Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Evolution of HRM
Uploaded by
ymeenamcaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Evolution of HRM
Uploaded by
ymeenamcaCopyright:
Available Formats
EVOLUTION OF HRM
There is no magic in the success of companies. The secret of their success is simply the way that treat their employees
Akio Morita Founder, Sony Corporation
OF HRM EVOLUTION
HR HISTORY
Hiring & Firing Unions emerged: Labour relations specialists Welfare Subspecialties as :
Staffing /Training/Compensation/Appraisal System
Late 70s HR professionals mastered the activities of
Staffing, Development, Appraisals & Rewards.
By 1980s organizational design and communication, got added
OF HRM EVOLUTION
HOW IS PM DIFFERENT FROM HRM
Personnel Management and HRM differ in scope
PM is viewed as a tool. The behavior of which could be manipulated for the benefit of the organization and replaced when it is worn out. It was a routine activity meant to hire new employees and to maintain personal records. It was never considered as a strategic management of business.
HRM would view people as an important source or asset to be used for the benefit of the organization , employees and society.
OF HRM
HOW IS PM DIFFERENT FROM HRM
PERSONNEL FUNCTION Maintenance oriented Orientation An independent function with independent subfunctions Reactive, responding to events when they occur Exclusive responsibility of personnel department Emphasis on monetary rewards Improved performance is a result of improved satisfaction & morale Tries to improve the efficiency of people & administration Consists of inter-dependant parts Structure Philosophy Responsibility Motivators Outcomes Aims Emphasis on higher order needs eg. Empowering people Better use of human resources leads to improved satisfaction & morale Tries to develop the organisation as a whole & its culture Proactive, trying to anticipate & get ready with appropriate responses Responsibility of all managers in the organisaiton POINTS OF DISCUSSION Development oriented HRM
EVOLUTION
OF HRM
ESSENTIALS IN THE DEFINITION OF HRM
It is people who staff the organization and manage organizations
HRM involves application of management functions and principals. Functions and principals are applied to acquisitioning, developing , maintaining and remunerating employees Decisions on different aspects of employees must be consistent with other decisions on HR Decisions made must influence the effectiveness of the organization, i.e. it should result in betterment of services to customers or productivity
EVOLUTION
OF HRM EVOLUTION
DEFINITIONS OF HRM
HRM is a series of integrated decisions that form the employment relationship; their quality contributes to the ability of the organization and the employees to achieve their objective.
HRM is concerned with the people dimension in management. Since every organization is made up of people , acquiring their services, developing their skills , motivating them to higher levels of performance and ensuring that they continue to maintain their commitments to the organization are essential to achieving organizational objectives.
EVOLUTION
OF HRM
DEFINITIONS OF HRM
HRM is management in planning, organizing, directing and controlling of the procurement, development, compensation, integration, maintenance and separation of human resources to the end that individual, organizational and social responsibilities are accomplished.
OF HRM EVOLUTION
MANAGERIAL FUNCTIONS OF HRM
Planning: Determination in advance of a personal program that will contribute to goals established for the enterprise Organising : This is required to carry out the plans. Designing the structure of relationships among jobs , personnel and physical factors. Directing : Before the action is started direction is necessary; this may be in the form of motivation actuation or command .This is to get people to work willingly and effectively Controlling: Observation of action and its comparison with plans and correction of any deviation that may occur at any time.
