Holt McDougal Algebra 2
B
x=3
11-4 Sum and Difference Identities
Check It Out! Example 3 Continued
r=5
y=4
r=5
A
x
x2 + 42 = 52
Thus, sin A =
and cos A =
Holt McDougal Algebra 2
B
x=3
52 32 = y2
Thus, cos B =
and sin B =
11-4 Sum and Difference Identities
Check It Out! Example 3 Continued
Step 2 Use the angle-difference identity to find
sin (A B).
sin (A B) = sinAcosB cosAsinB
sin(A B) =
Holt McDougal Algebra 2
Apply the identity for
sin (A B).
Substitute for sin
A and sin B, for
cos A, and for
cos B.
Simplify.
11-4 Sum and Difference Identities
To rotate a point P(x,y) through an angle use a
rotation matrix.
The sum identities for sine and cosine are used to
derive the system of equations that yields the
rotation matrix.
Holt McDougal Algebra 2
11-4 Sum and Difference Identities
Example 4: Using a Rotation Matrix
Find the coordinates, to the nearest hundredth,
of the points (1, 1) and (2, 0) after a 40
rotation about the origin.
Step 1 Write matrices for a 40 rotation and for
the points in the question.
Rotation matrix.
Matrix of point
coordinates.
Holt McDougal Algebra 2
11-4 Sum and Difference Identities
Example 4 Continued
Step 2 Find the matrix product.
Step 3 The approximate coordinates of the points
after a 40 rotation are (0.12, 1.41) and
(1.53, 1.29).
Holt McDougal Algebra 2
11-4 Sum and Difference Identities
Check It Out! Example 4
Find the coordinates, to the nearest hundredth,
of the points in the original figure after a 60
rotation about the origin.
Step 1 Write matrices for a 60 rotation and for
the points in the question.
R60 =
S=
Holt McDougal Algebra 2
Rotation matrix.
Matrix of point
coordinates.
11-4 Sum and Difference Identities
Check It Out! Example 4 Continued
Step 2 Find the matrix product.
R60 x s =
Holt McDougal Algebra 2
11-4 Sum and Difference Identities
Lesson Quiz: Part I
1. Find the exact value of cos 75
2. Prove the identity sin
3. Find tan (A B) for sin A =
cos B =
with 0 <B<
Holt McDougal Algebra 2
= cos
with 0 <A<
and
11-4 Sum and Difference Identities
Lesson Quiz: Part II
4. Find the coordinates to the nearest hundredth
of the point (3, 4) after a 60 rotation about
the origin.
Holt McDougal Algebra 2
You might also like
- 16 Inverses of Trig FunctionsDocument22 pages16 Inverses of Trig Functionsaechel writesNo ratings yet
- Module No. 4Document30 pagesModule No. 4John Michael Vincent CamuaNo ratings yet
- Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz: Holt Mcdougal Algebra 2 Holt Algebra 2 Holt Mcdougal Algebra 2Document27 pagesWarm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz: Holt Mcdougal Algebra 2 Holt Algebra 2 Holt Mcdougal Algebra 2Rica MelchorNo ratings yet
- Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson QuizDocument22 pagesWarm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson QuizAmalAbdlFattah0% (1)
- Worksheet in Trigonometry: A. VectorsDocument2 pagesWorksheet in Trigonometry: A. VectorsIsaac Louise BaraquielNo ratings yet
- Factoring The Difference of Two SquaresDocument11 pagesFactoring The Difference of Two SquaresTolentino Magalona BobbieNo ratings yet
- CNS - Unit 2Document29 pagesCNS - Unit 2alameenNo ratings yet
- Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz: Holt Mcdougal Geometry Holt Geometry Holt Mcdougal GeometryDocument13 pagesWarm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz: Holt Mcdougal Geometry Holt Geometry Holt Mcdougal GeometryMahisa AgniNo ratings yet
- 11 4insrcibed AnglesDocument26 pages11 4insrcibed AnglesMarijule Paulen JumuadNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument23 pagesUntitledapi-242725078No ratings yet
- ECSE-4760 Real-Time Applications in Control & Communications Experiments in Digital Logic DesignDocument24 pagesECSE-4760 Real-Time Applications in Control & Communications Experiments in Digital Logic DesignMitu BaralNo ratings yet
- Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications 7th Edition Rosen Test BankDocument23 pagesDiscrete Mathematics and Its Applications 7th Edition Rosen Test Banktriposariette9vot100% (18)
- Dot ProductDocument41 pagesDot ProductsaneleNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document51 pagesUnit 2jana kNo ratings yet
- Title Mec 3/4 Marine Engineering Science 1: 1. Arithmetic 2. Algebra 3. Graphs 4. Trigonometry 5. Geometry 6. MensurationDocument57 pagesTitle Mec 3/4 Marine Engineering Science 1: 1. Arithmetic 2. Algebra 3. Graphs 4. Trigonometry 5. Geometry 6. MensurationpankajNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1674112820186 7021738098160681138Document335 pagesOrca Share Media1674112820186 7021738098160681138Rodulfo Capinig GabritoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Theory MCQDocument278 pagesElectromagnetic Theory MCQSatwik DasNo ratings yet
- Miller Indices ClassDocument35 pagesMiller Indices ClassDhiyaAldeenAl-SerhanyNo ratings yet
- The Quadratic Formula and The DiscriminantDocument57 pagesThe Quadratic Formula and The DiscriminantRami AssafNo ratings yet
- 03carl PDFDocument14 pages03carl PDFPANKOPANKNo ratings yet
- Geometric SequencesDocument31 pagesGeometric SequencesRydan MinorNo ratings yet
- DS Lecture 10 Number TDocument32 pagesDS Lecture 10 Number TTazeen zahraNo ratings yet
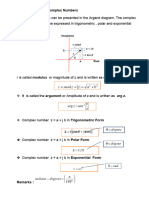
- CHAPTER 2.2 Complex NumbersDocument15 pagesCHAPTER 2.2 Complex NumbersCT MarNo ratings yet
- Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson QuizDocument31 pagesWarm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson QuizSophia GabiaNo ratings yet
- 11.4 Sum and Difference IdentitiesDocument23 pages11.4 Sum and Difference Identitiesyoussefmsamir2050No ratings yet
- Geometric SequencesDocument30 pagesGeometric SequencesRey Hisona100% (2)
- Polar Forms of Conic Sections: Lesson 9-4Document35 pagesPolar Forms of Conic Sections: Lesson 9-4Fran LeeNo ratings yet
- Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz: Holt Mcdougal Algebra 1 Holt Algebra 1 Holt Mcdougal Algebra 1Document30 pagesWarm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz: Holt Mcdougal Algebra 1 Holt Algebra 1 Holt Mcdougal Algebra 1Kim Falcutila TarrangcoNo ratings yet
- Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz: Holt Mcdougal Algebra 2 Holt Algebra 2 Holt Mcdougal Algebra 2Document39 pagesWarm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz: Holt Mcdougal Algebra 2 Holt Algebra 2 Holt Mcdougal Algebra 2Drew StrauchNo ratings yet
- A2 ch01 01Document27 pagesA2 ch01 01AmalAbdlFattahNo ratings yet
- VECTORSDocument31 pagesVECTORSAlicia HaughtonNo ratings yet
- Booklet CH 2 HCV VectorsDocument15 pagesBooklet CH 2 HCV VectorsgayatrirajneeshmuthaNo ratings yet
- Vectors and The Geometry of SpaceDocument75 pagesVectors and The Geometry of SpacesamNo ratings yet
- X Cha1Document50 pagesX Cha1api-2341668060% (1)
- Logic PDFDocument24 pagesLogic PDFcorazonpuroNo ratings yet
- 9-1 Geometric SequencesDocument30 pages9-1 Geometric SequencesDAISY TABUCOLNo ratings yet
- ENG1091 - Lecture Notes 2011Document159 pagesENG1091 - Lecture Notes 2011Janet LeongNo ratings yet
- Vinesh Xact Mathematics XDocument198 pagesVinesh Xact Mathematics Xpreetim1980100% (4)
- Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz: Holt Algebra 2 Holt Algebra 2Document24 pagesWarm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz: Holt Algebra 2 Holt Algebra 2Reneé SantosNo ratings yet
- 6-4 MathDocument37 pages6-4 MathZehan SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Mathes 8Document64 pagesMathes 8murty99100% (1)
- Econ 299 Chapter 5.0Document38 pagesEcon 299 Chapter 5.0Elon MuskNo ratings yet
- Dot Product (Lec # 3) - 231102 - 215318Document37 pagesDot Product (Lec # 3) - 231102 - 215318Sana UllahNo ratings yet
- 9 1 Geometric SequencesDocument29 pages9 1 Geometric SequencesPabora KennethNo ratings yet
