Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hand Safety Toolkit
Uploaded by
ahmer09Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hand Safety Toolkit
Uploaded by
ahmer09Copyright:
Available Formats
HAND SAFETY TOOL KIT
Five Toolbox Topics
on Hand Safety
HAND SAFETY TOOL KIT
Guide for Supervisors:
What hazards to the hands are
foreseeable with this task?
Do your people have the knowledge,
skills and training necessary to complete
the task safely?
Can the hazards be eliminated, isolated,
or minimized?
Are gloves appropriate (e.g. rotating
equipment)?
Is the glove application appropriate for
the hazard?
HAND SAFETY TOOL KIT
Danger
Zone!
Toolbox Talk No 1
Five Toolbox Talks, which focus on hand safety
Each features a Danger Zone area
A concept that can be used in each Toolbox Talk
is shown below
Each talk will be about how you keep hands out
of Danger Zones by primary or secondary
means
Secondary means are typically accomplished by
gloves, but should always be used in
conjunction with primary control method
Never rely solely on gloves for protection
Good Hand Position
BARRIER
Have a look at the examples of real injuries in
this presentation and discuss how to avoid the
injuries that can occur in each
Dange
r
Zone!
Poor Hand Position
Dange
r
Zone!
HAND SAFETY TOOL KIT
Primary Hand Protection
One of the best and most effective means of
primary hand protection is good hand position. Dont
position your hands where they can be:
Cut or punctured by sharp objects
Burned by hot objects or chemicals
Pinched between objects
that
you properly
position your hands,
In order
Struck
by objects
(stored energy)
first recognize the hazard, then develop a work
practice to keep hands out of The Danger Zone!
The best safety device for your hands is your
mind. By being alert and aware you can avoid poor
hand positioning and keep them out of The
Danger Zone
HAND SAFETY TOOL KIT
Saw Wound on the Index Finger
HAND SAFETY TOOL KIT
Toolbox Talk No: 2
Injuries Caused by Sharp Objects
The hands and fingers are the most often injured
parts of the body and its very easy to understand
why. There are few work activities, which do not
involve the hands. The potential for injury is always
there
AVOID THE DANGER ZONE
The most common types of hand injury are
puncture wounds and lacerations. These involve:
cutting fingers through misuse of knives
crushing injuries through entrapment
chemical burns
HAND SAFETY TOOL KIT
Incision and Inside Front of Hand
HAND SAFETY TOOL KIT
Toolbox Talk No: 2 (contd)
As you can tell, all these injuries occurred during normal, everyday type job activities
When we ask ourselves how we could have avoided these injuries, our first impulse is to
say better glove usage
You might be surprised to know that in most of these incidents, gloves were being worn
Gloves should always be considered as a secondary level of defense
While proper gloves for the task, in good condition, prevent many injuries primary
levels of defense are much more effective
Examples Include:
Proper planning each job activity
Checking material/equipment for rough or sharp edges before handling
Maintaining an effective barrier between hands and hazards by using tools or other aids
Good housekeeping on workbenches etc.
Making sure moving machinery is guarded
HAND SAFETY TOOL KIT
Toolbox Talk No. 2 (contd)
On the previous slide are a few of the things to
consider (primary levels of defense) in order to
prevent exposure to hazards, before considering
whether gloves (secondary level of defense) are
appropriate for the job
Keep this concept in mind and do whatever it takes
to keep your hands out of:
THE DANGER ZONE
HAND SAFETY TOOL KIT
Wound Caused by Chainsaw
HAND SAFETY TOOL KIT
Incision to Palm of Hand
HAND SAFETY TOOL KIT
Knife Blade Gripped
HAND SAFETY TOOL KIT
Toolbox Talk No: 3
Thermal/Chemical Contact Injuries
Thermal and chemical contact hand injuries, along with the
other types of hand injuries, are easily prevented if hands
are kept out of:
THE DANGER ZONE
The most common hand injuries associated with
contact with hot surfaces and chemicals include:
burns - both chemical and thermal
types of dermatitis, known as skin rash
Both types of injuries can be serious and painful
Laundry detergents and other household varieties
can cause not only dermatitis, but also chemical
burns - skin contact with detergents must be avoided
To clean any part of the body ensure that the
detergent or cleaners has been specifically designed
for skin contact
HAND SAFETY TOOL KIT
Skin Graft to Burn Injury
HAND SAFETY TOOL KIT
Split Skin Graft
HAND SAFETY TOOL KIT
Toolbox Talk No 3 (Contd)
Chemicals and hot surfaces or materials
greatest source of exposure
Chemical exposure can be associated with those used
in process, during construction and/or repair and
maintenance activities
Usually involves paints, coatings, thinners and other
solvents
Materials such as fibreglass insulation and steel wool
can also cause dermatitis through mechanical irritation
Burns can result from contact with chemicals such as
acid or caustic and of course from hot surfaces, liquid
or materials
For all of the risks associated with the hazards listed
above, the primary line of defense is safe working
practices - all intended to keep our hands out of :
are the
KEEP OUT OF THE DANGER ZONE
HAND SAFETY TOOL KIT
Toolbox Talk No 3 (Contd)
Below are examples of safe working
practices
relative to the prevention of hand injuries from thermal
or chemical contact:
substitute chemicals for less hazardous products
that wont cause dermatitis or burns
use simple tools such as pliers to move or
hold
hot materials
place hot warning signs near hot objects
use containers which have been specifically
designed to carry and contain chemicals
good hygiene, includes methods to remove
contaminated gloves without skin contact
good housekeeping associated with removal of
contaminated materials
The second line of defense should be gloves, but they
must be the right type for the job
heavy duty leather for hot metal etc.