OF HRM EVOLUTION
OPERATIVE FUNCTIONS OF HRM
Procurement: Obtaining proper kind and number of personnel necessary to accomplish organizational goals Development: Increasing the skill through training that is necessary for proper job performance Compensation: Adequate and equitable remuneration of personnel for their contribution to organization objectives. Integration : It is concerned with a reasonable reconciliation of individual , societal and organizational interests . Maintenance: Maintenance is concerned with the continuation of this state , this is heavily effected by communication with employees. Separation : Separations and return of that person to society. Could be retirement , lay off , out-placements and discharge
OF HRM EVOLUTION
THE HUMAN RESOURCE CYCLE
HRM Concept Michigan School
Rewards
Selection
Performance Management
Performance
Development
1. Selection: 2. Appraisal: 3. Rewards:
Matching available human resources to jobs Performance management It must reward short as well as long-term achievements Developing high quality employees
4. Development:
OF HRM EVOLUTION
THE HARVARD FRAMEWORK FOR HRM
Stakeholder Interests Shareholders Management Employee groups Government Community
Situational factors Workforce characteristics Business strategy and conditions Management philosophy Labour market Unions Tasks technology Law & societal values
HRM policies Employee influence Human resource flow Reward systems Work systems
HRM outcomes Commitment Competence Congruence Cost effectiveness
Long-term consequences Individual wellbeing Organizational effectiveness Societal wellbeing
OF HRM
THE 5-P MODEL OF STRETEGIC HRM
Organization Strategy
EVOLUTION
Internal Characteristics
External Characteristics
Strategic business needs
Strategic Human Resources Management Activities Human Resources Philosophy - Expresses how to treat and value people Human Resources Policies - Guidelines for action on people related business and HR programs Human Resources Programs - Help to address and change major people related business issues Human Resources Practices - Motivates needed role behavior Human Resources Processes - Defines how these activities are carried out
OF HRM EVOLUTION
HUMAN RESOURCE WHEELS
The American Society for Training & Development (ASTD) has developed a Human Resource Wheel in 1983 highlighting different functions of HRM leading to quality of work life, productivity and readiness for change.
Employee assistance
Union/ Labor relations T& D
Compensation/ Benefits Personnel research and information systems
HR areas output: Quality of work life Productivity readiness for change
Organization/ Job design
HRP Selection and staffing
OF HRM
HUMAN RESOURCE WHEELS
T & D focus Identifying, assessing and through planned learning---helping develop the key competencies which enable individuals to perform current or future jobs.
EVOLUTION
OD focus Assuring healthy inter- and inter-personal relationships and helping groups initiate and manage change.
Organization/Job design focus Defining how tasks, authority and systems will be organized and integrated across organization units and in individual jobs.
HRP focus Determining the organizations major HR needs strategies and philosophies.
OF HRM
HUMAN RESOURCE WHEELS
Selection and staffing Matching people and their career needs and capabilities with jobs and career paths. Personnel research and information systems Assuring a personal information base. Compensation/Benefits focus Assuring compensation and benefits fairness and consistency. Employee assistance focus Providing counseling to individual employees, for personal problem-solving. Union/Labour relations focus Assuring healthy union/organization relationships.
EVOLUTION
Nature of HRM
THE
HRM MODEL
Human Resource Planning Job analysis Recruitment Selection Placement Training &development Environment Remuneration Motivation
Participative Management
Communication Safety, health & Welfare Promotions etc.
Competent & Willing work force
Industrial relations
Trade Unionism Disputes & their settlement International HRM
Organisational Goals
Ethical issues in HRM
OF HRM EVOLUTION
HUMAN RESOURCE FUNCTIONS
Forecasting the human resource requirements necessary for the organization to achieve its objective both in terms of number of employees and skills. Developing and implementing a plan to meet the manpower requirements.
Carrying out job analysis to establish the specific requirements for individual jobs within an organization.
Recruiting and selecting personnel to fill specific jobs within an organization. Designing systems for appraising the performance of individuals. Orienting and training employees. Designing and implementing management and organizational development programmes.
OF HRM EVOLUTION
HUMAN RESOURCE FUNCTIONS
Designing and implementing compensation system for all employee and have systems for promotions and transfer
Assisting employees in developing career plans.
Employee communication , personal counseling, personal research etc
Departmental administration programs Planning, record keeping, reporting ,policy formulation , and general administration.
Implement activities to ensure proper health and sanitation and safe work place
Adherence to Government norms and regulations
OF HRM
CHALLENGES FACED BY HRM
Globalization
EVOLUTION
Build value chain for business competitiveness
Profitable through cost and growth
Capability Focus
Change Technology Attracting and retaining intellectual capital
OF HRM EVOLUTION
CONCLUSION
Organizations are now defined as : The core competencies within the organization The people within the organization The organizational culture or shared values and knowledge or learning. The HR systems needs to be retained and constantly upgraded and changed: People will always need to be hired and trained Process will always need to be created and upgraded Cultures will always need to be established and transformed. HR practices must
Be aligned to business realities, meeting deadlines , making profits, leveraging technology, satisfying investors and to serving customers ,.
