Professional Documents
Culture Documents
9akk105151d0109 - Process Mapping
Uploaded by
Fran JimenezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
9akk105151d0109 - Process Mapping
Uploaded by
Fran JimenezCopyright:
Available Formats
ABB Basic Quality Tools Series
Process Mapping
Document the sequence of events in any process for
a product or service.
ABB Group 9AKK105151D0109
15 July 2010, Slide 1
Process Mapping - Content
What is it for?
Visually documenting the sequence of events required to produce an No judgement or
criticism
Quantity more
specific outcome. than quality
Let ideas follow
one another
Ensures there is a thorough understanding of the process and Combine and
modify ideas
activities.
Where could I use it?
To document and standardize a process.
Use it in teams, to create shared understanding and build teamwork.
How do I use it?
Identify the output generated by the process.
Determine the level of detail for mapping of activity.
Follow the inputs as they are processed, recording each activity.
Identify activities that generate COPQ or waste.
Verify accuracy of map with individuals involved in the process.
Identify opportunities for removal of waste or actions which increase
variation in the outputs.
Risks and how to avoid them
Example
ABB Group 9AKK105151D0109
15 July 2010, Slide 2
Process Mapping - What is it for?
Uses of this tool:
Process mapping is used to create a visual diagram of the sequential flow of material and manpower
to produce a specific output.
Associated with this activity is the establishment of a standard method for a process.
Expected Benefits:
Each step in the process is identified and agreed to by the improvement team, this promotes a
consistent understanding of the current situation.
Actions that create or support waste, COPQ, or non-value adding activity can be identified and
targeted for improvement.
ABB Group 9AKK105151D0109
15 July 2010, Slide 3
Process Mapping - Where could I use it?
Background: Uses:
Many activities are not defined or have a Document the flow of material in the creation of a
standard way of working. product.
Where multiple people perform the same Understand the sequence of actions taken in a
task, there may be variations in how the task process.
is performed.
Communicate the steps to be followed in the
Process maps can be scaled to provide the execution of a procedure.
level of detail necessary to analyze the
Evaluate an activity for waste or COPQ.
process and provide an understanding of the
activities. Document the future method for a process
following an improvement project.
ABB Group 9AKK105151D0109
15 July 2010, Slide 4
Process Mapping - How do I use it?
Procedure and Guidance Notes:
Identify the outcome of the process. Consider the extent of your ability to change a
Define the
Determine the starting point, i.e. what are the inputs to the process. process and keep the mapping within your
process teams scope of authority.
Decide if supporting activities are to be included in the map.
boundaries
Understand purpose of the map. Some map templates require extensive
Determine the Select template that supports recording and display of activities and collection of data and may not be a good use of
type of map data. your teams time and resources.
Walk the process interviewing those involved in the activities. Information that you record in this step will be
Observe and
Record the information that you observe times, quantities, used to create the diagram that represents the
record the equipment, physical layout, personnel, quality, procedures, etc. process, take care to fully understand what is
process Understand the inputs, outputs and controls for each step. happening.
Using the template and symbols, transfer the information that you This step may take more than one iteration as
Diagram the
collected in the observations onto the process map. you refine the picture of the activities and their
process on the Create linkages between activities to show relationships. relationships.
map template
Discuss the map with personnel involved in the process, identify any Accuracy to the actual way of working is
areas that do not reflect the actual way work is performed. important in understanding sources of COPQ,
Verify the map Walk the process using the new map to validate that it accurately waste and variation. Take care not to assume
represents the actions. that actions are taken or procedures are true.
Working with the diagram, look for areas where the work flow is not Inventory can be a sign of inefficiency, look for
Identify areas of smooth or there are unclear expectations. waste in all forms. Quality levels will also reflect
opportunity Identify situations where agreement was not reached on how the work situations where the requirements are not
was performed. clearly understood.
Working with the team, create a map of the desired process. Remove This may require the assistance of process
Create a to-be activities that do not add value or create variation in the process. experts. Use any resources available to the
map Use the to-be map as the basis for standardizing the work in a more team to eliminate wasteful activities.
efficient process.
ABB Group 9AKK105151D0109
15 July 2010, Slide 5
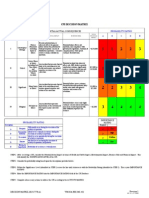
Process Mapping - Risks and how to avoid them
Risks : Steps to avoid them :
Too high level for adequate understanding of the process. Decide in the beginning the level of detail necessary to
provide data for your improvement project.