specifically designed to suit chemical type
either of synthetic or natural rubber material
check the MSDS to determine glove type
KEEP OUT OF THE DANGER ZONE
HAND SAFETY TOOL KIT
Toolbox Talk No: 4
Injuries Involving Stored Energy
Consider what can we do to protect our hands
from injuries that are caused by stored energy
When we refer to stored energy we mean pentup energy, that could be released unexpectedly if
not maintained under control
Stored energy includes:
hydraulic fluids under pressure
compressed air
energy stored in compressed springs
process chemicals under pressure
potential energy from suspended objects
arm energy e.g. when you push/pull a wrench
HAND SAFETY TOOL KIT
Ring Finger Amputation
HAND SAFETY TOOL KIT
Ring Finger Amputation
HAND SAFETY TOOL KIT
Toolbox Talk No: 4 (contd)
How do we protect our hands from stored energy
However, stored energy is not always easily
recognizable
The electrical power source on an item of
workshop equipment may be locked out, but
pressure may still be present in a hydraulic
cylinder
A valve or blank in line may have pressure against
it because a valve further upstream has leaked or
has been cracked open
An unrecognized high centre of gravity may cause
a piece of equipment to topple over unexpectedly
Firstly, we need to recognise it exists prior to
commencing an activity
HAND SAFETY TOOL KIT
Toolbox Talk No 4 (contd)
Consider what work practices we can follow to
prevent hand injuries associated with stored or
pent-up energy
always lock-off and tag energy sources before placing
hands in the Danger Zone
determine if there are multiple energy sources present
on the same piece of equipment
remember to bleed off stored energy in cylinders,
receivers, pipelines etc.
look out for alternate supply feeds, bypassed
interlocks or valves that may not be properly closed
when applying force (push or pull) be prepared for an
unexpected slip or release
keep hands from under suspended loads
consider the force of gravity
always use the right tools for the job and ensure those
tools are in good condition
recognize that gloves will not offer you the means of
total protection from injuries where stored energy is
present
KEEP YOUR HANDS OUT OF
THE DANGER ZONE
HAND SAFETY TOOL KIT
Toolbox Talk No 5:
Injuries Received From Pinch Points
Take a brief moment to look at your hands:
Your hands tell a lot about you and give some
indication of your past
If you are like most people, one or more visible
scars will exist
Each scar will have a unique story of misfortune
attached to it
These scars will perhaps have been the result of
being caught in a pinch-point
Pinch points are created any time two objects
come together
A classic example of a pinch-point is where a
closing door and door frame come together, a
time and a place where you dont want your
hand
KEEP OUT OF THE DANGER ZONE
HAND SAFETY TOOL KIT
Fingers Crushed by a Press
HAND SAFETY TOOL KIT
Toolbox Talk No 5 (Contd)
In this industry we have sustained many injuries
involving pinch points
Examples include:
Floorman and Driller removing elevators from bales, thumb
caught in pinch point between elevators and bales causing
laceration that required sutures
Crewmember attempted to hold door to prevent it from
slamming, finger caught between door and jamb causing
laceration that required sutures
In each of those examples gloves did little to prevent the
injury
The key to avoiding those injuries is the identification
and recognition of pinch-points associated with each
task
