Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diagnostic Center Imaging Services
Uploaded by
Danish Yaseen0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageOriginal Title
Presentation1.pptxdignostic center.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageDiagnostic Center Imaging Services
Uploaded by
Danish YaseenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
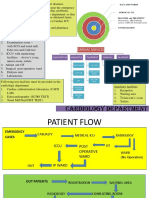
DIAGN0STIC CENTER
The most common types of diagnostic
Medical diagnosis is the process of determining which disease or Radiology Lab radiology exams include :
condition explains a person's symptoms and signs. It is most often Radiology represents a branch of medicine that deals with X-ray Radiography,
referred to as diagnosis with the medical context being implicit. radiant energy (energythat travels by waves or particles) Ultrasound,
in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases Computed Tomography
The most important labs in the hospital are: Nuclear Medicine Including
Radiology lab. Parts and components of the Radiology lab: Positron Emission
Pathology lab. Tomography (PET), And
X-ray rooms.
Pathology lab: Control room. Magnetic
Parts and components of the Pathology: Waiting area. ResonanceImaging(MRI)
Work area. Staff office. x-rays
Waiting area. Utility room. IMAGING
Sample room. Dark room.
Cleaning room. Film view.
Staff offices. Store.
Location:
Location:
Very close to the emergency department and external
clinics. Very close to the emergency department
Easily accessible from internal division. and external clinics.
Easily accessible from maternity and surgery Easily accessible from internal division.
departments. Ground floor is preferred.
Accessibility from central storages. Area of the department:
1. U.S. Public Health Service (USPHS):
Area of the department: 50-100 bed hospital area = 65-104 m 2
1. U.S. Public Health Service 200 bed hospital area = 220-240 m 2
(USPHS):
50 bed hospital area = 25 m2
100 bed hospital area = 60 m2
Or 200
areabed
canhospital areaby
be counted = 103 m2
the number of the beds
You might also like
- Parts and Components of The Radiology Lab:: Diagn0Stic CenterDocument1 pageParts and Components of The Radiology Lab:: Diagn0Stic CenterDanish YaseenNo ratings yet
- HosDocument56 pagesHosOmar MahameedNo ratings yet
- Hospital Classification and DepartmentsDocument68 pagesHospital Classification and DepartmentsNit56122No ratings yet
- Rockland Hospital Case StudyDocument2 pagesRockland Hospital Case StudyDheeraj Yadav73% (11)
- Hospital - Data Collection & Literature StudyDocument42 pagesHospital - Data Collection & Literature StudyNagateja MallelaNo ratings yet
- Literature Study of Hospital: Bipasa Das A92204017017 Sem 6 B.ArchDocument48 pagesLiterature Study of Hospital: Bipasa Das A92204017017 Sem 6 B.ArchBipasa DasNo ratings yet
- Letrature ConclusionDocument28 pagesLetrature ConclusionWazir Sajid AliNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Services "Physical Therapy"Document7 pagesTherapeutic Services "Physical Therapy"Aveen MahdiNo ratings yet
- Administration of A Radiological FacilityDocument92 pagesAdministration of A Radiological Facilitykyuleen05No ratings yet
- Radiation Therapy & Nuclear MedicineDocument38 pagesRadiation Therapy & Nuclear MedicineGarima KwatraNo ratings yet
- Understand The Design of General HospitalDocument22 pagesUnderstand The Design of General HospitalAveen MahdiNo ratings yet
- Hospital Design Module 8 - 13Document107 pagesHospital Design Module 8 - 13At Sa Wakas Ay100% (6)
- Lecture 01 - Health and Medical Care Facilities - HospitalsDocument40 pagesLecture 01 - Health and Medical Care Facilities - Hospitalsnikka csmNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - Hospital DesignDocument79 pagesGroup 1 - Hospital DesignSubhasree Dutta100% (1)
- Cardiology Department: Iccu and WardsDocument12 pagesCardiology Department: Iccu and WardsPoojaNo ratings yet
- Teaching HospitalDocument12 pagesTeaching Hospitalnazar zaidiNo ratings yet
