Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Financial System - Flow of Funds - Money & Capital Market
Uploaded by
Devansh DubeyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Financial System - Flow of Funds - Money & Capital Market
Uploaded by
Devansh DubeyCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 2
The Financial System
THE INDIAN
FINANCIAL SYSTEM
Financial Management: Principles and Practice
By G. Sudarsana Reddy
Himalaya Publishing House
Chapter 2
The Financial System
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Define system financial system
Say why to study financial system
Discuss the functions of financial system
Define, Classify financial assets
Define, Classify financial markets
List out the instruments of money market and capital market
Distinguish between money market and capital market
Give the structure of Indian financial intermediaries
Discuss the regulatory bodies RBI, SEBI, IRDA.
Financial Management: Principles and Practice
By G. Sudarsana Reddy
Himalaya Publishing House
Chapter 2
The Financial System
System
System is a set of inter-related components
working together to achieve some purpose
Financial Management: Principles and Practice
By G. Sudarsana Reddy
Himalaya Publishing House
Chapter 2
The Financial System
Financial System
Financial System
Financial Institutions Financial Markets Financial Instruments Financial Services
Shares
Commercial Banks
Merchant Banking
Money Market
Debentures / Bonds
Industrial Banks
Project
Commercial Paper (CPs)
Consultancy
Provident Funds Capital Market
Certificate of Deposits
(CDs)
Mutual Public DepositS PDs)
Funds
Mutual Fund Units
NBFCs
Insurance Policies
Government Bonds Financial Management: Principles and Practice
By G. Sudarsana Reddy
Himalaya Publishing House
Chapter 2
The Financial System
Functions of Financial System
Payment system
Mobilisation of savings
Size transformation
Maturity transformation
Risk transformation
Provision of liquidity
Cost reduction
Price information
Financial advice
Financial Management: Principles and Practice
By G. Sudarsana Reddy
Himalaya Publishing House
Chapter 2
The Financial System
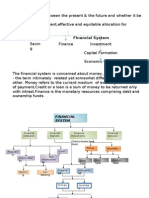
Savers / Lenders
Flow of Funds
Householders
Funds Securities:
Business Firms
Shares/Bonds
Government
Foreigners
Deposits/Policies/Units Funds
S
e
c
Financial Institutions u Financial
Banks r Markets
Provident Funds Funds i F
Insurance Companies t u Money Market
Mutual Funds i Private n Capital Market
e d
NBFCs Placement Over-the-Counter
s s Market
Mode
Securities
Investors/Borrowers
Householders
Loans Business Firms
Government Fund
Foreigners s
Securities:
Funds Shares/Bonds
Financial Management: Principles and Practice
By G. Sudarsana Reddy
Himalaya Publishing House
Chapter 2
The Financial System
Assets and Financial Assets
Assets are the rights of owners
Fixed assets can be seen and can be touched (Tangible)
Financial Management: Principles and Practice
By G. Sudarsana Reddy
Himalaya Publishing House
Chapter 2
The Financial System
Classification of Financial Assets
Financial Assets
Non-Marketable Marketable
Bank Post Office Insuranc Shares Govt. Debe - MF
Deposits Certificates e Securitie ntures Units
Schemes s
Equity Preference
Shares Shares
Financial Management: Principles and Practice
By G. Sudarsana Reddy
Himalaya Publishing House
Chapter 2
The Financial System
Return on Financial Assets
Bonds
Debentures
Interest
Debt
Preference share
Equity share Dividend
Financial Management: Principles and Practice
By G. Sudarsana Reddy
Himalaya Publishing House
Chapter 2
The Financial System
Functions of Financial Markets
Price information
Marketability/Liquidity
Reduction of Transaction cost
Promotes savings and investments
Financial Management: Principles and Practice
By G. Sudarsana Reddy
Himalaya Publishing House
Chapter 2
The Financial System
Distinguish between Money Market and
Capital Market
Points of Difference Money Market Capital Market
1.Maturity of Funds Less than one year Above one year
2.Instruments Call Money market, Treasury Bills Equity Shares, preference
(TBs) Market, Commercial Bills (CBs) shares, debentures,
market, Commercial Papers (CPs) Government securities and
market, Certificate of Deposits (CDs), loans
Bankers Acceptances (Bas),
Repurchase Agreements (Repos),
Money Market Mutual Funds
(MMMF), etc.