Too much detail is trying to be recorded and therefore it
increases the time and effort to document the process. Evaluate the different types of maps and which will best
meet your needs: Value Stream Maps, Swim-lane map,
Type of map can impact the ease of
Flow chart, Cross-functional map
evaluation/understanding of the process.
Involve personnel who are performing the work in the
Map does not portray the actual current situation.
creation of the map. Validate the accuracy by walking
Activities are not correctly identified, leading to wrong the process and checking that all is recorded.
conclusions.
Use the appropriate symbols for the style of map
chosen. Verify that you understand the reason for
activities before you assign a work classification.
ABB Group 9AKK105151D0109
15 July 2010, Slide 6
Process Mapping - Example
7. Create To-Be Map
1. Define Process Boundaries
Construction Process from
Estimate to Invoice
2. Select type of Process Map
Use Swim lane to which
departments are involved
6. Identify Opportunities
3. Observe, Record Process
5. Verify the Map
4. Diagram the Process
ABB Group 9AKK105151D0109
15 July 2010, Slide 7
You might also like
- Operational Readiness Review A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandOperational Readiness Review A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- Project Quality Management A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionFrom EverandProject Quality Management A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNo ratings yet
- Sipoc: Document The Top Level Process Steps in Any Process For A Product or ServiceDocument7 pagesSipoc: Document The Top Level Process Steps in Any Process For A Product or ServicetonyNo ratings yet
- BP Mapping I WorkshopDocument29 pagesBP Mapping I WorkshopJohn RockNo ratings yet
- Process Mapping (A Case Study) : Dechen Angmo (17042047) & Santosh K Singh (17042048)Document11 pagesProcess Mapping (A Case Study) : Dechen Angmo (17042047) & Santosh K Singh (17042048)UditChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Best Practice A Guide To Process Mapping1 PDFDocument4 pagesBest Practice A Guide To Process Mapping1 PDFlezazaNo ratings yet
- Analyze causes and effects with Fishbone diagramsDocument3 pagesAnalyze causes and effects with Fishbone diagramsDoren Joy BatucanNo ratings yet
- Process and Procedure Documentation OverviewDocument14 pagesProcess and Procedure Documentation OverviewmeddouNo ratings yet
- SIPOC2Document27 pagesSIPOC2karen dejoNo ratings yet
- Business Process Re EngineeringDocument65 pagesBusiness Process Re EngineeringjeetpajwaniNo ratings yet
- Test Automation Framework IntroductionDocument11 pagesTest Automation Framework Introductionravikumar4itNo ratings yet
- 04 The Six Sigma MethodologyDocument53 pages04 The Six Sigma Methodologychteo1976No ratings yet
- Stage: Business Analysis and Acceptance User Acceptance Test (UAT) PlanDocument7 pagesStage: Business Analysis and Acceptance User Acceptance Test (UAT) PlanAkashah ArshadNo ratings yet
- Post Implementation Reviews Made SimpleDocument17 pagesPost Implementation Reviews Made SimpleNaushad SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- BPM Presentation.Document21 pagesBPM Presentation.Qurat Ul Ain RiazNo ratings yet
- Benchmarking Activity - pptx1Document10 pagesBenchmarking Activity - pptx1Mary Rose Vilchez100% (1)
- Impact Analysis Checklist For Requirements ChangesDocument3 pagesImpact Analysis Checklist For Requirements Changessumitkalra3962100% (3)
- 7 Steps To Business Process MappingDocument1 page7 Steps To Business Process MappingCreative Technology and DesignNo ratings yet
- Data Quality: An Introduction To The Role and Value of Data Quality in OrganisationsDocument47 pagesData Quality: An Introduction To The Role and Value of Data Quality in OrganisationsSam 1980No ratings yet
- Software Test EstimationDocument15 pagesSoftware Test EstimationJatinNo ratings yet
- Toyota's 5-Step Process for Continuous Improvement ImplementationDocument6 pagesToyota's 5-Step Process for Continuous Improvement Implementationdbryant1435100% (1)
