Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Power System-Ii (Protection & Switchgear) : Unit-1 Substation
Uploaded by
Vicky LakhwalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Power System-Ii (Protection & Switchgear) : Unit-1 Substation
Uploaded by
Vicky LakhwalCopyright:
Available Formats
POWER SYSTEM-II(PROTECTION
& SWITCHGEAR)
Unit-1
SUBSTATION
Er. Meenakshi Goyal
Email: meenakshigoyal555@gmail.com
SUBSTATION
SUBSTATION - A station in the power transmission system at
which electric power is transformed to a conveniently used
form. The station may consist of transformers, switches, circuit
breakers and other auxiliary equipment. Its main function is to
receive energy transmitted at high voltage from the generating
station, by either step-up or step-down the voltage to a value
appropriate for local use and provide facilities for switching.
Its provide points where safety devices may be installed to
disconnect circuits or equipment in the event of trouble.
Some substation, such as power plant switchyard are
simply switching stations where different connections can be
made between various transmission lines.
Er. Meenakshi Goyal
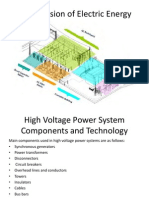
Typical Components of a Power Plant
Substation (Switchyard)
CONNECT A - Busbar
CONNECT & DIS-CONNECT B - Disconnector
CONNECT, DIS-CONNECT &
DETECT C - Circuit Breaker
DETECT & TRANSFORM D - Current Transformer
DETECT & TRANSFORM E - Voltage Transformer
PROTECT & SAFETY F - Earthing Switch
PROTECT G - Surge Arrestor
Er. Meenakshi Goyal
A. BUSBAR
BUSBAR (or bus, for short) is a term we use for a main bar
or conductor carrying an electric current to which many
connection may be made.
Buses are merely convenient means of connecting
switches and other equipment into various arrangements. The
usual arrangement of connections in most substations permit
working on almost any piece of equipment without
interruption to incoming or outgoing feeders. In the switchyard
or substation, buses are open to the air. Aluminum or copper
conductors supported on porcelain insulators, carry the electric
energy from point to point.
Er. Meenakshi Goyal
Busbars
(long heavy
tube type)
Er. Meenakshi Goyal
B. DISCONNECTS
DISCONNECT is an easily removed piece of the actual
conductor of a circuit. The purpose of disconnects is to isolate
equipment. Disconnects are not used to interrupt circuits; they
are no-load devices. A typical use of disconnects is to isolate a
circuit breaker by installing one disconnect on either side of
the circuit breaker (in series with the breaker). Operation of
disconnects is one of the most important and responsible jobs
of a power plant operator. One error in isolation of equipment,
or the accidental grounding of line equipment, can be a fatal
mistake.
Er. Meenakshi Goyal
Disconnect Switch
( moving contact rod (A) &
contacts with flexible
fingers (B) )
B
A
Er. Meenakshi Goyal
C. CIRCUIT BREAKER
CIRCUIT BREAKER is used to interrupt circuits while
current is flowing through them. The making and breaking of
contacts in a Oil type circuit breaker are done under oil, this oil
serves to quench the arc when the circuit is opened. The
operation of the breaker is very rapid when opening. As with
the transformer, the high voltage connections are made
through bushings. Circuit breakers of this type are usually
arranged for remote electrical control from a suitably located
switchboard.
Some recently developed circuit breakers have no oil, but
put out the arc by a blast of compressed air; these are called air
circuit breakers. Another type encloses the contacts in a
vacuum or a gas (sulfur hexafluoride, SF6) which tends to self
maintain the arc. Er. Meenakshi Goyal
Operating
Mechanism
Panel
Circuit Breakers
( Connected in a typical 3-
phase circuit )
Position
Indicator
Er. Meenakshi Goyal
D. CURRENT TRANSFORMER
CURRENT TRANSFORMER Current transformer are
used with ammeters, watt meters, power-factor meters, watt-
hour meters,compensators, protective and regulating relays
and the trip coil of circuit breakers. One current transformer
can be used to operate several instruments, provided that the
combined burden does not exceed that for which the
transformer is designed and compensated. The current
transformer is connected directly in series with the line.
