Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eukaryotic Cells: Chapter 7-2: Cell Structure
Uploaded by
jmunozbio@yahoo.com0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
110 views10 pagesOrganelles of a eukaryotic cell Each perform a specific job for the cell. Cytoskeleton acts as both muscle and skeleton, for movement and stability. Endoplasmic Reticulum is a network of interconnected membranes forming channels within the cell. Also contains enzymes for detoxifying chemicals including drugs and pesticides.
Original Description:
Original Title
Eukaryotic Cells
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentOrganelles of a eukaryotic cell Each perform a specific job for the cell. Cytoskeleton acts as both muscle and skeleton, for movement and stability. Endoplasmic Reticulum is a network of interconnected membranes forming channels within the cell. Also contains enzymes for detoxifying chemicals including drugs and pesticides.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
110 views10 pagesEukaryotic Cells: Chapter 7-2: Cell Structure
Uploaded by
jmunozbio@yahoo.comOrganelles of a eukaryotic cell Each perform a specific job for the cell. Cytoskeleton acts as both muscle and skeleton, for movement and stability. Endoplasmic Reticulum is a network of interconnected membranes forming channels within the cell. Also contains enzymes for detoxifying chemicals including drugs and pesticides.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
Eukaryotic Cells
Chapter 7-2 : Cell Structure
Major organelles and their functions
Vocabulary
Organelle Ribosomes
Cytoplasm Mitochondria
Nucleus
Endoplasmic reticulum
Golgi apparatus
Chromosomes
Chromatin
nucleolus
Organelles
“Little organs” of a eukaryotic cell
Each perform a specific job for the cell
Two major parts of the cell
Cytoplasm-portion of the cell outside
the nucleus.
Nucleus-controls the cell processes
and contains all the hereditary
information of DNA.
Inside and Out
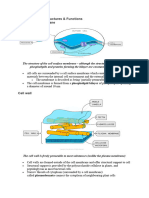
Plasma Membrane
A lipid/protein/
carbohydrate complex,
providing a barrier and The cytoskeleton acts as
containing transport and both muscle and
signaling systems. skeleton, for movement
Cytoskeleton and stability. The long
The cytoskeleton is fibers of the cytoskeleton
unique to eukaryotic cells. are polymers of subunits.
It is a dynamic three- The primary types of
dimensional structure that fibers comprising the
fills the cytoplasm. cytoskeleton are
microfilaments,
microtubules, and
intermediate filaments.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Rough endoplasmic Smooth endoplasmic
reticulum (RER) reticulum (SER)
A network of A network of
interconnected interconnected
membranes forming membranes forming
channels within the cell. channels within the cell. A
Covered with Ribosomes site for synthesis and
(causing the "rough" metabolism of lipids. Also
appearance) which are in contains enzymes for
the process of making detoxifying chemicals
proteins for secretion. including drugs and
pesticides.
Ribosomes Lysosymes
Protein and RNA complex
A membrane bound
responsible for protein
organelle that is
synthesis.
responsible for
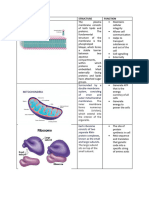
Mitochondria breakdown of proteins
Surrounded by a double and membranes in the
membrane with a series cell. Also helps digest
of folds called cristae. materials ingested by the
Functions in energy cell.
production through cell Peroxisomes or
respiration. Contains its
Microbodies
own DNA, and is believed
Produce and degrade
to have originated as a
hydrogen peroxide, a
captured bacterium.
toxic compound that can
be produced during
metabolism.
Golgi Apparatus
A series of stacked membranes.
Vesicles carry materials from the RER
to the Golgi apparatus.
Vesicles move between the stacks
while the proteins are "processed" to
a mature form.
Vesicles then carry newly formed
membrane and secreted proteins to
their final destinations
secretion or part of the membrane.
Exclusive to plants
Chloroplasts Vacuoles
Surrounded by a Membrane
double membrane, surrounded "bags"
containing stacked that contain water and
thylakoid membranes. storage materials in
Responsible for plants.
photosynthesis. Cell Wall
Contains DNA, and Plants have a rigid cell
like mitochondria is wall as their outer
believed to have membrane.
originated as a
captured bacterium.
Nucleus
Surrounded by the nuclear envelope which
is double membrane surrounding the
chromatin and the nucleolus.
Pores allow specific communication with
the cytoplasm.
The nucleolus is a site for synthesis of
Ribosomes.