- Electrical Sem 3 IMP Question Bank Complete 2023 All SubjectDocument18 pagesElectrical Sem 3 IMP Question Bank Complete 2023 All Subjectsong pictureNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Summer Vacation Task 2023-24Document3 pagesGrade 9 Summer Vacation Task 2023-24Akasha AhsanNo ratings yet
- 07 BooleanAlgebraDocument21 pages07 BooleanAlgebraGans GanesanNo ratings yet
- Ca Mod01 Les03Document29 pagesCa Mod01 Les03api-259243211No ratings yet
- Geometry Lesson 4Document28 pagesGeometry Lesson 4Harold Valiente Sainz Jr.No ratings yet
- g12m Differential CalculusDocument66 pagesg12m Differential Calculusapi-235269401No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Theory MCQ (1) - Removed (1) - WatermarkDocument278 pagesElectromagnetic Theory MCQ (1) - Removed (1) - WatermarkNEROB KUMAR MOHONTO XRLNZGkUXmNo ratings yet
- Modular ArithmeticDocument15 pagesModular ArithmeticNica Fullin SenicaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Lecture Notes - Part3Document36 pagesTrigonometry Lecture Notes - Part3hataki878No ratings yet
- Modular ArithmeticDocument14 pagesModular Arithmeticmani chandNo ratings yet
- Dot Product (Lec # 3)Document22 pagesDot Product (Lec # 3)Hamid RajpootNo ratings yet
- Number Theory: 4.1 Factors and MultiplesDocument13 pagesNumber Theory: 4.1 Factors and Multiplessahil ahmedNo ratings yet
- Learning Module in Math 8: How To Join The VSMART?Document7 pagesLearning Module in Math 8: How To Join The VSMART?Marvelous VillafaniaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument4 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelMarly MarlNo ratings yet
- Basic GeometryDocument7 pagesBasic GeometryTBubble10120No ratings yet
- Manova: Presented ByDocument13 pagesManova: Presented ByAmalAbdlFattahNo ratings yet
- Lock Rossman Js M Montreal 2013Document53 pagesLock Rossman Js M Montreal 2013AmalAbdlFattahNo ratings yet
- Introduction ECO605 Lecture1Document9 pagesIntroduction ECO605 Lecture1AmalAbdlFattahNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document3 pagesCH 10AmalAbdlFattahNo ratings yet
- Lab 1: Use of Microsoft ExcelDocument10 pagesLab 1: Use of Microsoft ExcelAmalAbdlFattahNo ratings yet
- Sample Size Calculation:: Source: G-Power SoftwareDocument2 pagesSample Size Calculation:: Source: G-Power SoftwareAmalAbdlFattahNo ratings yet
- Self-Assessment Answers: 24 Continuous Distributions: 1. Let Volume of Coffee (ML) Dispensed Be V. Then VDocument1 pageSelf-Assessment Answers: 24 Continuous Distributions: 1. Let Volume of Coffee (ML) Dispensed Be V. Then VAmalAbdlFattahNo ratings yet
- Getting Started: 0.1 Opening RemarksDocument10 pagesGetting Started: 0.1 Opening RemarksAmalAbdlFattahNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test: Name: - DateDocument4 pagesDiagnostic Test: Name: - DateAmalAbdlFattahNo ratings yet
- The Clown GameDocument3 pagesThe Clown GameAmalAbdlFattahNo ratings yet
- AP Statistics Review 1Document2 pagesAP Statistics Review 1AmalAbdlFattahNo ratings yet
- Book 2Document191 pagesBook 2AmalAbdlFattahNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1Document3 pagesWorksheet 1AmalAbdlFattahNo ratings yet
- Spss ExercisesDocument12 pagesSpss ExercisesAmalAbdlFattah100% (1)
- Index: 2.1 Mathematics Department - Middle School 2.1.1 Exam GradesDocument15 pagesIndex: 2.1 Mathematics Department - Middle School 2.1.1 Exam GradesAmalAbdlFattahNo ratings yet
- Econ3061 Slides 3Document62 pagesEcon3061 Slides 3AmalAbdlFattahNo ratings yet
- 5 Continuous Prob DistributionsDocument2 pages5 Continuous Prob DistributionsAmalAbdlFattahNo ratings yet
- Course Specifications 611Document3 pagesCourse Specifications 611AmalAbdlFattahNo ratings yet
- OLS Stata9Document13 pagesOLS Stata9AmalAbdlFattahNo ratings yet
- 2016 2017Document25 pages2016 2017AmalAbdlFattahNo ratings yet
- 14.1 Derivatives of Trig FunctionsDocument5 pages14.1 Derivatives of Trig FunctionsAmalAbdlFattahNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Functions NotesDocument9 pages4.1 Functions NotesAmalAbdlFattahNo ratings yet