3. Existence of Secondary No Yes
market
4. Place of Market No specific place Stock Exchanges
Financial Management: Principles and Practice
By G. Sudarsana Reddy
Himalaya Publishing House
Chapter 2
The Financial System
Financial Instruments
Securities issued to public to raise funds
Example
Equity Share
Reference Share
Debenturers
Commercial papers
Certificate of Deposits etc.,
Financial Management: Principles and Practice
By G. Sudarsana Reddy
Himalaya Publishing House
Chapter 2
The Financial System
Financial Intermediaries
FIs that act as bridge between savers and investors and provides
needed funds to investors
Example:
Banks
NBFCs
Financial Management: Principles and Practice
By G. Sudarsana Reddy
Himalaya Publishing House
Chapter 2
The Financial System
Structure of Indian Financial
Intermediaries
Structure of Financial
Intermediaries in India
RBI SEBI IRDA
Public and Pvt.
Commercial
Banks
Mutual Funds Private Sector
Insurance
All India Companies
Development
Banks
Specialised
Financial
Institutions Exim
Bank, IFCI Venture Capital Public Sector
Funds Insurance
Companies
Refinance
Institutions
NABARD, NHB
NBFCs
Financial Management: Principles and Practice
By G. Sudarsana Reddy
Himalaya Publishing House
Chapter 2
The Financial System
Regulatory Institutions
RBI
SEBI
IRDA
NABARD
NHB
Financial Management: Principles and Practice
By G. Sudarsana Reddy
Himalaya Publishing House
Chapter 2
The Financial System
Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
Objectives
The objectives of establishment (Central Bank) of RBI are to:
Maintain the internal value of the nations currency;
Preserve the external value of the currency;
Secure reasonable price stability; and
Promote economic growth through increasing employment, output and real income.
Functions
The functions of RBI may be classified into two categories:
a) Traditional functions, and b) Developmental functions
a) Traditional Functions:
RBI acts as a lender of last resort;
It acts as a banker to banks;
It issues currency and operates the clearing system for banks;
It supervises the operations of credit institutions;
Financial Management: Principles and Practice
By G. Sudarsana Reddy
Himalaya Publishing House
Chapter 2
The Financial System
RBI Contd..
It acts as the custodian of the foreign reserves;
It formulates and implements monetary and credit policies;
It moderates the fluctuations in the exchange value of the rupee.
b) Developmental Functions:
The prime developmental function is to integrate the unorganized
financial sector with the organized financial sector;
It encourages opening of semi-urban and rural branches;
It provides education and training to banking personnel of commercial
and co-operative banks;
It influences the allocation of credit;
It promotes the collection pooling and dissemination of credit
information among banks;
It promotes the establishment of new institutions.
Financial Management: Principles and Practice
By G. Sudarsana Reddy
Himalaya Publishing House
Chapter 2
The Financial System
Securities Exchange Board of India (SEBI)
Objectives
The SEBI has been entrusted with both the regulatory and
developmental functions.
The following are the objectives of SEBI:
Investor protection with a view to get steady flow of savings into capital
market;
Ensuring fair practices by the issues of securities by which corporations
can raise resources of least cost;
Promotion of efficient services by brokers, merchant bankers, and other
intermediaries with a view to make them competitive and professional;
Development and regulation of securities market.
Financial Management: Principles and Practice
By G. Sudarsana Reddy
Himalaya Publishing House
Chapter 2
The Financial System
SEBI Contd..
Functions
a) Regulatory Functions
Registration and Regulation of capital market
intermediaries (Brokers, sub-brokers, and other players in
the market);
Register and regulate the working of venture capital
funds and Collective Investment Schemes including
mutual funds;
Regulate the business in Stock Exchanges and any other
securities market;
Promoting and regulating Self Regulatory Organisations
(SRO);
Prohibition of all fraudulent and unfair trade practices
relating to securities market;
Prohibition of insider trading and takeover bids and
imposing penalties for such practices;
Financial Management: Principles and Practice
By G. Sudarsana Reddy
Himalaya Publishing House
Chapter 2
The Financial System
SEBI Contd..