HRM is to create organizational capabilities that will lead to competitiveness
You might also like
- CH 1 Introduction of HRMDocument42 pagesCH 1 Introduction of HRMKaaliNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Resource ManagementDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Human Resource Managementchandruc65No ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument34 pagesHuman Resource ManagementPhạm Nguyên ThảoNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Study GuideDocument13 pagesFinal Exam Study GuideDakotaMontanaNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Short Term Non Routine Decisions TheoryDocument9 pages2.1 Short Term Non Routine Decisions TheoryAyna McrmptNo ratings yet
- Taganito Mining Corporation vs. CIRDocument10 pagesTaganito Mining Corporation vs. CIRAJ AslaronaNo ratings yet
- HRM Objectives and CSR Activities of AppleDocument9 pagesHRM Objectives and CSR Activities of AppleAbhishek SinhaNo ratings yet
- Monopolistic Competition and Equilibrium ModelsDocument20 pagesMonopolistic Competition and Equilibrium ModelsRanjeet KumarNo ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument12 pagesHuman Resource ManagementBirendra Pushpakar100% (1)
- Arrival Under Stress and ShipwrecksDocument14 pagesArrival Under Stress and ShipwrecksKevin CastilloNo ratings yet
- Transformation ProcessDocument6 pagesTransformation ProcessMohd DawamiNo ratings yet
- Managerial Decision Making: Part 2 Planning Challenges in The 21st CenturyDocument30 pagesManagerial Decision Making: Part 2 Planning Challenges in The 21st CenturyMuhammad MuzammelNo ratings yet
- Chap004 Strategic Capacity ManagementDocument31 pagesChap004 Strategic Capacity ManagementSyarifatuz Zuhriyah UmarNo ratings yet
- Prelim-Examination-Case-Analysis - Timpug, Anne Catherine C - B-122Document4 pagesPrelim-Examination-Case-Analysis - Timpug, Anne Catherine C - B-122Ry Gonzales100% (1)
- Cost Accounting MidtermDocument4 pagesCost Accounting MidtermMieryle DioctonNo ratings yet
- University of CebuDocument5 pagesUniversity of CebuLouelie Jean AlfornonNo ratings yet
- Civil Service Exam Complete Reviewer PhilippinesDocument52 pagesCivil Service Exam Complete Reviewer PhilippinesJesmark CentinoNo ratings yet
- Summary EthicsDocument5 pagesSummary EthicsLance BautistaNo ratings yet
- Book - International Human Resource Management 6e, Peter J. Dowling, Marion Festing and Allen D.Engle, SRDocument25 pagesBook - International Human Resource Management 6e, Peter J. Dowling, Marion Festing and Allen D.Engle, SRPillai BalaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Human Resource ManagementDocument9 pagesStrategic Human Resource ManagementDineshNo ratings yet
- 2017 CSC ReviewerDocument57 pages2017 CSC ReviewerMaureen Mae EstanolNo ratings yet
- Social SDGsDocument61 pagesSocial SDGsAarti Pal100% (1)
- Fringe Benefits Guide for Small Business OwnersDocument5 pagesFringe Benefits Guide for Small Business Ownerspawan bathamNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Business Policy and StrategyDocument2 pagesEvolution of Business Policy and StrategyGarcia, Ralph Gio P.No ratings yet
- Introduction to Key Concepts of Human Resource ManagementDocument22 pagesIntroduction to Key Concepts of Human Resource ManagementDipen SarmaNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 The Business MissionDocument27 pagesChap 2 The Business MissionFarith HanafiNo ratings yet
- Module 1 The Nature of Strategic Management2Document8 pagesModule 1 The Nature of Strategic Management2Julienne LobchoyNo ratings yet
- MP5 - Option For The Bottom of The PyramidDocument25 pagesMP5 - Option For The Bottom of The Pyramid22ccg2f7d2No ratings yet
- Entry and Contracting ODDocument5 pagesEntry and Contracting ODDavid Dickens100% (3)
- Santos Timber Company Management Case Study ExplainedDocument25 pagesSantos Timber Company Management Case Study ExplainedNeshia May BariquitNo ratings yet
- Institute of Accounts Business and Finance Business Administration DepartmentDocument35 pagesInstitute of Accounts Business and Finance Business Administration Departmentjanna ria libatiuqeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - The Changing Environment of OrganizationDocument41 pagesChapter 4 - The Changing Environment of OrganizationGel-lai TootsNo ratings yet