Contains cell DNA which contains coded
instructions for making proteins
You might also like
- Basic Building Blocks of Life Smallest Living Unit of An OrganismDocument2 pagesBasic Building Blocks of Life Smallest Living Unit of An OrganismkikomagsaysayNo ratings yet
- Cellular Biology: Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument7 pagesCellular Biology: Cell Structure and TaxonomyFelyn Roseann AretaNo ratings yet
- Introduction CellDocument48 pagesIntroduction CellabdNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Endomembrane System, Mitochondria, Chloroplasts, Cytoskeleton and Extracellular ComponentsDocument65 pagesThe Cell: Endomembrane System, Mitochondria, Chloroplasts, Cytoskeleton and Extracellular ComponentsMeljean Kalaw CastilloNo ratings yet
- A Cell Is The Smallest Unit of A Living ThingDocument4 pagesA Cell Is The Smallest Unit of A Living ThingJONAVIE DEMALATANo ratings yet
- CellsDocument9 pagesCellsjasmineNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles Structure & FunctionDocument4 pagesCell Organelles Structure & FunctionDaniel ChinNo ratings yet
- Structural and Functional Manifestation of LifeDocument6 pagesStructural and Functional Manifestation of LifeKaila StefanieNo ratings yet
- DNA, The Genetic MaterialDocument6 pagesDNA, The Genetic MaterialMarinelle TumanguilNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells: ProkaryotesDocument8 pages1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells: Prokaryotesdavid tsaiNo ratings yet
- Cell Organales & StructuresDocument12 pagesCell Organales & StructuresRavi DesaiNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument12 pagesCell Structure and FunctionsInshaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 Notes PDFDocument88 pagesUNIT 2 Notes PDFAjNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument70 pagesFunctional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsTrixie De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Comparison of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cellsDocument3 pagesComparison of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cellsAdean AhmedNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Structures Notes SVDocument10 pagesEukaryotic Cell Structures Notes SValkbbushra25No ratings yet
- Cell Organelles - Lec. 1Document27 pagesCell Organelles - Lec. 1Hamza KaisNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Introduction To BiochemistryDocument34 pagesWeek 2 - Introduction To BiochemistryPaula LouiseNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles ExplainedDocument4 pagesCell Organelles ExplainedVeronica AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Research: Animal Eukaryotic Cell StructureDocument11 pagesResearch: Animal Eukaryotic Cell StructurelucyyeldingNo ratings yet
- Research: Animal Eukaryotic Cell StructureDocument11 pagesResearch: Animal Eukaryotic Cell StructurelucyyeldingNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Basic Unit of LifeDocument11 pagesThe Cell: Basic Unit of LifeMartin ClydeNo ratings yet
- 1.3. Components of The Cell IISubcellular Organelles 070141Document31 pages1.3. Components of The Cell IISubcellular Organelles 070141Angel CaroNo ratings yet
- 1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesDocument45 pages1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesMaham AdnanNo ratings yet
- The Cell - The Basic Unit of LifeDocument45 pagesThe Cell - The Basic Unit of LifeMaham AdnanNo ratings yet
- ER and Golgi Apparatus: Structure and Functions of Key Cell OrganellesDocument5 pagesER and Golgi Apparatus: Structure and Functions of Key Cell OrganellesJohn Rey BandongNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument17 pagesThe CelluissojohnyzNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic DNA OrganizationDocument26 pagesProkaryotic DNA OrganizationKerberos DelabosNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Study NotesDocument134 pagesIB Biology Study NotesManav Parikh100% (2)
- 1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells (Main)Document46 pages1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells (Main)MeryemNo ratings yet
- The Basic Unit of LifeDocument18 pagesThe Basic Unit of LifeKenneth Myro GarciaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3.4: Cellular Parts and FunctionsDocument17 pagesLesson 3.4: Cellular Parts and FunctionskyzylgabunalesqNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Cell BiologyDocument43 pagesChapter 1-Cell Biologyapi-374357No ratings yet
- Infografia_de_biologiaDocument4 pagesInfografia_de_biologiafrancosebastianbcNo ratings yet
- Cell STRUCTURE and Function Worksheet. HomeworkDocument5 pagesCell STRUCTURE and Function Worksheet. HomeworkMichael WrightNo ratings yet
- Cell_The unit of lifeDocument5 pagesCell_The unit of lifeharifire050No ratings yet