Registering and regulating the working of depositors,
custodians of securities, FIIs, credit rating agencies;
Regulating substantial acquisition of shares and takeover
of companies.
Development Function of SEBI is to promote investors
education, training intermediaries and conduct research
and publish information
b) Developmental Functions
Promote investors education;
Training of intermediaries;
Promotion of fair practices and code of conduct for all
SROs
Conduct research and publishing information useful to all
market participants.
Financial Management: Principles and Practice
By G. Sudarsana Reddy
Himalaya Publishing House
Chapter 2
The Financial System
Insurance Regulatory
Functions Development Authority
To exercise all powers and functions of controller of insurance;
Protection of the interests of the policyholders;
To issue, renew, modify, withdraw or suspend certification of registration;
To specify requisite qualifications and training for insurance intermediaries and agents;
To promote and regulate professional organisations connected with insurance;
To conduct inspection / investigations etc.;
To regulate investment of funds and margins of solvency;
To prescribe method of insurance accounting;
To adjudication upon disputes;
To conduct inspection and audit of insurers, intermediaries and other organisations
concerned with insurance.
Financial Management: Principles and Practice
By G. Sudarsana Reddy
Himalaya Publishing House
You might also like
- 99 Minute Millionaire - The Simp - Scott Alan Turner PDFDocument576 pages99 Minute Millionaire - The Simp - Scott Alan Turner PDFhasitha100% (2)
- How a Financial System Works to Facilitate Economic GrowthDocument25 pagesHow a Financial System Works to Facilitate Economic GrowthArpitNo ratings yet
- Notes On Introduction To Financial ServicesDocument18 pagesNotes On Introduction To Financial ServicesKirti Giyamalani100% (1)
- Variable - Online Mock ExamDocument11 pagesVariable - Online Mock ExamMitziRawrrNo ratings yet
- Memorial For Appellants 2Document35 pagesMemorial For Appellants 2Faraz Ali100% (4)
- Financial Services CPC6A Modules SummaryDocument82 pagesFinancial Services CPC6A Modules Summaryjeganrajraj100% (1)
- Printicomm's Proposed Acquisition of Digitech - Negotiating Price and Form of PaymentDocument103 pagesPrinticomm's Proposed Acquisition of Digitech - Negotiating Price and Form of PaymentKunal MehtaNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Analysis - Economic AnalysisDocument15 pagesFundamental Analysis - Economic AnalysisVaidyanathan RavichandranNo ratings yet
- Nicholas Sleep Final Collection of Nomad LettersDocument245 pagesNicholas Sleep Final Collection of Nomad Letterssean75% (4)
- Fundamentals of Financial Management Lecture Notes 21mar2021Document311 pagesFundamentals of Financial Management Lecture Notes 21mar2021Ruchita SinghalNo ratings yet
- Types of Law: Municipal, International, Procedural & SubstantiveDocument13 pagesTypes of Law: Municipal, International, Procedural & SubstantiveDevansh DubeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Anchoring BiasDocument18 pagesChapter 6 - Anchoring BiasNehal NabilNo ratings yet
- FIN - Chapter 6 - Cost of Capital - PDFDocument14 pagesFIN - Chapter 6 - Cost of Capital - PDFUtpal BaruaNo ratings yet
- Business FinanceDocument18 pagesBusiness FinanceAnnaNo ratings yet
- Lect 16123Document4 pagesLect 16123filmon dissanNo ratings yet
- CLASS NOTES - Sudeshna DuttaDocument97 pagesCLASS NOTES - Sudeshna DuttaBikash Kumar DashNo ratings yet
- CHP 1 Intro To FS TextbkDocument31 pagesCHP 1 Intro To FS TextbkVenom BhaiyaNo ratings yet
- Indian Financial System: DCOM304/DCOM503Document318 pagesIndian Financial System: DCOM304/DCOM503Bhavana MurthyNo ratings yet
- MFS Master of Business Administration Financial Management SpecializationDocument3 pagesMFS Master of Business Administration Financial Management SpecializationabhanidharaNo ratings yet