- HOSPITAlstudybipasaDocument26 pagesHOSPITAlstudybipasaBipasa DasNo ratings yet
- Icu PDFDocument49 pagesIcu PDFVidya GopiNo ratings yet
- Radiation PleisotherapyDocument33 pagesRadiation PleisotherapyBavadharaniNo ratings yet
- Hospital StudyDocument38 pagesHospital StudySharandeep SandhuNo ratings yet
- Drjamescllee Chairman, NCC Radiation Safety CommitteeDocument11 pagesDrjamescllee Chairman, NCC Radiation Safety CommitteeLilNuttzNo ratings yet
- RMADocument98 pagesRMAAriel PonioNo ratings yet
- Republic of The PhilippinesDocument8 pagesRepublic of The PhilippinesShaira Mea GajilaNo ratings yet
- Library StudyDocument6 pagesLibrary Studytribenortheast projectNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Clinical RadiologyDocument38 pagesIntroduction To Clinical RadiologyMUBIRU SAMUEL EDWARDNo ratings yet
- Health Care: Chan I Cruz I Diwa I Dilig I Palma I Selga I Teves March10, 2017Document7 pagesHealth Care: Chan I Cruz I Diwa I Dilig I Palma I Selga I Teves March10, 2017jheyfteeNo ratings yet
- Types of Hospitals: Gynecology Services & Other Facilities Pharmacy LaboratoryDocument6 pagesTypes of Hospitals: Gynecology Services & Other Facilities Pharmacy LaboratoryMaham ShahidNo ratings yet
- Imaging Techniques in Biomedical Engineering (Thermal Imaging)Document67 pagesImaging Techniques in Biomedical Engineering (Thermal Imaging)Karminder SinghNo ratings yet
- MI - Course Syllabus - With LabDocument3 pagesMI - Course Syllabus - With LabAbdi Teferi50% (2)
- MIT Lab 01 (MRI Scan)Document5 pagesMIT Lab 01 (MRI Scan)MUHAMMAD ARSLANNo ratings yet
- Dental RadiologyDocument30 pagesDental RadiologyRobertNo ratings yet
- Matrix Layout6Document1 pageMatrix Layout6J ANo ratings yet
- DESIGN 8 Final PlateDocument12 pagesDESIGN 8 Final PlateXtian HadapNo ratings yet
- IIE/RA Contest ProblemsDocument8 pagesIIE/RA Contest ProblemsIsaac JimenezNo ratings yet
- hp415 Rad Proj PresDocument20 pageshp415 Rad Proj Presapi-624904071No ratings yet
- Architectural Design VI Daignostics: Group Members-Anubhav Gupta Pranav Sharma Saalim Jia BhattDocument33 pagesArchitectural Design VI Daignostics: Group Members-Anubhav Gupta Pranav Sharma Saalim Jia BhattAnubhav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Rajindra Hospital, Patiala: (Manual - 1) Particulars of Organization, Functions and DutiesDocument2 pagesRajindra Hospital, Patiala: (Manual - 1) Particulars of Organization, Functions and DutiesJs KalerNo ratings yet
- Hospital Mamagment System DocumentationDocument53 pagesHospital Mamagment System DocumentationNahom WendNo ratings yet
- New Advanced in RadiotherapyDocument49 pagesNew Advanced in RadiotherapyIndonesian Journal of CancerNo ratings yet
- Khasilva ReportDocument21 pagesKhasilva ReportTarus El AzizzNo ratings yet
- DOH Schematic Plans and Technical Requirements of A 25 Bed HospitalDocument17 pagesDOH Schematic Plans and Technical Requirements of A 25 Bed HospitalJeffrey ManansalaNo ratings yet
- Oncology Unit for Chemotherapy and RadiotherapyDocument17 pagesOncology Unit for Chemotherapy and RadiotherapyXTINCT Mobile LegendsNo ratings yet
- Use of Radioactive in MedicalDocument28 pagesUse of Radioactive in MedicalroseyacobNo ratings yet
- MRI FinalDocument25 pagesMRI FinalMunazzah IjazNo ratings yet
- AIA AAH Webinar March 10 - 2020 FinalDocument63 pagesAIA AAH Webinar March 10 - 2020 FinalMinhNo ratings yet
- Hospital ResearchDocument14 pagesHospital ResearchDAVID, Jaeron V.No ratings yet
- Library StudyDocument14 pagesLibrary StudyUtakars AnandNo ratings yet
- CM Identify Medical Imaging PPDocument21 pagesCM Identify Medical Imaging PPJoão Paulo Lucas BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Radiology Department OverviewDocument17 pagesRadiology Department OverviewHarlan Putra WNo ratings yet
- Radi 694 Brochure 1Document2 pagesRadi 694 Brochure 1api-356213702No ratings yet
- Hi-Tech Tele Radiology BrochureDocument6 pagesHi-Tech Tele Radiology BrochurevyadkikarNo ratings yet