An objective over the next week is to identify pinch
points in our work environment
Identify them and then decide how they can be avoided
Use mechanical means to move material or equipment,
as opposed to manual application
KEEP OUT OF THE DANGER ZONE
HAND SAFETY TOOL KIT
Injury Types
Danger Zones
Bu
rn
s
Derm
atitis
ains
r
t
S
and
s
n
i
a
Spr
ti o
ns
Fr
scatnu
e
r
u
a c t ra
s
ion
era
at
loc
s
s
i
drDe
Lac
Handling or struck by sharp
objects
Caught in rotating
equipment
Energized systems
Struck by or against objects
Caught in pinch points
Miss-use of portable power
tools; working on energized
tools
Contact with hot objects or
materials
Contact with caustic or
corrosive materials
Poor hygiene practices
Repetitive motion/poor
equipment design
Improperly dressed wounds
Poor hand or body position
HAND SAFETY TOOL KIT
KEEP OUT OF THE DANGER ZONE
Danger
Zone
Primary Level
of Defence
Awareness
Safe Work Practices:
Tool Holders
Tag Lines
Correct Tools
Push Tools
Good Hygiene
Body and Hand Position
Training/Competence
Distance
Equipment Guarding
Physical Barrier
Safety
Buffer
Secondary Level
of Defence
Safety
Buffer
PPE:
Gloves required?
Correct gloves?
ARE BOTH LEVELS IN PLACE?
You might also like
- Hand Safety: National Institute of Occupational Safety and HealthDocument48 pagesHand Safety: National Institute of Occupational Safety and HealthTir Dan Knight100% (1)
- Sec B Batch 5 Fabrication of Excavator TeethDocument27 pagesSec B Batch 5 Fabrication of Excavator TeethSai DeepthiNo ratings yet
- Essco Catalogue 2021Document62 pagesEssco Catalogue 2021venkat2674No ratings yet
- Technical Session On Ripper Dozer: PDF Created With Pdffactory Trial VersionDocument26 pagesTechnical Session On Ripper Dozer: PDF Created With Pdffactory Trial Versionanupamkher100% (1)
- Hardox400 PDFDocument2 pagesHardox400 PDFZairullah El-AzharNo ratings yet
- List of Gear StandardDocument7 pagesList of Gear StandardManoj SinghNo ratings yet
- Oil Analysis Report: Test DetailsDocument1 pageOil Analysis Report: Test DetailsdnoaisapsNo ratings yet
- Hce Vibro Attachments Catalogue en 211122Document6 pagesHce Vibro Attachments Catalogue en 211122hamdi galipNo ratings yet
- Non Road Diesel Study CrackDocument183 pagesNon Road Diesel Study CrackDonatas Pagojus100% (1)
- NHTSA Study Finds Link Between Tire Rolling Resistance and Vehicle Fuel EconomyDocument153 pagesNHTSA Study Finds Link Between Tire Rolling Resistance and Vehicle Fuel EconomySuchismita SahooNo ratings yet
- Solutions: Fleet ManagementDocument13 pagesSolutions: Fleet ManagementRajipah OsmanNo ratings yet
- CAT HighwallDocument16 pagesCAT HighwallJelena IvazNo ratings yet
- Louis Berger S.A.: 805. Equipment in WorkshopDocument7 pagesLouis Berger S.A.: 805. Equipment in Workshoprelu1986No ratings yet
- Hw300 AssembleDocument111 pagesHw300 AssembleAndreiNo ratings yet
- 4-Stroke Diesel Engine InternshipDocument14 pages4-Stroke Diesel Engine InternshipBairi Rajesh100% (1)
- Hoist Inspection - SOWDocument10 pagesHoist Inspection - SOWAbdallah AbdelrehimNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training Presentation NBCDocument31 pagesIndustrial Training Presentation NBCSuraj Singh Mehta100% (2)
- Vehicle Tracking and Fuel Monitoring SystemDocument6 pagesVehicle Tracking and Fuel Monitoring SystemIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Basic Operation and ControlsDocument109 pagesBasic Operation and Controlsluy nguyen100% (1)
- API 7K Revisions Rev 5Document5 pagesAPI 7K Revisions Rev 5msm.ele2009No ratings yet