- 2.1.1 Notes Ocr A BiologyDocument5 pages2.1.1 Notes Ocr A BiologyLuke BeaumontNo ratings yet
- Module 2 CytogeneticsDocument17 pagesModule 2 CytogeneticsFrances Riane SimoyNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles GuideDocument43 pagesCell Organelles GuideMariam Qais100% (1)
- Cell OrganellesDocument3 pagesCell OrganellesMotie KassabNo ratings yet
- Cells: Electron MicroscopeDocument7 pagesCells: Electron MicroscopeGabriela ZahiuNo ratings yet
- CELL STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONSDocument5 pagesCELL STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONSNorjanah H. M. AmbolaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure: Rebecca MaynardDocument11 pagesCell Structure: Rebecca Maynardbecki93No ratings yet
- BIO104E - Laboratory Activity (The Cell)Document5 pagesBIO104E - Laboratory Activity (The Cell)Stephen AzaresNo ratings yet
- Premidterms NotesDocument4 pagesPremidterms NotesRenee Andrei Concepcion MozarNo ratings yet
- Chem 104D MidtermsDocument27 pagesChem 104D MidtermsCASTAÑEDA, Jameela AnneNo ratings yet
- MicroDocument5 pagesMicrotahashahzad9901No ratings yet
- Biochem Notes 1Document10 pagesBiochem Notes 1Coy NuñezNo ratings yet
- Cell TheoryDocument146 pagesCell TheoryGynewNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Tissues & Cells 2020Document32 pagesTopic 2 - Tissues & Cells 2020Yan ZochowskiNo ratings yet
- Cells Memorization SheatDocument2 pagesCells Memorization SheatNiomi ButtermilkNo ratings yet
- Module 2 LectureDocument13 pagesModule 2 LectureJeal NochefrancaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document29 pagesChapter 4skywalkerNo ratings yet
- Introductiontophysiologylecture 101020230212 Phpapp02Document34 pagesIntroductiontophysiologylecture 101020230212 Phpapp02DR KARSHAN NANDANIYANo ratings yet
- Bio Cells ReviewerDocument4 pagesBio Cells ReviewerKimberly LuistroNo ratings yet
- Compare Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument4 pagesCompare Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsJung Somin100% (1)
- 04 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument23 pages04 Cell Structure and Functionธนเสฐฐ์ กิตติวรรธโนทัยNo ratings yet
- #1 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument3 pages#1 Cell Structure and FunctionCharlene EpilepsiaNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Biology NotesDocument36 pagesPreliminary Biology NotesSaad KashifNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Biology Final Study GuideDocument2 pagesBiology Final Study Guidejmunozbio@yahoo.com100% (1)
- Musculoskeletal SystemDocument13 pagesMusculoskeletal Systemjmunozbio@yahoo.com100% (3)
- Immune SystemDocument16 pagesImmune Systemjmunozbio@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Speciation VocabDocument1 pageSpeciation Vocabjmunozbio@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- CH 16 RG F07Document1 pageCH 16 RG F07jmunozbio@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Physiology Study GuideDocument1 pagePhysiology Study Guidejmunozbio@yahoo.com100% (1)
- Hivaids OnlineDocument1 pageHivaids Onlinejmunozbio@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Genetic DiversityDocument20 pagesGenetic Diversityjmunozbio@yahoo.com100% (1)
- Excretory System & DigestiveDocument15 pagesExcretory System & Digestivejmunozbio@yahoo.com100% (2)
- Cardiovascular & Respiratory SystemDocument17 pagesCardiovascular & Respiratory Systemjmunozbio@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Physiology UnitDocument2 pagesPhysiology Unitjmunozbio@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Evolution Big IdeasDocument1 pageEvolution Big Ideasjmunozbio@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Human GeneticsDocument11 pagesHuman Geneticsjmunozbio@yahoo.com100% (1)
- Human Genetics Test Big IdeasDocument1 pageHuman Genetics Test Big Ideasjmunozbio@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Allele Frequency LabDocument1 pageAllele Frequency Labjmunozbio@yahoo.com100% (1)
- Probability and Mendeilian Genetics LabDocument4 pagesProbability and Mendeilian Genetics Labjmunozbio@yahoo.com100% (6)
- Evolution: Process by Which Organisms Gradually Change Over Time Due To AdaptationsDocument11 pagesEvolution: Process by Which Organisms Gradually Change Over Time Due To Adaptationsjmunozbio@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Sex Linked Genetic DiseaseDocument9 pagesSex Linked Genetic Diseasejmunozbio@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Karyotype OnlineDocument1 pageKaryotype Onlinejmunozbio@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Human GeneticsDocument11 pagesHuman Geneticsjmunozbio@yahoo.com100% (1)