- KSI Project Charter Outline and InstructionsDocument11 pagesKSI Project Charter Outline and InstructionsValentyne KwambokaNo ratings yet
- Change Management Strategy TemplateDocument5 pagesChange Management Strategy TemplateAkram UddinNo ratings yet
- Core Banking System Implementation PropoDocument8 pagesCore Banking System Implementation PropoIsmael GirmaNo ratings yet
- Asset-V1 TUMx+QPLS1x+2T2018+type@asset+block@SixSigma Process-Improvement Methods ToolsDocument85 pagesAsset-V1 TUMx+QPLS1x+2T2018+type@asset+block@SixSigma Process-Improvement Methods ToolsAmar MohammedNo ratings yet
- 10 Quality Function DeploymentDocument33 pages10 Quality Function DeploymentRian JanuarsyahNo ratings yet
- Typical Elements in A Project CharterDocument28 pagesTypical Elements in A Project CharterKGrace Besa-angNo ratings yet
- Controlling and Quality ManagementDocument18 pagesControlling and Quality ManagementNisma Shrestha100% (1)
- 7 Best Practices in Business Process ManagementDocument11 pages7 Best Practices in Business Process ManagementSrikanth SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Customer Complaint Management SystemsDocument31 pagesCustomer Complaint Management SystemsBains M CollinzNo ratings yet
- Quality Management System (QMS)Document14 pagesQuality Management System (QMS)Lina VelásquezNo ratings yet
- Project Charter Document: Format For System/Process Improvement or Design ProjectDocument2 pagesProject Charter Document: Format For System/Process Improvement or Design ProjectmarouaNo ratings yet
- Business Process Models ReviewDocument16 pagesBusiness Process Models ReviewPavan Kumar DamarajuNo ratings yet
- ProArch Energy & UtilitiesDocument20 pagesProArch Energy & Utilitiesdheer4dheerNo ratings yet
- (WEEK 2) Process Identification 1Document36 pages(WEEK 2) Process Identification 1AVICENA NAUFALDONo ratings yet
- Quality ManualDocument132 pagesQuality ManualstacayNo ratings yet
- Basic Process Improvement TrainingDocument116 pagesBasic Process Improvement Trainingfiesta22No ratings yet
- SipocDocument18 pagesSipocJunior GiganteNo ratings yet
- 2.06 SIPOC DiagramDocument4 pages2.06 SIPOC DiagramJulioRomeroNo ratings yet
- Business Process Re-Engineering & Government Process Re-EngineeringDocument42 pagesBusiness Process Re-Engineering & Government Process Re-Engineeringrocky bayasNo ratings yet
- Computing PolicyDocument12 pagesComputing Policyaami6No ratings yet
- Test PlanDocument10 pagesTest PlanrajeevNo ratings yet
- Process Matching Module 1Document30 pagesProcess Matching Module 1Thanh Vũ Nguyễn100% (1)
- Test Automation Framework & Design For XXXXX Project: Author: XXXXXXDocument14 pagesTest Automation Framework & Design For XXXXX Project: Author: XXXXXXqtpencyclopediaNo ratings yet
- Control Charts & GO NO GO GageDocument6 pagesControl Charts & GO NO GO GageRishi AndicoNo ratings yet
- A Step by Step Guide To PMP CertifcationDocument14 pagesA Step by Step Guide To PMP CertifcationAfolayan Iyanuoluwa JoshuaNo ratings yet
- 100 years of Quality management evolutionDocument1 page100 years of Quality management evolutionGenGyan Global Business Solutions Pvt LtdNo ratings yet
- What Is Business Process MappingDocument8 pagesWhat Is Business Process Mappingsheebakbs5144No ratings yet
- LEAN Continuous Improvement KaizenDocument4 pagesLEAN Continuous Improvement KaizenHafis BonterNo ratings yet
- Business Process Lifecycle ManagementDocument12 pagesBusiness Process Lifecycle ManagementOrlando100% (1)
- Integration (PPT) - Chapter 4 PMBOKDocument13 pagesIntegration (PPT) - Chapter 4 PMBOKEric GunnerNo ratings yet
- Quality: Prince 2 Approach To QualityDocument3 pagesQuality: Prince 2 Approach To Qualityquree25No ratings yet
- Vendor EvaluationDocument20 pagesVendor EvaluationRahul pawadeNo ratings yet
- Inbound Storage Tank Management Process DiagramDocument1 pageInbound Storage Tank Management Process DiagramEddy ChenNo ratings yet
- Risk Analysis Method: FMEA/FMECA in The OrganizationsDocument9 pagesRisk Analysis Method: FMEA/FMECA in The OrganizationsrusitadianNo ratings yet