Er. Meenakshi Goyal
Er. Meenakshi Goyal
E. VOLTAGE TRANSFORMER
VOLTAGE TRANSFORMER also know as potential
transformer, are used with volt-meters, wattmeters, watt-hour
meters, power-factor meters, frequency meters, synchroscopes
and synchronizing apparatus, protective and regulating relays
and the no-voltage and over-voltage trip coils of automatic
circuit breakers. One transformer can be used for a number of
instruments at the same time if the total current taken by the
instrument does not exceed that for which the transformer is
designed and compensated. The ordinary voltage transformer
is connected across the line, and the magnetic flux in the core
depends upon the primary voltage
Er. Meenakshi Goyal
Er. Meenakshi Goyal
F. EARTHING SWITCH
EARTHING SWITCH also known as ground disconnect,
which used to connects the equipment to a grid of electrical
conductors buried in the earth on the station property. It is
intended to protect people working on the grounded
equipment. It does this by completing a circuit path, thereby
reducing the voltage difference between the equipment and its
surroundings. For safety reasons, it is important that ground
disconnects and all associated connections have good contact
and low resistance. It is also important that the protective
ground not be accidentally remove, that is why all the earthing
switches, disconnect switches and circuit breakers are all
interlocked to each other and proper/correct sequencing must
be followed.
Er. Meenakshi Goyal
G. SURGE ARRESTOR
SURGE ARRESTOR are devices used to provide the
necessary path to ground for such surges, yet prevent any
power current from following the surge. An ideal arrester must
therefore have the following properties:
1. Ability to remove the surge energy from the line in a min. time.
2. High resistive to flow of power current.
3. A valve action automatically allowing surge to pass and then
closing up so as not to permit power current to flow to ground.
4. Always ready to perform.
5. Performance such that no system disturbances are introduced
by its operation.
6. Economically feasible
Er. Meenakshi Goyal
Er. Meenakshi Goyal
OVERHEAD GROUND WIRE by a ground wire is meant
a wire, generally of steel, supported from the top of
transmission-line towers and solidly grounded at each tower. It
is considered a preventive device, but it does not entirely
prevent the formation of travelling waves on a line.
Furthermore, those lines which are not equipped with ground
wires will be subjected to disturbances which produce surges
that must be allowed to escaped to ground, or the apparatus
connected to the line must be strong enough to reflect or
absorb these surges until they are entirely damped out.
Er. Meenakshi Goyal
Er. Meenakshi Goyal
PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
BUSBARS & OVERHEAD GROUND WIRE
At least once a year
Visual Inspection & Examination of all wiring connectors.
Check Insulator , clean or apply HVIC if necessary.
Check the physical condition of bus (cables or bars)
For ground wire, check or test the grounding system.
DISCONNECT & EARTHING SWITCHES
At least once a month
Visual Inspection.
Check heating resistor located at its control panel for proper functioning.
At least once a year
Clean contacts of disconnectors as well as earthing switches and apply electrical
contact grease , if necessary.
Er. Meenakshi Goyal
Check disconnectors and earthing switches, joints and bearings of the operating
linkages for deformed bearing points.
Check flexible connections of earthing switches.
Check all screwed joints for tight fit.
Clean insulators if necessary, when an excessive amount of dirt has accumulated.
Carry-out the maintenance of operating mechanism.
VOLTAGE TRANSFORMER
At least once a month
Inspect the voltage divider to be sure that no oil leak or serious accumulation of
soot, dust or salt composite is present.
Inspect the intermediate voltage transformer and check the minimum permissible
oil level.
At least once a year
Check all screwed joints & contact for tight fit.
Clean insulators if necessary, when an excessive amount of dirt has accumulated.
Er. Meenakshi Goyal
CURRENT TRANSFORMER
At least once a month
Visual Inspection to check oil level and defects or possible oil leaks.
At least once a year
Check all screwed joints & contact for tight fit.
Clean insulators if necessary, when an excessive amount of dirt has accumulated.
Check primary and secondary connectors and conduct necessary tightening.
Note: Never open a secondary winding of a CT while on service.
Er. Meenakshi Goyal
SURGE ARRESTOR
At least once a year
Visual Inspection & Examination of all wiring connectors.
Check Insulator and metal circular ring, clean or apply HVIC if necessary.
Check the physical condition of bus (cables or bars)
For ground wire, check or test the grounding system.
Note: Arrestors should never be touched unless completely disconnected from all
live lines and equipment and effectively connected to ground at the line side of
the arrestor.