- Architecture II: Prepared By:-Architect Engineer, A/kadir Dahir A/llahiDocument65 pagesArchitecture II: Prepared By:-Architect Engineer, A/kadir Dahir A/llahiaman100% (1)
- Histrory of Radiology.: and in Many Clinical SpecialtiesDocument2 pagesHistrory of Radiology.: and in Many Clinical SpecialtiesMyung KimNo ratings yet
- Architecture II: Prepared By:-Architect Engineer, A/kadir Dahir A/llahiDocument65 pagesArchitecture II: Prepared By:-Architect Engineer, A/kadir Dahir A/llahiritika100% (1)
- St. Joseph College of Engineering and Technology: Post Box No.11007, Dar Es Salaam, TanzaniaDocument4 pagesSt. Joseph College of Engineering and Technology: Post Box No.11007, Dar Es Salaam, Tanzaniaignatius1972No ratings yet
- 7th Weekly Report - M2021HO021Document20 pages7th Weekly Report - M2021HO021Dr.Marufa FaruqiNo ratings yet
- Hospital Inventory Management Ca2Document5 pagesHospital Inventory Management Ca2Sneha MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Medical Exposures Fact Sheet PDFDocument4 pagesMedical Exposures Fact Sheet PDFSrinivas VenkataramanNo ratings yet
- Textbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 35, Urgent Care Imaging and InterpretationFrom EverandTextbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 35, Urgent Care Imaging and InterpretationNo ratings yet
- Storm FiberDocument1 pageStorm FiberDanish YaseenNo ratings yet
- Terms and Conditions Customer Acknowledgement 12082016 PDFDocument2 pagesTerms and Conditions Customer Acknowledgement 12082016 PDFM Umar MughalNo ratings yet
- Conclusions FinalDocument33 pagesConclusions FinalDanish YaseenNo ratings yet
- 2458 Ambitious Mumbai Project Cluster Development For Large Scale Redevelopment of Urban HabitatDocument9 pages2458 Ambitious Mumbai Project Cluster Development For Large Scale Redevelopment of Urban HabitatDanish YaseenNo ratings yet
- 5hylwdol) Dwlrqri8Uedq3Xeolf6Sdfhv$Qryhuylhz: SciencedirectDocument8 pages5hylwdol) Dwlrqri8Uedq3Xeolf6Sdfhv$Qryhuylhz: SciencedirectDanish YaseenNo ratings yet
- Architectural Research MethodsDocument2 pagesArchitectural Research MethodsDanish YaseenNo ratings yet
- Abstract 9Document1 pageAbstract 9Danish YaseenNo ratings yet
- Zia 140615013313 Phpapp01 - 2Document17 pagesZia 140615013313 Phpapp01 - 2Danish YaseenNo ratings yet
- Conclusions FinalDocument33 pagesConclusions FinalDanish YaseenNo ratings yet
- Mbbs Entry Requirements International 2018Document11 pagesMbbs Entry Requirements International 2018Danish YaseenNo ratings yet
- Mbbs Entry Requirements International 2018Document11 pagesMbbs Entry Requirements International 2018Danish YaseenNo ratings yet
- AhtashmDocument6 pagesAhtashmDanish YaseenNo ratings yet
- Worldcities Notes CasestudiesDocument15 pagesWorldcities Notes CasestudiesDanish YaseenNo ratings yet
- Architectural Research MethodsDocument2 pagesArchitectural Research MethodsDanish YaseenNo ratings yet
- 5hylwdol) Dwlrqri8Uedq3Xeolf6Sdfhv$Qryhuylhz: SciencedirectDocument8 pages5hylwdol) Dwlrqri8Uedq3Xeolf6Sdfhv$Qryhuylhz: SciencedirectDanish YaseenNo ratings yet
- Writeup: Submitted To Ar. Aujala Ar. Shahid AkbarDocument4 pagesWriteup: Submitted To Ar. Aujala Ar. Shahid AkbarDanish YaseenNo ratings yet
- 10 Chapter 5Document8 pages10 Chapter 5Danish YaseenNo ratings yet
- CMH Lahore Medical College Fee Structure 2017-18 for MBBS & BDS DegreesDocument1 pageCMH Lahore Medical College Fee Structure 2017-18 for MBBS & BDS DegreesDanish YaseenNo ratings yet
- 01 NMC 2016Document36 pages01 NMC 2016Qamar IqbalNo ratings yet
- Textile Design Is Essentially The Process of Creating Designs For Woven, Knitted or PrintedDocument1 pageTextile Design Is Essentially The Process of Creating Designs For Woven, Knitted or PrintedDanish YaseenNo ratings yet
- 2 EgyptianDocument20 pages2 EgyptianfransescatomasilaNo ratings yet
- 2250 2Document3 pages2250 2Danish YaseenNo ratings yet