- 7 Bibingka ExpressDocument100 pages7 Bibingka ExpressExugeNo ratings yet
- Import CSV file and format Excel workbookDocument5 pagesImport CSV file and format Excel workbookchingchongNo ratings yet
- Sample For Reflection PaperDocument3 pagesSample For Reflection PaperMalish sob0% (1)
- Differences between entrepreneurship and intrapreneurshipDocument6 pagesDifferences between entrepreneurship and intrapreneurshipHimadhar SaduNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Sole ProprietorshipDocument5 pagesDifferences Between Sole ProprietorshipUsman KhalidNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Organizational Behaviour: StructureDocument10 pagesUnit 4 Organizational Behaviour: StructureCharminda WewelpanawaNo ratings yet
- Labor Migration and The Global FilipinoDocument17 pagesLabor Migration and The Global FilipinoRaisa Neith SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Process Strategy ChapterDocument15 pagesProcess Strategy ChapterDeN Z100% (2)
- Presentation Of: Implementing Rules and Regulations (IRR) and Code of Policies (COP)Document15 pagesPresentation Of: Implementing Rules and Regulations (IRR) and Code of Policies (COP)Clifford TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Organizational DesignsDocument25 pagesOrganizational DesignsSaroj Kumar RaiNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Environmental ManagementDocument4 pagesCase Study - Environmental ManagementManu MuraleedharanNo ratings yet
- Calo Vs RoldanDocument35 pagesCalo Vs RoldanSachuzen23No ratings yet
- Understanding the Shift from Control-Based to Commitment-Based HRM ModelsDocument4 pagesUnderstanding the Shift from Control-Based to Commitment-Based HRM Modelsaxl16hkNo ratings yet
- NARRATIVE REPORT - International Business TradeDocument1 pageNARRATIVE REPORT - International Business TradeChristian BustilloNo ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument2 pagesFinancial Managementbakayaro92No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 FullDocument73 pagesChapter 1 FullAnjali Angel ThakurNo ratings yet
- PCPPIDocument24 pagesPCPPIMarx Allana Infiesto CadaNo ratings yet
- Corporate Governance and Other StakeholdersDocument44 pagesCorporate Governance and Other Stakeholdersswatantra.s8872450% (1)
- Organizational Environment and CultureDocument3 pagesOrganizational Environment and CultureShameel Kaleel100% (1)
- Ethics in International BusinessDocument18 pagesEthics in International BusinessAniketKaradeNo ratings yet
- IRR NHIAct 2013 PDFDocument118 pagesIRR NHIAct 2013 PDFMariver LlorenteNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship DevelopmentDocument36 pagesEntrepreneurship DevelopmentshakilhmNo ratings yet
- What is a Partnership BusinessDocument15 pagesWhat is a Partnership BusinessHarshraj Ahirwar100% (1)
- Phases of Strategic ManagementDocument3 pagesPhases of Strategic ManagementIm Kitty StephanieNo ratings yet
- Emerging Aspects of Organizationa L Behavior: Organizational Behavior Across Cultures Miranda, Aprille DaneDocument30 pagesEmerging Aspects of Organizationa L Behavior: Organizational Behavior Across Cultures Miranda, Aprille DaneYssa SottoNo ratings yet
- A Conceptual Model of Corporate Moral DevelopmentDocument12 pagesA Conceptual Model of Corporate Moral DevelopmentmirianalbertpiresNo ratings yet
- Customers Switching Intentions Behavior in Retail Hypermarket Kingdom of Saudi Arabia: Customers Switching Intentions Behavior in Retail HypermarketFrom EverandCustomers Switching Intentions Behavior in Retail Hypermarket Kingdom of Saudi Arabia: Customers Switching Intentions Behavior in Retail HypermarketNo ratings yet
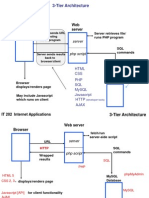
- 3-Tier Architecture: Browser Client Web ServerDocument2 pages3-Tier Architecture: Browser Client Web ServerymeenamcaNo ratings yet
- Unit I: The 8086 Processor - Software AspectsDocument15 pagesUnit I: The 8086 Processor - Software AspectsymeenamcaNo ratings yet
- Evolution of HRMDocument21 pagesEvolution of HRMymeenamcaNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument47 pagesIntroductionymeenamcaNo ratings yet
- First Doctoral Committee: Researcher: B.MadasamyDocument25 pagesFirst Doctoral Committee: Researcher: B.MadasamyymeenamcaNo ratings yet