- Performance Improvement in Hospitals and Health Systems Managing Analytics and Quality in Healthcare (2nd Edition), Cap 5Document32 pagesPerformance Improvement in Hospitals and Health Systems Managing Analytics and Quality in Healthcare (2nd Edition), Cap 5Daniela LópezNo ratings yet
- PMP QuickRef by Robert PerrineDocument16 pagesPMP QuickRef by Robert Perrinereddysham4uNo ratings yet
- 7 How To Write A Report and Presentation v3Document7 pages7 How To Write A Report and Presentation v3Jeremiah HiiNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Approaches For Different Production MethodsDocument14 pagesMaintenance Approaches For Different Production MethodsGerardo MartinNo ratings yet
- Operational Excellence InsightsDocument45 pagesOperational Excellence InsightsFran JimenezNo ratings yet
- OEMS OverviewDocument20 pagesOEMS OverviewEn NdyNo ratings yet
- Reliability and Maintenance (RAM) : The Path To World-Class PerformanceDocument27 pagesReliability and Maintenance (RAM) : The Path To World-Class PerformanceFran JimenezNo ratings yet
- TPM ConceptDocument18 pagesTPM ConceptFran JimenezNo ratings yet
- Fast Guide To Oee PDFDocument27 pagesFast Guide To Oee PDFAtakan TunaliNo ratings yet
- The Next Generation of Internal Auditors The Fight For TalentDocument38 pagesThe Next Generation of Internal Auditors The Fight For TalentFran JimenezNo ratings yet
- The Complete Guide to Simple OEE MeasurementDocument26 pagesThe Complete Guide to Simple OEE MeasurementWan Sek Choon100% (2)
- Barriers in TPM Implementation in Industries PDFDocument6 pagesBarriers in TPM Implementation in Industries PDFFran JimenezNo ratings yet
- Learning by DoingDocument39 pagesLearning by DoingFran JimenezNo ratings yet
- 8th Maintenance Forum Presentation FinalDocument31 pages8th Maintenance Forum Presentation FinalFran JimenezNo ratings yet
- Barriers in TPM Implementation in Industries PDFDocument6 pagesBarriers in TPM Implementation in Industries PDFFran JimenezNo ratings yet
- Jidoka ToyotaDocument20 pagesJidoka Toyotajesham124100% (1)
- ABB Reliability FingerprintDocument17 pagesABB Reliability FingerprintFran JimenezNo ratings yet
- El Rol Del Planeador de MantenimientoDocument2 pagesEl Rol Del Planeador de MantenimientoFran JimenezNo ratings yet
- FMC Screw ConveyorsDocument101 pagesFMC Screw ConveyorsOscar Alvitez DominguezNo ratings yet
- Introduction to TPM - Total Productive MaintenanceDocument31 pagesIntroduction to TPM - Total Productive MaintenanceFran JimenezNo ratings yet
- CoalDocument24 pagesCoalFran JimenezNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Screw ConveyorDocument5 pagesTroubleshooting Screw ConveyorFran JimenezNo ratings yet
- Lubrication PDFDocument123 pagesLubrication PDFFran JimenezNo ratings yet
- 4 Phases of Reliability Centered LubricationDocument4 pages4 Phases of Reliability Centered LubricationFran JimenezNo ratings yet
- Goodman Screw Conveyor PDFDocument9 pagesGoodman Screw Conveyor PDFFran JimenezNo ratings yet
- Article Cement Plant Modernization GCM 12-2016 2Document4 pagesArticle Cement Plant Modernization GCM 12-2016 2Muhammad RomzuddinNo ratings yet
- Texto MineriaDocument6 pagesTexto MineriaNoir LagNo ratings yet
- Cement Grinding OPtimizationDocument13 pagesCement Grinding OPtimizationTgemunuNo ratings yet
- Cement Grinding OptimizationDocument9 pagesCement Grinding OptimizationFran JimenezNo ratings yet
- Cement Grinding Process SimulationDocument13 pagesCement Grinding Process SimulationKalindaMadusankaDasanayakaNo ratings yet
- Ball Mill OptimizationDocument7 pagesBall Mill OptimizationWael Fanous100% (1)
- CementDocument4 pagesCementFran JimenezNo ratings yet
- SYS600 - Visual SCIL Application DesignDocument144 pagesSYS600 - Visual SCIL Application DesignDang JinlongNo ratings yet
- The Stolen Bacillus - HG WellsDocument6 pagesThe Stolen Bacillus - HG Wells1mad.cheshire.cat1No ratings yet
- Inner WordDocument7 pagesInner WordMico SavicNo ratings yet