- Indian Financial SystemDocument260 pagesIndian Financial SystemRamya Gowda0% (1)
- Indian Financial SystemDocument24 pagesIndian Financial SystemsarthakNo ratings yet
- Session 3-4Document43 pagesSession 3-4jaitik nagpalNo ratings yet
- Department of Finance and Accounting: IBS, IFHE, HyderabadDocument54 pagesDepartment of Finance and Accounting: IBS, IFHE, HyderabadRUTHVIK NETHANo ratings yet
- SYBCom - Financial Services and Production Management - Module 2Document26 pagesSYBCom - Financial Services and Production Management - Module 2Yash SuranaNo ratings yet
- Merchant Banking and Financial ServicesDocument16 pagesMerchant Banking and Financial ServicesAaziya ANo ratings yet
- Introduction To Accounting: Caec 1 & 2: Financial Accounting and ReportingDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Accounting: Caec 1 & 2: Financial Accounting and ReportingKlucifer XinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial Management 2Document11 pagesIntroduction To Financial Management 2Jiro SukehiroNo ratings yet
- Session 1Document62 pagesSession 1Sam NaikNo ratings yet
- SEMESTER 2: MBA 2021-23: Course: Indian Financial System and Financial Markets (Ifsfm)Document53 pagesSEMESTER 2: MBA 2021-23: Course: Indian Financial System and Financial Markets (Ifsfm)Cally CallisterNo ratings yet
- Financial System and Markets OverviewDocument19 pagesFinancial System and Markets OverviewSachin KhoriaNo ratings yet
- Bharathidasan University MBA Elective Course Merchant BankingDocument257 pagesBharathidasan University MBA Elective Course Merchant BankingParivel ParivelNo ratings yet
- Indian Financial SystemDocument2 pagesIndian Financial SystemAbdul Manaf SNo ratings yet
- The Financial System: Centre For Financial Management, BangaloreDocument26 pagesThe Financial System: Centre For Financial Management, BangaloreRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Intel College: Course Name: Business Finance and EconomicsDocument2 pagesIntel College: Course Name: Business Finance and EconomicsRocky Kaur100% (1)
- Financial Inclusion: A Indian PerspectiveDocument14 pagesFinancial Inclusion: A Indian Perspective9415351296No ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To Financial SystemDocument25 pages1 Introduction To Financial SystemAnil KingNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2.1.1 Indian Financial System - An OverviewDocument22 pagesLecture 2.1.1 Indian Financial System - An OverviewDeepansh SharmaNo ratings yet
- 1 SEM BCOM - Indian Financial SystemDocument35 pages1 SEM BCOM - Indian Financial SystemShambhavi JNo ratings yet
- 1 SEM BCOM - Indian Financial System PDFDocument35 pages1 SEM BCOM - Indian Financial System PDFLohithashva Nanjesh Gowda100% (5)
- 1 SEM BCOM - Indian Financial System PDFDocument35 pages1 SEM BCOM - Indian Financial System PDFShambhavi JNo ratings yet
- Financial Management Instruction MapDocument7 pagesFinancial Management Instruction MapCruz AlmigthaNo ratings yet
- Post-Graduate Diploma in Management (Banking & Financial Services) 2021-23 Term IDocument5 pagesPost-Graduate Diploma in Management (Banking & Financial Services) 2021-23 Term IAbhinav MahajanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Research Methdology: Objective of The StudyDocument86 pagesChapter 1 - Research Methdology: Objective of The StudyHiren PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and Services (FMSDocument60 pagesFinancial Markets and Services (FMSPrachi AsawaNo ratings yet
- Intro Mon Pol - Oct 19 ABRDocument150 pagesIntro Mon Pol - Oct 19 ABRSoumya JainNo ratings yet
- Gabaran Kimberly G. Bsma-3B: Investment Banks Spot MarketsDocument3 pagesGabaran Kimberly G. Bsma-3B: Investment Banks Spot MarketsKim GabaranNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Financial System: ObjectivesDocument19 pagesUnit 1 Financial System: ObjectivesSHYAM GOELNo ratings yet