- Brosur SPX FlowDocument8 pagesBrosur SPX FlowAltino Mangiwa100% (1)
- Tomar - Industrial Signalling CatalogDocument82 pagesTomar - Industrial Signalling CatalogPrejit RadhakrishnaNo ratings yet
- Shovel Lubrication PDFDocument2 pagesShovel Lubrication PDFSounak SasmalNo ratings yet
- Interlocking PrinciplesDocument11 pagesInterlocking PrinciplesVignesh BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Flashback ArrestorDocument6 pagesFlashback ArrestorahmedNo ratings yet
- Highwall Miner HWM 300Document20 pagesHighwall Miner HWM 300Amit100% (1)
- 24 Volt ManualDocument13 pages24 Volt ManualCirilo JuniorNo ratings yet
- 2 - Rolling Bearing FundamentalsDocument35 pages2 - Rolling Bearing FundamentalsZiggy Gregory100% (1)
- Total LubricantsDocument3 pagesTotal LubricantsE Rudy SaputroNo ratings yet
- Machine Guarding BasicsDocument30 pagesMachine Guarding BasicsAjay meena Ajay meenaNo ratings yet
- DonalsonDocument6 pagesDonalsonrockyttpmcNo ratings yet
- Kobelco PDFDocument16 pagesKobelco PDFshekharNo ratings yet
- HEMM Dumper16Document8 pagesHEMM Dumper16miningnova2No ratings yet
- Angle GrinderDocument47 pagesAngle GrinderJane Geronimo100% (1)
- RTJ Catalogue Rev1Document9 pagesRTJ Catalogue Rev1steventrigochasin3537No ratings yet
- Trane SemiHermetic CompressorsDocument169 pagesTrane SemiHermetic CompressorsGerson RomeroNo ratings yet
- B Gen 200 0903Document16 pagesB Gen 200 0903Joan CzNo ratings yet
- Bharat Stage Emission StandardsDocument41 pagesBharat Stage Emission Standardsishans258No ratings yet
- Hydraulic Power and ControlDocument12 pagesHydraulic Power and ControlRavindra_1202No ratings yet
- Coating Performance Standard (CPS) : Guide For The Class NotationDocument11 pagesCoating Performance Standard (CPS) : Guide For The Class NotationGilberto Zamudio100% (1)
- Instruction Manual: Nash Type Vacuum PumpsDocument16 pagesInstruction Manual: Nash Type Vacuum Pumpsdiscovery channelNo ratings yet
- Air FilterDocument3 pagesAir FiltermarkooNo ratings yet
- Black Smoke: Causes, Impacts, and PreventionDocument1 pageBlack Smoke: Causes, Impacts, and PreventionAbdelsattar Ali AhmedNo ratings yet
- 23.bladder AccumlatorDocument12 pages23.bladder AccumlatorM S GokulNo ratings yet
- M0101873-00 - The Frame Fore Aft Beam May Crack On Certain 793FDocument2 pagesM0101873-00 - The Frame Fore Aft Beam May Crack On Certain 793FPercy Herrera Zeballos100% (1)
- 05 HD785-7 Engine 12V140-2 Presentation Part1Document9 pages05 HD785-7 Engine 12V140-2 Presentation Part1Satria Fajri100% (1)
- Machine Profiles: 844 Wheel TractorsDocument7 pagesMachine Profiles: 844 Wheel TractorsJavier Pagan TorresNo ratings yet
- Guideline Formulation for Petrolad 9200 LubricantsDocument4 pagesGuideline Formulation for Petrolad 9200 LubricantsAbhishek AgrawalNo ratings yet
- FS110 - What Causes Engine Oil ConsumptionDocument4 pagesFS110 - What Causes Engine Oil ConsumptionPrabakar MahesanNo ratings yet
- Machine Profiles: 994, 994D Wheel LoadersDocument9 pagesMachine Profiles: 994, 994D Wheel LoadersAldo Cesar Mina SosaNo ratings yet
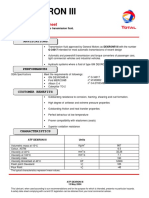
- Atf Dexron Iii: Data SheetDocument7 pagesAtf Dexron Iii: Data Sheetwilliam bryantNo ratings yet
- PacificValvesCastSteelBoltedBonnetCatalogCV 421 PDFDocument28 pagesPacificValvesCastSteelBoltedBonnetCatalogCV 421 PDFGoutham KSNo ratings yet
- For The Health of Your BusinessDocument14 pagesFor The Health of Your BusinessMauricio Santana0% (1)