- Understanding Pakistani Culture Through Its Diverse Ethnic GroupsDocument1 pageUnderstanding Pakistani Culture Through Its Diverse Ethnic GroupsDanish YaseenNo ratings yet
- Aaim Completeguide PDFDocument38 pagesAaim Completeguide PDFDanish YaseenNo ratings yet
- What is an expansion joint and why are they neededDocument12 pagesWhat is an expansion joint and why are they neededDanish YaseenNo ratings yet
- BTU and Ton HVAC Sizing GuideDocument17 pagesBTU and Ton HVAC Sizing GuideDanish YaseenNo ratings yet
- Proposal PDFDocument9 pagesProposal PDFDanish YaseenNo ratings yet
- What is an expansion joint and why are they neededDocument12 pagesWhat is an expansion joint and why are they neededDanish YaseenNo ratings yet
- JEE 2023 Session-1 24th Jan To 1st Feb 2023Document37 pagesJEE 2023 Session-1 24th Jan To 1st Feb 2023Harshith Reddy GantaNo ratings yet
- Gap Analysis Identifies Gaps in Retention Strategy DefinitionsDocument4 pagesGap Analysis Identifies Gaps in Retention Strategy DefinitionsNeotrixnikxNo ratings yet
- Saddle Positioning (500m3)Document1 pageSaddle Positioning (500m3)solquihaNo ratings yet
- Ddec V VanhoolDocument30 pagesDdec V VanhoolVeterano del CaminoNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Physics Extended 10e CH 3 SolutionsDocument6 pagesFundamentals of Physics Extended 10e CH 3 Solutionssin8310% (1)
- Art07 EngDocument8 pagesArt07 Engcerbu_bass_cdcNo ratings yet
- Study On Process Management in Supply Chain Industry - NCDocument49 pagesStudy On Process Management in Supply Chain Industry - NCRohit KumbharNo ratings yet
- Major Assiignment A - The Brisbane Metro (Balvinder Singh Gill)Document4 pagesMajor Assiignment A - The Brisbane Metro (Balvinder Singh Gill)Gill BalvinderNo ratings yet
- G. David Garson-Correspondence Analysis-Statistical Associates Publishing (2012)Document37 pagesG. David Garson-Correspondence Analysis-Statistical Associates Publishing (2012)andresNo ratings yet
- Curriculum GuideDocument6 pagesCurriculum Guidemerlie olaloNo ratings yet
- Servo Amplifier Mr-j2s - ADocument323 pagesServo Amplifier Mr-j2s - AGeuris David Estèvez BelliardNo ratings yet
- Application of Newton-Raphson Method in Optimal Design of Water Distribution NetworksDocument16 pagesApplication of Newton-Raphson Method in Optimal Design of Water Distribution NetworksAhmed adelNo ratings yet
- StationsDocument172 pagesStationsJuan Pablo Reina MontañezNo ratings yet
- National Immunization ProgramDocument9 pagesNational Immunization Programjuanamay30gmailcomNo ratings yet
- District Heating NorwayDocument8 pagesDistrict Heating Norwaymahmoud4871No ratings yet
- Marantz PM4200 AmpDocument17 pagesMarantz PM4200 Ampffar1No ratings yet
- Milk Water The Presence of Water Can Be by Putting A Drop of Milk On A Polished Slanting SurfaceDocument1 pageMilk Water The Presence of Water Can Be by Putting A Drop of Milk On A Polished Slanting SurfaceNithish KannaNo ratings yet
- VN200 Datasheet Rev2Document2 pagesVN200 Datasheet Rev2Joost TrompNo ratings yet
- Tero Cell Hydrogen GeneratorDocument21 pagesTero Cell Hydrogen Generatorfakiris3100% (1)
- History 6Sem621History English HistoryandCulDocument207 pagesHistory 6Sem621History English HistoryandCul12nakulNo ratings yet
- Mve 500 - 3Document2 pagesMve 500 - 3Amol SarinNo ratings yet
- Spring 2019 Journal WebDocument28 pagesSpring 2019 Journal WebCarlos Jose Prada RangelNo ratings yet
- ING Group 2Document4 pagesING Group 2Puneet JainNo ratings yet
- Sar SkinradDocument8 pagesSar SkinradEmf RefugeeNo ratings yet
- 7th 6 Sunday VEIL 1Document1 page7th 6 Sunday VEIL 1reatabs12No ratings yet
- The Pasts - RothDocument28 pagesThe Pasts - RothElizabeth MataNo ratings yet
- Solid Works Aerofoil GuideDocument3 pagesSolid Works Aerofoil GuideMuhammad JawadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4, 5, 6, 7, 9Document37 pagesLecture 4, 5, 6, 7, 9Madeeha DanishNo ratings yet
- SEM TheoryDocument50 pagesSEM TheoryKamiNo ratings yet
- Thomas W.hungerford, AlgebraDocument1 pageThomas W.hungerford, AlgebraJoan Tamayo RiveraNo ratings yet