- Finance Is A Bridge Between The Present & The FutureDocument10 pagesFinance Is A Bridge Between The Present & The FutureanuradhaNo ratings yet
- L-1Document15 pagesL-1vijayareddy112222No ratings yet
- Corporate Governance Rating and Its ImpactDocument10 pagesCorporate Governance Rating and Its ImpactBudhaditya ChakrbortyNo ratings yet
- Lunar International College School of Graduate Studies Masters of Business Administration (MBA)Document52 pagesLunar International College School of Graduate Studies Masters of Business Administration (MBA)Sintayehu MeseleNo ratings yet
- Evolution: - The Traditional Phase - The Transitional Phase - The Modern PhaseDocument19 pagesEvolution: - The Traditional Phase - The Transitional Phase - The Modern PhasevijayluckeyNo ratings yet
- Financial System - An OverviewDocument16 pagesFinancial System - An OverviewAamir Hamza MehediNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Indian Financial SystemDocument31 pagesUnit 1 - Indian Financial SystemPrasad IngoleNo ratings yet
- Cab PDFDocument35 pagesCab PDFhgcgfNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets & ServicesDocument32 pagesFinancial Markets & ServicesSam GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Financial Management: R.P. RustagiDocument16 pagesFundamentals of Financial Management: R.P. Rustagiimranrog11No ratings yet
- Financial System of IndianotesDocument60 pagesFinancial System of IndianoteshiteshNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and ServicesDocument3 pagesFinancial Markets and Serviceshussainmba30No ratings yet
- Finncial Markets and Services Course HandoutDocument6 pagesFinncial Markets and Services Course HandoutBasheer AcNo ratings yet
- Advanced Financial ManagementDocument15 pagesAdvanced Financial ManagementHIGGSBOSON304No ratings yet
- QUICK CapsuleDocument52 pagesQUICK CapsuleJatin GargNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and Institutions: Chapter-1Document54 pagesFinancial Markets and Institutions: Chapter-1Anubhuti BazazNo ratings yet
- Commerce and Modern Management Business Finance-Bca2101: Faculty of CourseDocument103 pagesCommerce and Modern Management Business Finance-Bca2101: Faculty of CoursemohamedNo ratings yet
- Marketing of Consumer Financial Products: Insights From Service MarketingFrom EverandMarketing of Consumer Financial Products: Insights From Service MarketingNo ratings yet
- T R A N S F O R M A T I O N: THREE DECADES OF INDIA’S FINANCIAL AND BANKING SECTOR REFORMS (1991–2021)From EverandT R A N S F O R M A T I O N: THREE DECADES OF INDIA’S FINANCIAL AND BANKING SECTOR REFORMS (1991–2021)No ratings yet
- Unlocking Financial Opportunities: A Comprehensive Guide on How to Establish Business CreditFrom EverandUnlocking Financial Opportunities: A Comprehensive Guide on How to Establish Business CreditNo ratings yet
- BR Sawhny 2017 Moot PropositionDocument5 pagesBR Sawhny 2017 Moot PropositionDevansh DubeyNo ratings yet
- Does Being "Master of The Roster" Mean That CJI Remains Unaccountable & Cannot Be Questioned - Justice AP Shah (Full Text of BG Verghese Memorial Lecture) - Live Law PDFDocument22 pagesDoes Being "Master of The Roster" Mean That CJI Remains Unaccountable & Cannot Be Questioned - Justice AP Shah (Full Text of BG Verghese Memorial Lecture) - Live Law PDFDevansh DubeyNo ratings yet
- Topic 4Document68 pagesTopic 4Devansh DubeyNo ratings yet
- Patna CaseDocument16 pagesPatna CaseDevansh Dubey100% (1)
- Immanuel KantDocument4 pagesImmanuel KantDevansh DubeyNo ratings yet
- 1813Document5 pages1813Devansh DubeyNo ratings yet
- Police Custody Guidelines to Prevent Torture/TITLEDocument14 pagesPolice Custody Guidelines to Prevent Torture/TITLEDevansh DubeyNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Natural Law TheoryDocument4 pagesContemporary Natural Law TheoryDevansh DubeyNo ratings yet