Er. Meenakshi Goyal
Er. Meenakshi Goyal
You might also like
- High Voltage Components PresentationsDocument28 pagesHigh Voltage Components Presentationschristian fruto100% (1)
- Power Plant Substation ComponentsDocument22 pagesPower Plant Substation ComponentsRanndolf JavierNo ratings yet
- Switchyard Components GuideDocument22 pagesSwitchyard Components GuideAnand SwamiNo ratings yet
- Substation DesignDocument22 pagesSubstation Designsanthosh kumarNo ratings yet
- SUBSTATIONDocument22 pagesSUBSTATIONAmrit Aggarwal100% (1)
- Substation Equipment's & One Line DiagramDocument10 pagesSubstation Equipment's & One Line DiagramMr Hassan RazaNo ratings yet
- Bhakra Beas Management BoardDocument39 pagesBhakra Beas Management BoardGabriela MaerskNo ratings yet
- 220 KV SubstationDocument24 pages220 KV SubstationPuneet Agarwal100% (1)
- Sustation DesignDocument38 pagesSustation DesignFaheem FarooqNo ratings yet
- Safety Competency TrainingDocument21 pagesSafety Competency TrainingsemajamesNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Presentation: Electricity Distribution System AT 220 KV Sub-Station, SahibabadDocument23 pagesSummer Training Presentation: Electricity Distribution System AT 220 KV Sub-Station, SahibabadMarut Awasthi100% (1)
- Shivam Report On Substation VisitDocument18 pagesShivam Report On Substation VisitShivam KaushalNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Substations Electrical Power GenerationsDocument18 pagesPresentation On Substations Electrical Power GenerationsUday KoliNo ratings yet
- Study of Substation Equipments & Protection: Konark Institute of Science & Technology BhubaneswarDocument19 pagesStudy of Substation Equipments & Protection: Konark Institute of Science & Technology BhubaneswarDev KumarNo ratings yet
- Six Week Industrial Training at 66 KV SubDocument32 pagesSix Week Industrial Training at 66 KV SubGurinderdeep Singh67% (3)
- Introduction To Switch Gear and ProtectionDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Switch Gear and ProtectionKrishna PrasadNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training: Summer Internship PresentationDocument15 pagesIndustrial Training: Summer Internship PresentationPoonam BhaduNo ratings yet
- Power System III (1.0)Document62 pagesPower System III (1.0)Emmanuel AgyemangNo ratings yet
- Switchgears and Other Equipments S RaoDocument114 pagesSwitchgears and Other Equipments S Rao2041016166.sourashishpatra100% (1)
- Major Electrical EquipmentsDocument52 pagesMajor Electrical EquipmentsGrant Arvin SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Substation ReportDocument12 pagesSubstation ReportAmandeep KhereNo ratings yet
- Torque Prod Ac DrivesDocument32 pagesTorque Prod Ac DrivesThanigaivelu SubrmanianNo ratings yet
- Training Review of 132 KV SubstationDocument21 pagesTraining Review of 132 KV SubstationUpender SinghNo ratings yet
- IES Darshan Study MaterialDocument76 pagesIES Darshan Study MaterialPatel Neel50% (2)
- Apparatus and Circuit Elements of SubstationDocument24 pagesApparatus and Circuit Elements of SubstationNaveen D SouzaNo ratings yet
- Classification of Substations: Step-Up or Primary SubstationsDocument24 pagesClassification of Substations: Step-Up or Primary SubstationsamittenserNo ratings yet
- Switchgear PresentationDocument2 pagesSwitchgear PresentationAhmad Yaseen100% (1)
- Electrical SubstationDocument16 pagesElectrical SubstationAjay Gahlot100% (3)
- Fault Protection: Presented By: Sky Roegen Gayatgay G. & Alexis Emmanuel Gesulgon GDocument29 pagesFault Protection: Presented By: Sky Roegen Gayatgay G. & Alexis Emmanuel Gesulgon GIsaac100% (1)