- Topics 1 and 2 Review MarkschemeDocument14 pagesTopics 1 and 2 Review MarkschemeAmalAbdlFattah50% (2)
- Tutorial Week 6Document2 pagesTutorial Week 6AmalAbdlFattahNo ratings yet
- (PDF) Simple Introduction To ArchitectureDocument10 pages(PDF) Simple Introduction To ArchitectureAr Srinivas PullogiNo ratings yet
- Periodicity and ExtremevaluesDocument5 pagesPeriodicity and ExtremevaluesHemanth JNo ratings yet
- Civil Engrg Maths 1 Lecture Notes For 2019 - 20Document275 pagesCivil Engrg Maths 1 Lecture Notes For 2019 - 20Sarah HaiderNo ratings yet
- Class XI Syllabus 2023-24Document13 pagesClass XI Syllabus 2023-24SuinNo ratings yet
- IGCSEFM TrigonometryII ExercisesDocument4 pagesIGCSEFM TrigonometryII ExercisessreelakshmiNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Investigation Memo 2024Document4 pagesGrade 10 Investigation Memo 2024juniorkubikiNo ratings yet
- Mambusao National High School Pre - Final Examination in Mathematics 9Document4 pagesMambusao National High School Pre - Final Examination in Mathematics 9Marjo Gaspar CelosoNo ratings yet
- 1.3-1.4 Test Review: Convert Each Degree Measure Into Radians and Each Radian Measure Into DegreesDocument2 pages1.3-1.4 Test Review: Convert Each Degree Measure Into Radians and Each Radian Measure Into DegreesheyyyaleNo ratings yet
- ITF MCQDocument4 pagesITF MCQHARSH MAHTONo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 07-Nov-2021Document8 pagesAdobe Scan 07-Nov-2021Kruthi BalajiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.2 - Inscribed and Central AnglesDocument6 pagesLesson 2.2 - Inscribed and Central AnglesMuhammad Asif ZamanNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2023 Revision Notes On Trigonometry - Free PDF DownloadDocument6 pagesJEE Main 2023 Revision Notes On Trigonometry - Free PDF Downloadlogin3868No ratings yet
- Trigonometry - AnwsersDocument22 pagesTrigonometry - AnwsersMariaNo ratings yet
- 5.4 Integration Trigonometric FunctionsDocument12 pages5.4 Integration Trigonometric Functionshariz syazwanNo ratings yet
- Inequalities Cheat Sheet PDFDocument3 pagesInequalities Cheat Sheet PDFBiswadeep ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 6.2 Circular Functions: NameDocument4 pagesWorksheet 6.2 Circular Functions: Namesex01No ratings yet
- Guide To Math Needed To Study String TheoryDocument7 pagesGuide To Math Needed To Study String TheoryAshwin Balaji100% (1)
- Route Surveying and Design 5th ED Carl F. Meyer & David W. GibsonDocument568 pagesRoute Surveying and Design 5th ED Carl F. Meyer & David W. GibsonAref MalkawiNo ratings yet
- Angles of Elevation and DepressionDocument33 pagesAngles of Elevation and DepressionSafara BullockNo ratings yet
- Maths April QP & Memo Gauteng 2021 Gr12Document22 pagesMaths April QP & Memo Gauteng 2021 Gr12Kgalema KgomoNo ratings yet
- Imong MamaDocument25 pagesImong MamaJeuz Andre DionglayNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 4, Week 1 - Module 1Document24 pagesMathematics: Quarter 4, Week 1 - Module 1Gabs Gary50% (2)
- MODULE in OBLIQUE TRIANGLEDocument19 pagesMODULE in OBLIQUE TRIANGLEJinky Mae VelascoNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios Involving Special Angles (Week 2)Document18 pagesTrigonometric Ratios Involving Special Angles (Week 2)Gwen MiñonNo ratings yet
- Well Design - 2D: Process FlowchartDocument11 pagesWell Design - 2D: Process FlowchartSlim.BNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry RevisionDocument2 pagesTrigonometry RevisionZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- LM Pre Calculus Q2 M16 V2-GuttierezDocument20 pagesLM Pre Calculus Q2 M16 V2-GuttierezTERESA N. DELOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Math PDFDocument66 pagesMath PDFBenjamin Benicarlo Juanillo IIINo ratings yet
- Circles Test ReviewDocument17 pagesCircles Test ReviewGeromme TudNo ratings yet
- CH 3 SAILINGSDocument33 pagesCH 3 SAILINGSJeet Singh100% (1)