- Hand Safety Toolkit - From IADC WebsiteDocument27 pagesHand Safety Toolkit - From IADC WebsiteProject Sales Corp100% (1)
- Hand Safety Essentials KitDocument27 pagesHand Safety Essentials KitAlex JNo ratings yet
- Hand Safety Training EssentialsDocument37 pagesHand Safety Training EssentialsAngel AngeleyeNo ratings yet
- BSD - Hand Safety TrainingDocument39 pagesBSD - Hand Safety TrainingArslan AhsanNo ratings yet
- Hand Safety PresentationDocument42 pagesHand Safety PresentationKarthik Duraisamy100% (1)
- Muhammad Rizwan resume with 15+ years experienceDocument1 pageMuhammad Rizwan resume with 15+ years experienceahmer09No ratings yet
- Danish CV PDFDocument1 pageDanish CV PDFahmer09No ratings yet
- Abdullah's Resume for HSE and Accounting RolesDocument2 pagesAbdullah's Resume for HSE and Accounting Rolesahmer09No ratings yet
- 10 PDFDocument90 pages10 PDFaniprk.995100% (3)
- Tell Me About YourselfDocument2 pagesTell Me About Yourselfahmer09No ratings yet
- 7198 - Emci - 20171220 22 EIA ProcessDocument92 pages7198 - Emci - 20171220 22 EIA Processahmer09No ratings yet
- Smmary Ahmer-SA8000Document1 pageSmmary Ahmer-SA8000ahmer09No ratings yet
- HAZOP STUDY CONDENSERDocument8 pagesHAZOP STUDY CONDENSERahmer09No ratings yet
- Saudi Aramco Interview QuestionsDocument3 pagesSaudi Aramco Interview QuestionsFahad Khan80% (20)
- Safety Questions and AnswersDocument30 pagesSafety Questions and Answersmiaicarba86% (50)
- Definitions of Key Words in NEBOSHDocument3 pagesDefinitions of Key Words in NEBOSHAmir SherafatipourNo ratings yet
- Definitions of Key Words in NEBOSHDocument3 pagesDefinitions of Key Words in NEBOSHAmir SherafatipourNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment CleaningDocument7 pagesRisk Assessment Cleaningahmer09No ratings yet
- Risk Assessment CleaningDocument7 pagesRisk Assessment Cleaningahmer09No ratings yet
- Loss Prevention EngineerDocument1 pageLoss Prevention Engineerahmer09No ratings yet
- Blank Noise Ass TemplateDocument16 pagesBlank Noise Ass TemplateMouctarNo ratings yet
- Bank AddressDocument2 pagesBank Addressahmer09No ratings yet
- Cleaning: Risk Assessment For: Establishment: Assessment By: DateDocument4 pagesCleaning: Risk Assessment For: Establishment: Assessment By: DateEzzati AzizNo ratings yet
- Hazard Identification and ControlDocument37 pagesHazard Identification and Controlahmer09No ratings yet
- HO CHIEN Enterprise Co., Ltd. Failure Analysis / Corrective Action ReportDocument2 pagesHO CHIEN Enterprise Co., Ltd. Failure Analysis / Corrective Action ReportMaruan MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Occupational HealthDocument37 pagesOccupational HealthEthel Marie OlvezNo ratings yet
- BK 123Document60 pagesBK 123Fadlul Akbar HerfiantoNo ratings yet
- Insert Company Name (Logo) Here:: Toolbox Meeting Form TemplateDocument1 pageInsert Company Name (Logo) Here:: Toolbox Meeting Form Templateahmer09No ratings yet
- Hazard Identification and ControlDocument37 pagesHazard Identification and Controlahmer09No ratings yet
- Occupational HealthDocument37 pagesOccupational HealthEthel Marie OlvezNo ratings yet
- Safety & Health Management System Training: Lesson 4 - Hazard Prevention & ControlDocument58 pagesSafety & Health Management System Training: Lesson 4 - Hazard Prevention & Controlokbangaet100% (1)
- Green Hands 20101112v2Document3 pagesGreen Hands 20101112v2ahmer09No ratings yet
- Cable Tray Works (SM Powertech)Document11 pagesCable Tray Works (SM Powertech)ahmer09No ratings yet