- Consumer Protection 2016 FADocument101 pagesConsumer Protection 2016 FADevansh DubeyNo ratings yet
- Sources of Law-PrecedentsDocument28 pagesSources of Law-PrecedentsDevansh DubeyNo ratings yet
- 5 (Recovered)Document20 pages5 (Recovered)Devansh DubeyNo ratings yet
- Cossijurah CasaeDocument15 pagesCossijurah CasaeDevansh Dubey0% (1)
- High Courts 1860Document62 pagesHigh Courts 1860Devansh Dubey0% (1)
- TORTSDocument21 pagesTORTSDevansh DubeyNo ratings yet
- Tribal Issues and Laws in IndiaDocument7 pagesTribal Issues and Laws in IndiaDevansh Dubey100% (1)
- Cyber Defamation Liabilities of Internet Service Providers Isps and IntermediaryDocument14 pagesCyber Defamation Liabilities of Internet Service Providers Isps and IntermediaryRaGa JoThiNo ratings yet
- CE-II Q. Key AnsDocument2 pagesCE-II Q. Key AnsDevansh DubeyNo ratings yet
- Case Study PsychologyDocument8 pagesCase Study PsychologyDevansh DubeyNo ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument16 pagesResearch PaperDevansh DubeyNo ratings yet
- Memorial Filed On Behalf of Respondent PDFDocument37 pagesMemorial Filed On Behalf of Respondent PDFjoy parimalaNo ratings yet
- Memorial Filed On Behalf of Petitioner PDFDocument36 pagesMemorial Filed On Behalf of Petitioner PDFKaran VyasNo ratings yet
- Memorial Filed On Behalf of Petitioner PDFDocument36 pagesMemorial Filed On Behalf of Petitioner PDFKaran VyasNo ratings yet
- MGT411 Midterm MCQ PDFDocument31 pagesMGT411 Midterm MCQ PDFJessica Chambers100% (2)
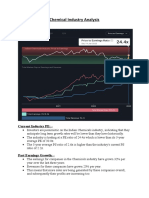
- Chemical Industry AnalysisDocument4 pagesChemical Industry AnalysisArmyboy 1804No ratings yet
- Question and Answer - 46Document30 pagesQuestion and Answer - 46acc-expertNo ratings yet
- Pepsi Multan Internship Report (Finance)Document39 pagesPepsi Multan Internship Report (Finance)Oye JanuNo ratings yet
- Buy-Back Process Under Companies Act & RulesDocument8 pagesBuy-Back Process Under Companies Act & Rulesdevendra bankarNo ratings yet
- Asset Master: Plan Summary (In PHP)Document15 pagesAsset Master: Plan Summary (In PHP)JULIUS TIBERIO100% (1)
- Interfor Corporation: Equity ResearchDocument6 pagesInterfor Corporation: Equity ResearchForexliveNo ratings yet
- MKT81752HL 02Document40 pagesMKT81752HL 020idmey4dNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 7 gearing risks shares margin calls futuresDocument2 pagesTutorial 7 gearing risks shares margin calls futuresmusuotaNo ratings yet
- Specimen For Qiuz & Assignment .........................................Document3 pagesSpecimen For Qiuz & Assignment .........................................Umair AmirNo ratings yet
- Practice8 10Document28 pagesPractice8 10mehdiNo ratings yet
- Security Market Indexes ExplainedDocument18 pagesSecurity Market Indexes ExplainedShihabHasanNo ratings yet
- NCFM Model Test PaperDocument36 pagesNCFM Model Test PaperSpl FriendsNo ratings yet
- Law NotesDocument19 pagesLaw NotesPranavNo ratings yet
- Santa Claus RallyDocument7 pagesSanta Claus Rallytanner3052No ratings yet
- Difference Between IPO and Secondary OfferingDocument2 pagesDifference Between IPO and Secondary OfferingUsman Khan100% (1)
- BALAKRISHNADocument8 pagesBALAKRISHNAbalki123No ratings yet
- Itaú Latam Big Book 2012Document247 pagesItaú Latam Big Book 2012Fernando ParaguassuNo ratings yet
- Account: IndividualDocument24 pagesAccount: Individualgh1482463No ratings yet
- Impairing The Microsoft - Nokia PairingDocument54 pagesImpairing The Microsoft - Nokia Pairingjk kumarNo ratings yet
- Investment Option Through BajajDocument57 pagesInvestment Option Through BajajSiddiqua AnsariNo ratings yet
- Thesis On Nepal Stock ExchangeDocument7 pagesThesis On Nepal Stock Exchangetmexyhikd100% (2)
- ON Financial Analysis of BSNL: A Project ReportDocument51 pagesON Financial Analysis of BSNL: A Project ReportNar CosNo ratings yet