- Design Theory: Boo Virk Simon Andrews Boo - Virk@babraham - Ac.uk Simon - Andrews@babraham - Ac.ukDocument33 pagesDesign Theory: Boo Virk Simon Andrews Boo - Virk@babraham - Ac.uk Simon - Andrews@babraham - Ac.ukuzma munirNo ratings yet
- RBI and Maintenance For RCC Structure SeminarDocument4 pagesRBI and Maintenance For RCC Structure SeminarcoxshulerNo ratings yet
- Roadmap For SSC CGLDocument11 pagesRoadmap For SSC CGLibt seoNo ratings yet
- Dswd-As-Gf-018 - Rev 03 - Records Disposal RequestDocument1 pageDswd-As-Gf-018 - Rev 03 - Records Disposal RequestKim Mark C ParaneNo ratings yet
- Blank Character StatsDocument19 pagesBlank Character Stats0114paolNo ratings yet
- Tutor Marked Assignment (TMA) SR Secondary 2018 19Document98 pagesTutor Marked Assignment (TMA) SR Secondary 2018 19kanna2750% (1)
- Propaganda and Counterpropaganda in Film, 1933-1945: Retrospective of The 1972 ViennaleDocument16 pagesPropaganda and Counterpropaganda in Film, 1933-1945: Retrospective of The 1972 ViennaleDanWDurningNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Prefixes ExercisesDocument2 pagesVocabulary Prefixes ExercisesMarina García CarrascoNo ratings yet
- Outgoing Call Block BroadcastReceiver ExampleDocument3 pagesOutgoing Call Block BroadcastReceiver ExampleZainUlAbidinNo ratings yet
- Two Monuments by C Mann 1493 Copy - PDF - OcredDocument23 pagesTwo Monuments by C Mann 1493 Copy - PDF - OcredStephania FrancoNo ratings yet
- Philippine Electronics & Communication Institute of TechnologyDocument3 pagesPhilippine Electronics & Communication Institute of TechnologyAngela MontonNo ratings yet
- ArrayList QuestionsDocument3 pagesArrayList QuestionsHUCHU PUCHUNo ratings yet
- Grillage Method Applied to the Planning of Ship Docking 150-157 - JAROE - 2016-017 - JangHyunLee - - 최종Document8 pagesGrillage Method Applied to the Planning of Ship Docking 150-157 - JAROE - 2016-017 - JangHyunLee - - 최종tyuNo ratings yet
- Decision MatrixDocument12 pagesDecision Matrixrdos14No ratings yet
- Watershed Management A Case Study of Madgyal Village IJERTV2IS70558Document5 pagesWatershed Management A Case Study of Madgyal Village IJERTV2IS70558SharadNo ratings yet
- Digital Logic Design: Dr. Oliver FaustDocument16 pagesDigital Logic Design: Dr. Oliver FaustAtifMinhasNo ratings yet
- Capitalism Communism Socialism DebateDocument28 pagesCapitalism Communism Socialism DebateMr. Graham Long100% (1)
- HTTP - WWW - Aphref.aph - Gov.au - House - Committee - Pjcis - nsl2012 - Additional - Discussion Paper PDFDocument61 pagesHTTP - WWW - Aphref.aph - Gov.au - House - Committee - Pjcis - nsl2012 - Additional - Discussion Paper PDFZainul Fikri ZulfikarNo ratings yet
- Boston Qualitative Scoring System for Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure Effective for Detecting Cognitive Impairment in Parkinson's DiseaseDocument9 pagesBoston Qualitative Scoring System for Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure Effective for Detecting Cognitive Impairment in Parkinson's DiseaseJuanNo ratings yet
- Moment Baseplate DesignDocument10 pagesMoment Baseplate DesignNeil JonesNo ratings yet
- Garden Silk Mills Ltd.Document115 pagesGarden Silk Mills Ltd.jkpatel221No ratings yet
- Saline Water Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers: A Case Study From BangladeshDocument6 pagesSaline Water Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers: A Case Study From BangladeshIOSRJEN : hard copy, certificates, Call for Papers 2013, publishing of journalNo ratings yet
- Platon Si Academia Veche de ZellerDocument680 pagesPlaton Si Academia Veche de ZellerDan BrizaNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Water Resources Projects - Preparation of DPRDocument148 pagesInvestigation of Water Resources Projects - Preparation of DPRN.J. PatelNo ratings yet
- Rhodium Catalyzed Hydroformylation - CH 07Document14 pagesRhodium Catalyzed Hydroformylation - CH 07maildesantiagoNo ratings yet
- WP 2 Final Draft 1Document5 pagesWP 2 Final Draft 1api-457082236No ratings yet
- Backup 2Document59 pagesBackup 2Fabiola Tineo GamarraNo ratings yet