- INTERNSHIPDocument29 pagesINTERNSHIPAnkita Mohanty0% (1)
- FinalDocument21 pagesFinalRahul Kumar Gupta100% (1)
- 33 KV SubstationDocument18 pages33 KV SubstationRohit PatilNo ratings yet
- Basic Chapter 7: Rectifier BasicsDocument46 pagesBasic Chapter 7: Rectifier BasicsNadaa safaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On A 132KV GSS NANGAL-SHERPURDocument27 pagesPresentation On A 132KV GSS NANGAL-SHERPURmanmohan meenaNo ratings yet
- Gas Insulated SwitchgearsDocument24 pagesGas Insulated Switchgearscody100% (3)
- Protective Elements in Power Systems: Circuit Breakers and RelaysDocument30 pagesProtective Elements in Power Systems: Circuit Breakers and RelaysvijayamargaretNo ratings yet
- Gas Insulated SwitchgearsDocument24 pagesGas Insulated Switchgearsemy1188No ratings yet
- Substation ComponentsDocument44 pagesSubstation Componentsgurkirat1108No ratings yet
- Turbo Generator at NalcoDocument13 pagesTurbo Generator at NalcoSanjay Kumar PandaNo ratings yet
- Ractical Training Seminar: Balveer Singh 132 KV G.S.S. Ultratech Cement LTDDocument14 pagesRactical Training Seminar: Balveer Singh 132 KV G.S.S. Ultratech Cement LTDAnupriya PandeyNo ratings yet
- High Voltage TechniquesDocument108 pagesHigh Voltage Techniquesممشط75% (4)
- Pge CompleteDocument198 pagesPge CompleteOMPRAKASH SM EE021No ratings yet
- A Project Presentation Review-01 On: 33/11KV SubstationDocument20 pagesA Project Presentation Review-01 On: 33/11KV SubstationChandu Raj100% (2)
- 132 KV GSSDocument26 pages132 KV GSSPhillip LongNo ratings yet
- 440kv GSSDocument37 pages440kv GSSready2cheerNo ratings yet
- 220kV Transmission Substation PresentationDocument17 pages220kV Transmission Substation PresentationadarshNo ratings yet
- MV/LV Switchboards: Components and FunctionsDocument20 pagesMV/LV Switchboards: Components and FunctionszarulNo ratings yet
- Power System PDFDocument63 pagesPower System PDFGeda Valley100% (1)
- IsolatorDocument10 pagesIsolatorsarkar1981No ratings yet
- Unit-3 NoteDocument21 pagesUnit-3 NoteSankara nathNo ratings yet
- Elements of SubstationDocument35 pagesElements of Substationjustog_12No ratings yet
- Modu LE5 SubstationDocument36 pagesModu LE5 SubstationRamya ShreyasNo ratings yet
- Grid Station PresentationDocument40 pagesGrid Station Presentationranafaizan773750% (2)
- Group 4 SwitchgearDocument10 pagesGroup 4 SwitchgearJordan Dator MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Application Form For Reg DR ARsoftDocument4 pagesApplication Form For Reg DR ARsoftVicky LakhwalNo ratings yet
- Time TableDocument2 pagesTime TableVicky LakhwalNo ratings yet
- Electricity Show2Document50 pagesElectricity Show2Naveen YallapuNo ratings yet
- Course PlanDocument43 pagesCourse PlanVicky LakhwalNo ratings yet
- What Is MPPTDocument5 pagesWhat Is MPPTVicky LakhwalNo ratings yet
- B - Tech Civil Batch 2011 PTU SyllabusDocument12 pagesB - Tech Civil Batch 2011 PTU SyllabusMohit Dev100% (1)
- Experiment 11 AimDocument3 pagesExperiment 11 AimVicky LakhwalNo ratings yet
- 74ls04 Not GateDocument9 pages74ls04 Not GateVicky LakhwalNo ratings yet
- Setup LogDocument261 pagesSetup LogwedihartoyoNo ratings yet
- Ece5 Lic May07Document2 pagesEce5 Lic May07Vicky LakhwalNo ratings yet
- Ece5 Lic May05Document4 pagesEce5 Lic May05Vicky LakhwalNo ratings yet
- NtbtlogDocument42 pagesNtbtlogVicky LakhwalNo ratings yet
- NtbtlogDocument42 pagesNtbtlogVicky LakhwalNo ratings yet
- SCHEDLGUDocument9 pagesSCHEDLGUVicky LakhwalNo ratings yet
- Read MeDocument2 pagesRead MeAndi AndaNo ratings yet
- Ptu SiteDocument1 pagePtu SiteVicky LakhwalNo ratings yet