- Genes & DominanceDocument11 pagesGenes & Dominancejmunozbio@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Reading GuideDocument1 pageChapter 14 Reading Guidejmunozbio@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument15 pagesMeiosisjmunozbio@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Dihybrid WorksheetDocument1 pageDihybrid Worksheetjmunozbio@yahoo.com100% (2)
- MeiosisDocument15 pagesMeiosisjmunozbio@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Mendel Big IdeasDocument1 pageMendel Big Ideasjmunozbio@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- CH 11.1-11.3 RGDocument1 pageCH 11.1-11.3 RGjmunozbio@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Genetics More PracticeDocument3 pagesGenetics More Practicejmunozbio@yahoo.com100% (1)
- Mono Hybrid WorksheetDocument1 pageMono Hybrid Worksheetjmunozbio@yahoo.com100% (1)
- Punnett Squares OnlineDocument4 pagesPunnett Squares Onlinejmunozbio@yahoo.com100% (2)
- Blueprint of LifeDocument11 pagesBlueprint of Lifetimeflies23No ratings yet
- Bailey and Love) Shock Is A LifeDocument14 pagesBailey and Love) Shock Is A LifeRaghav AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganelleDocument9 pagesCell OrganelleGwencytech DomingoNo ratings yet
- Human Behavior and Crisis ManagementDocument46 pagesHuman Behavior and Crisis ManagementkimkimkouiNo ratings yet
- A Proposed Evidence-Based Shoulder Special Testing Examination Algorithm - Clinical Utility Based On A Systematic Review of The LiteratureDocument14 pagesA Proposed Evidence-Based Shoulder Special Testing Examination Algorithm - Clinical Utility Based On A Systematic Review of The LiteratureAfonso MacedoNo ratings yet
- A Global Resource For Genomic Predictions of Antimicrobial Resistance and Surveillance of Salmonella Typhi at PathogenwatchDocument12 pagesA Global Resource For Genomic Predictions of Antimicrobial Resistance and Surveillance of Salmonella Typhi at PathogenwatchOkeke UcheeNo ratings yet
- PE 3 Modules StudentsDocument83 pagesPE 3 Modules StudentsHershey BaconNo ratings yet
- 2020-68 Annex A - Informed Consent101620Document3 pages2020-68 Annex A - Informed Consent101620roseAngelic ortizNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Ventilation Handout - AllenhoDocument23 pagesMechanical Ventilation Handout - AllenhoCarmen HerediaNo ratings yet
- Johnson & JohnsonDocument13 pagesJohnson & JohnsonShyam SundarNo ratings yet
- FEVER & INFLUENZA INFORMATION FROM HARAPANAHALLI TALUK - Doctor Detail Patient DetailDocument3 pagesFEVER & INFLUENZA INFORMATION FROM HARAPANAHALLI TALUK - Doctor Detail Patient DetailaeepwdNo ratings yet
- Negative Global Flows and ProcessesDocument4 pagesNegative Global Flows and ProcessesLABAJA, MEGUMI ERIKA O.50% (2)
- 2 02-Electrocardiography PDFDocument17 pages2 02-Electrocardiography PDFMiguel DomingoNo ratings yet
- 1 N-109 MCN 2 LEC Syllabus (2 S, AY 19-20) REVISED PDFDocument7 pages1 N-109 MCN 2 LEC Syllabus (2 S, AY 19-20) REVISED PDFCayla Mae CarlosNo ratings yet
- Lymphoma CancerDocument34 pagesLymphoma CancerwasihaiderkNo ratings yet
- Kode Diagnosa PenyakitDocument5 pagesKode Diagnosa PenyakitSelly RianiNo ratings yet
- YMMNO ProposalDocument2 pagesYMMNO ProposalYamon Min Nyunt OoNo ratings yet
- PharmacokineticsDocument7 pagesPharmacokineticsRonica MendozaNo ratings yet
- CAP Protocol-2016 Thyroid - HighlightedDocument8 pagesCAP Protocol-2016 Thyroid - Highlightedpath2016No ratings yet
- Difficult Decissions in TraumaDocument443 pagesDifficult Decissions in Traumajulio vilela100% (1)
- Preventing Mosquito BitesDocument1 pagePreventing Mosquito BitesmkumNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions For Hepatic Disorders - NURS 1028 Nursing TheoryDocument2 pagesPractice Questions For Hepatic Disorders - NURS 1028 Nursing TheoryNicholas ObasiNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument70 pagesPDFPaul Benjomin AgregadoNo ratings yet
- Cole Crops and Other Brassicas: Organic Production: AttraDocument20 pagesCole Crops and Other Brassicas: Organic Production: AttraRebecca SheaNo ratings yet
- The Neuro Metabolic Summit - TranscriptsDocument35 pagesThe Neuro Metabolic Summit - TranscriptsIONUT GRIGOROVNo ratings yet
- Ls Models Top 100 Preteen Models Non NudeDocument2 pagesLs Models Top 100 Preteen Models Non NudeFrancisco Lima de SousaNo ratings yet
- Leafy Vegetables HarvestingDocument18 pagesLeafy Vegetables HarvestingSonia BadaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Eight 8.0 Environmental Management and Safety 8.1 General IntroductionDocument8 pagesChapter Eight 8.0 Environmental Management and Safety 8.1 General IntroductionRichard ObinnaNo ratings yet
- What Is Hiv/Aids?: Human Immunodeficiency Virus (Hiv)Document2 pagesWhat Is Hiv/Aids?: Human Immunodeficiency Virus (Hiv)Rockie Geronda EsmaneNo ratings yet
- Parasitology TableDocument9 pagesParasitology TablehumanupgradeNo ratings yet