- Buildg Fire SR08Document81 pagesBuildg Fire SR08ahmer09No ratings yet
- 1.MSDS A1 RenasolDocument3 pages1.MSDS A1 RenasolImro FitrianiNo ratings yet
- 391Document6 pages391jubamajorNo ratings yet
- CORROSION DATA GUIDE FOR MEASURING INSTRUMENTSDocument8 pagesCORROSION DATA GUIDE FOR MEASURING INSTRUMENTSLê Tuấn Asia ValvesNo ratings yet
- Corrosive Alkalis - Google SearchDocument1 pageCorrosive Alkalis - Google SearchAidan AmsharNo ratings yet
- Sulfuric Acid 93-Pct WT-SA15 SDSDocument6 pagesSulfuric Acid 93-Pct WT-SA15 SDSnitroxx7No ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Checklist: Insert Company Logo HereDocument17 pagesRisk Assessment Checklist: Insert Company Logo HereRaffique HazimNo ratings yet
- HCL (Carlroth) PDFDocument16 pagesHCL (Carlroth) PDFMinjdeDiosNo ratings yet
- Thesis Autosaved XDocument77 pagesThesis Autosaved XDaniel Setyadi100% (1)
- Scientific Endeavour ExplainedDocument49 pagesScientific Endeavour ExplainedNadya Chalista Agusthine100% (1)
- AOCS CA 12-55 PhosphorusDocument2 pagesAOCS CA 12-55 PhosphorusLuki Wahyuning Tiyas100% (6)
- Boiler's Water PHDocument1 pageBoiler's Water PHDiaconu AndreiNo ratings yet
- API 571 SummaryDocument44 pagesAPI 571 SummaryTariq100% (2)
- Hydrochloric Acid MSDSDocument6 pagesHydrochloric Acid MSDSanurag6866No ratings yet
- Acetyl Chloride PDFDocument6 pagesAcetyl Chloride PDFRafika AnnurNo ratings yet
- LARSEN & TOUBRO LIMITED EVALUATION OF LEGAL COMPLIANCE FOR NEIGRIHMS PROJECTDocument177 pagesLARSEN & TOUBRO LIMITED EVALUATION OF LEGAL COMPLIANCE FOR NEIGRIHMS PROJECTMohammad Arif100% (1)
- MSDS - Calcium Hydroxide (LIME)Document6 pagesMSDS - Calcium Hydroxide (LIME)Eliz MelizaNo ratings yet
- MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET FOR DESCALING LIQUIDDocument6 pagesMATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET FOR DESCALING LIQUIDSanda AgungNo ratings yet
- MasterTile RSG 705 PART B Also MASTERTILE 550 REACTOR ONLYDocument9 pagesMasterTile RSG 705 PART B Also MASTERTILE 550 REACTOR ONLYSamseyla HunNo ratings yet
- 2016 Analysis of Copper-Bearing Rocks and Minerals For Their Metal Content Using Visible Spectros PDFDocument7 pages2016 Analysis of Copper-Bearing Rocks and Minerals For Their Metal Content Using Visible Spectros PDFRosa PatiñoNo ratings yet
- Safe Use of Hydrofluoric Acid (HFDocument18 pagesSafe Use of Hydrofluoric Acid (HFprasarnboon100% (1)
- Inox DMDocument6 pagesInox DMZoran DanilovNo ratings yet
- HazcomDocument56 pagesHazcomHamid Hamid100% (1)
- SUBJECT: A Few Rules of Thumb For Mechanical Seals 2-5Document8 pagesSUBJECT: A Few Rules of Thumb For Mechanical Seals 2-5Arsalan QadirNo ratings yet
- Wet Air Oxidation Pre Treatment of Spent Caustic For Discharge To Biological Wastewater Treatment Allowing For Water Recovery and ReuseDocument22 pagesWet Air Oxidation Pre Treatment of Spent Caustic For Discharge To Biological Wastewater Treatment Allowing For Water Recovery and ReuseAzam Khan100% (1)
- CASE IH MAXXUM 120 TRACTOR Service Repair Manual PDFDocument120 pagesCASE IH MAXXUM 120 TRACTOR Service Repair Manual PDFjfjksekdmeik100% (1)
- MSDS KresolDocument6 pagesMSDS Kresolshinta sariNo ratings yet
- Caustic Soda Data SheetDocument5 pagesCaustic Soda Data SheetKudakwashe Walter MakoniNo ratings yet
- Finishing Unitop PDFDocument1 pageFinishing Unitop PDFrashidafmNo ratings yet
- Urethane Chemical Resistance ChartDocument1 pageUrethane Chemical Resistance ChartJUANNo ratings yet
- Concresive 1315 PDFDocument5 pagesConcresive 1315 PDFFrancois-No ratings yet