- M (1) .Tech Syllabus 2Document33 pagesM (1) .Tech Syllabus 2Vicky LakhwalNo ratings yet
- Emerging Nokia Group Discusses Mobile Phone EvolutionDocument11 pagesEmerging Nokia Group Discusses Mobile Phone EvolutionArunachalamNo ratings yet
- A Conversation With Alan Cooper: The Origin of Interaction DesignDocument3 pagesA Conversation With Alan Cooper: The Origin of Interaction DesignCjay ChangNo ratings yet
- VRPP Technical ManualDocument16 pagesVRPP Technical ManualJegadeshwaran RNo ratings yet
- Maintain Equipment Request FormDocument5 pagesMaintain Equipment Request FormDwayne SmithNo ratings yet
- CV-JM Van StraatenDocument5 pagesCV-JM Van StraatenJovan Van StraatenNo ratings yet
- VoLTE 1Document28 pagesVoLTE 1raad79No ratings yet
- PDX SettingsDocument5 pagesPDX SettingsMichael HongNo ratings yet
- AVCCDocument3 pagesAVCCTanya WilkersonNo ratings yet
- Chlorination General SpecsDocument8 pagesChlorination General Specsraghuwanshi12No ratings yet
- Cs1802 Visual Programming: Unit I: Windows ProgrammingDocument47 pagesCs1802 Visual Programming: Unit I: Windows ProgrammingSuneel Kumar GoudaNo ratings yet
- Ludus Collaborative Digital Tool PresentationDocument8 pagesLudus Collaborative Digital Tool Presentationapi-448013261No ratings yet
- SQL Server 2019 Editions DatasheetDocument3 pagesSQL Server 2019 Editions DatasheetKeluarga ZulfanNo ratings yet
- Subaru Diesel - TuningDocument28 pagesSubaru Diesel - TuningEdwinNo ratings yet
- Statement of Account: Date Tran Id Remarks UTR Number Instr. ID Withdrawals Deposits BalanceDocument2 pagesStatement of Account: Date Tran Id Remarks UTR Number Instr. ID Withdrawals Deposits Balancech shanmugamNo ratings yet
- Industrial Engineering and Management by Ravi V PDFDocument2 pagesIndustrial Engineering and Management by Ravi V PDFErin BarryNo ratings yet
- Techagilecoach SampleDocument27 pagesTechagilecoach Sampletrha at hnepiNo ratings yet
- CNS-9101 SM PDFDocument70 pagesCNS-9101 SM PDFhadiiir pal100% (1)
- Adcmxl1021-1 - Sensor Analogic 1 Eixos FFT - Ideia de Fazer Do Acell Analog Um Digital Usando Adxl1002Document42 pagesAdcmxl1021-1 - Sensor Analogic 1 Eixos FFT - Ideia de Fazer Do Acell Analog Um Digital Usando Adxl1002FabioDangerNo ratings yet
- HTML Questions Answers to Front-end Job Interview QuestionsDocument7 pagesHTML Questions Answers to Front-end Job Interview Questionsmcn37803No ratings yet
- Spring Festival Events and CompetitionsDocument10 pagesSpring Festival Events and Competitions45.thiên ýNo ratings yet
- Teleprotection For Distance Protection: To AchieveDocument5 pagesTeleprotection For Distance Protection: To AchievebijoyNo ratings yet
- USM Engineering CampusDocument28 pagesUSM Engineering Campusfai-fai-fai-8153No ratings yet
- 50 Hydraulics Probs by Engr. Ben DavidDocument43 pages50 Hydraulics Probs by Engr. Ben DavidEly Jane DimaculanganNo ratings yet
- Multi Region DVD Codes Latest EditionDocument282 pagesMulti Region DVD Codes Latest Editionjelenjek83No ratings yet
- Customer Portal - User Manual 2021-07Document58 pagesCustomer Portal - User Manual 2021-07Nurul HidayatNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Drive Systems, Worldwide ServicesDocument32 pagesIntelligent Drive Systems, Worldwide Servicesjonas marquesNo ratings yet
- Myshri Techinal SeminarDocument21 pagesMyshri Techinal SeminarLikitha GNo ratings yet
- Security TrainingDocument14 pagesSecurity TrainingmmeridiusNo ratings yet
- TQMDocument2 pagesTQMMahaveer SepatNo ratings yet
- Serial IO and Data CommunicationDocument25 pagesSerial IO and Data Communicationapi-3724082100% (8)